12 Vestibular System
Vestibular System

Vestibular Dysfunction



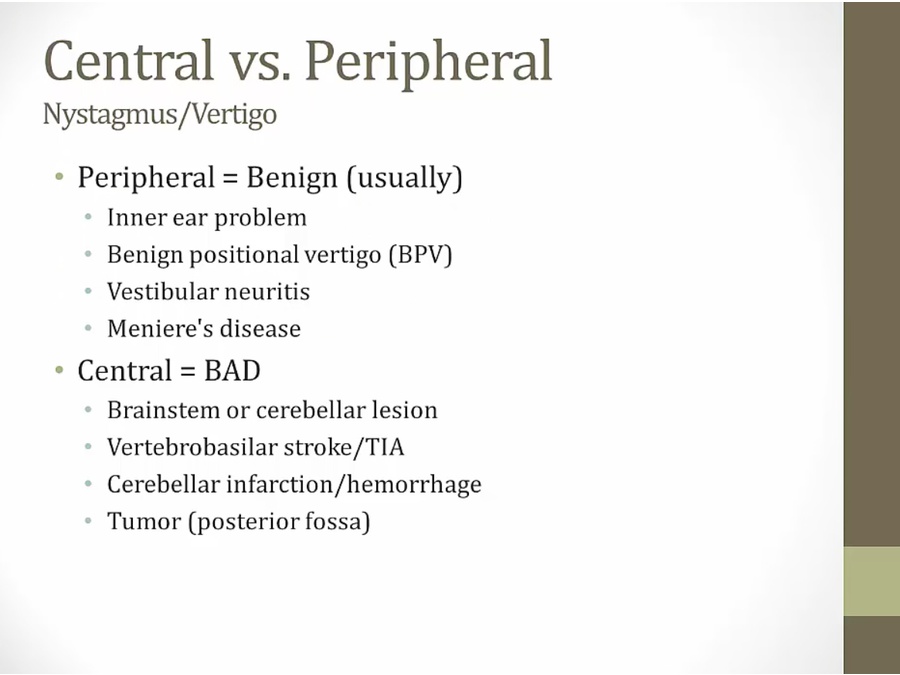
Central Vs Peripheral


Dix-Hallpike


Benign Positional Vertigo

Vestibular Neuronitis

Meniere's Disease



Last updated