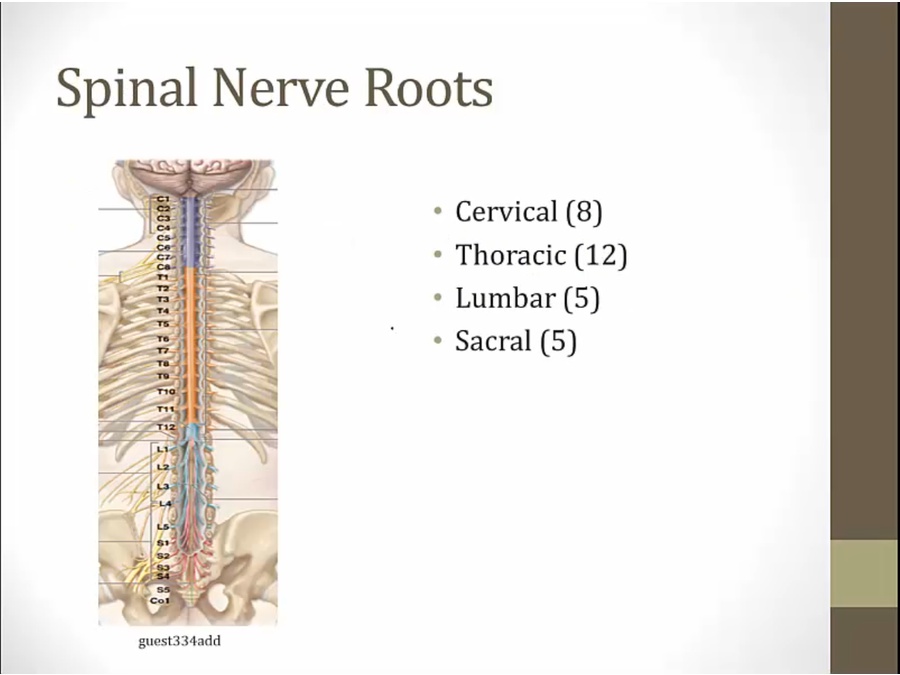
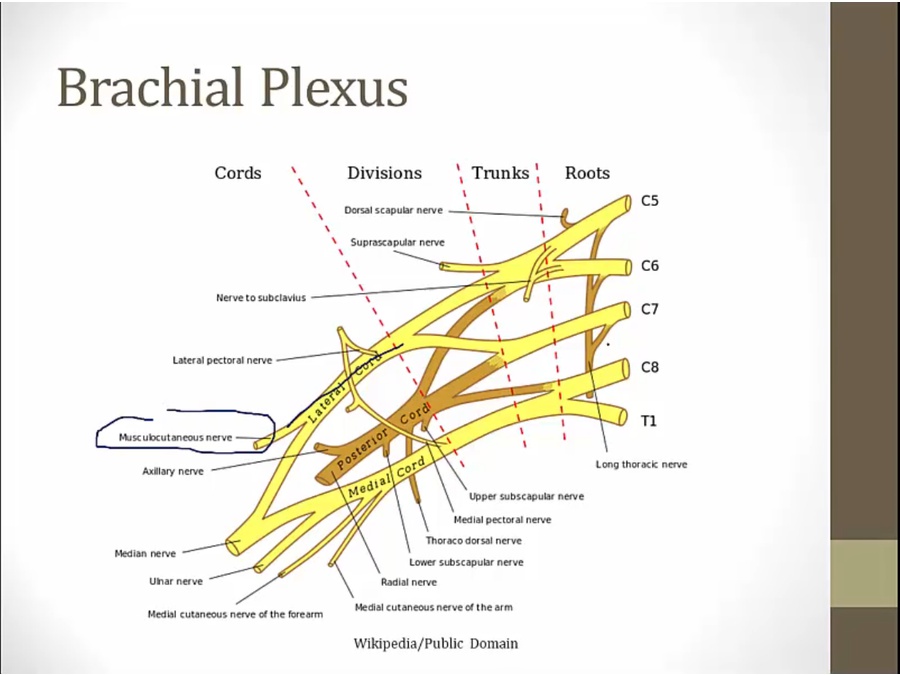
03 Brachial

from spinal cord


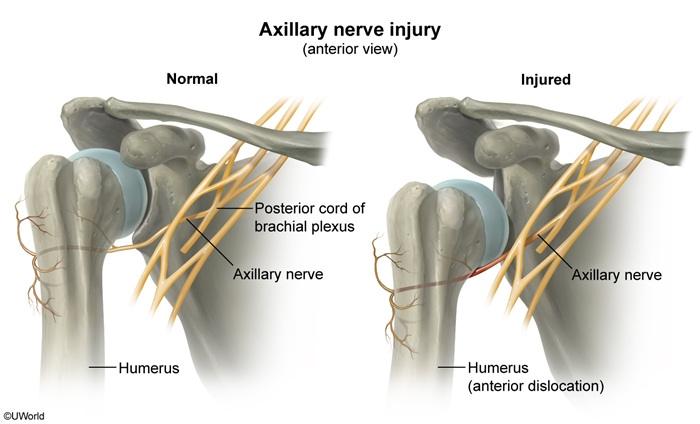
Axillary

The shoulder may dislocate anteriorly, inferiorly, or posteriorly, but anterior dislocations are by far the most common. Anterior dislocations are typically caused by a blow to an externally rotated and abducted arm.
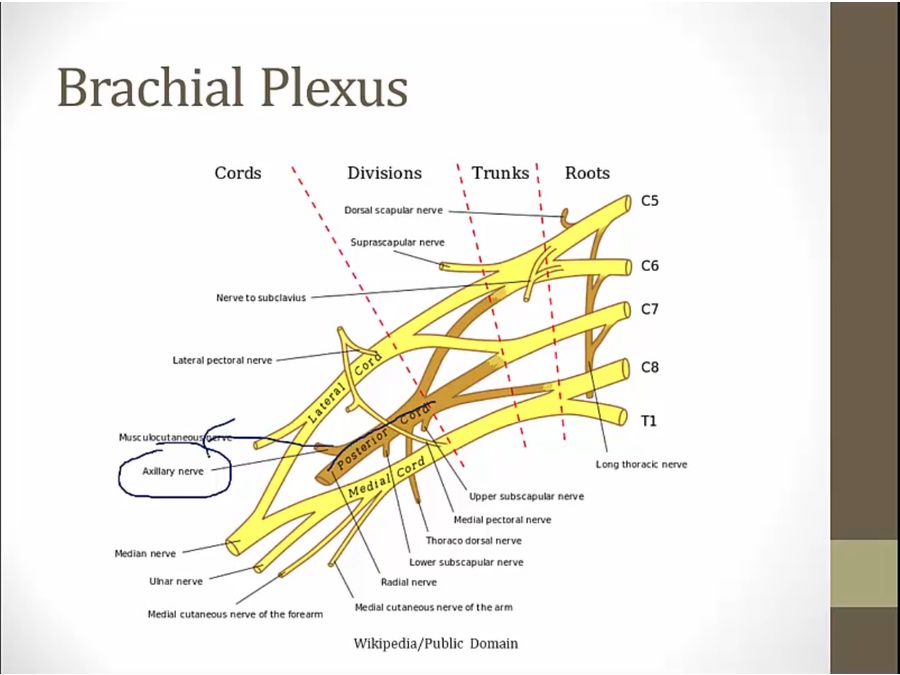
from posterior cord, top
thus mostly C5, C6
Radial

wraps around humerus, innervates muscles in back of forearm
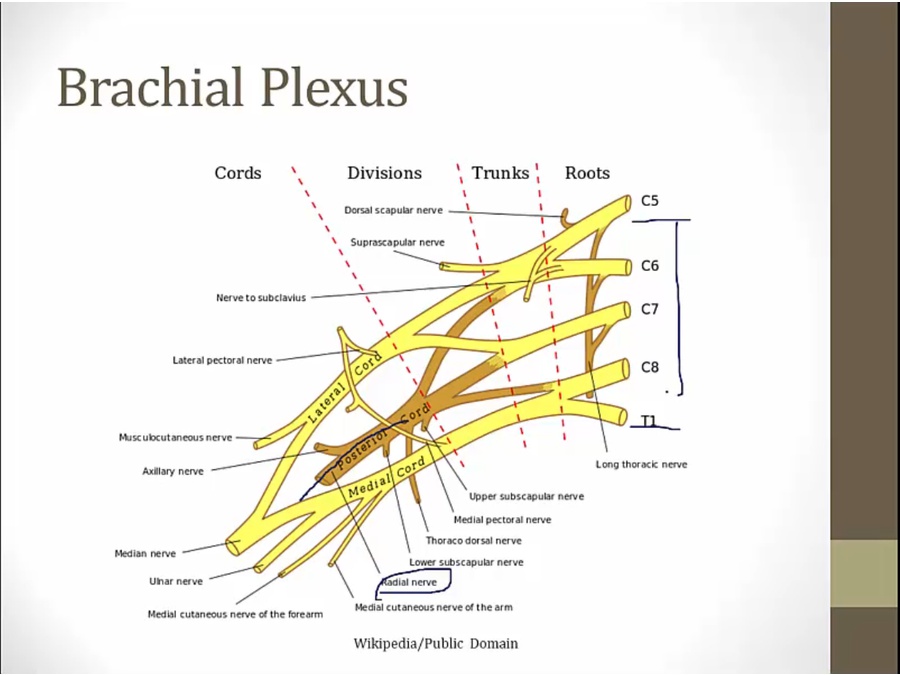
C5 to T1

lose radial nerve, flexors dominate
wrist drop

triceps injury: difficulty extending at elbow

alcoholics sleep


high up in arm

pink area: sensory by branches given off superficially before
radial groove damage: normally extension of elbow, loss of extension of wrist/finger, normal sensation of back arm
Ulnar
most common compression site at medial epicondyle at elbow
Brachial Artery

Impingement of the brachial artery results in loss of the brachial and radial artery pulses. Distal perfusion should always be assessed on examination. Motor and sensory function should also be assessed due to the risk of median nerve injury.
Treatment consists of analgesia and immobilization. Displaced fractures require orthopedic consultation. Neurovascular injury often resolves after orthopedic alignment and immobilization; patients who are treated promptly usually have a good prognosis.
Musculocutaneous

lateral forearm: thumb side
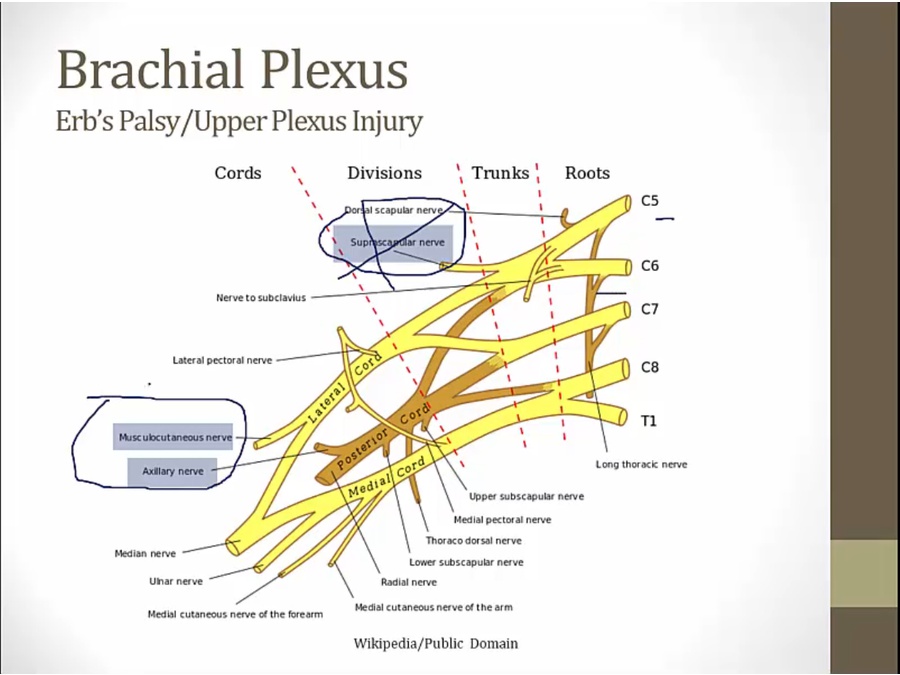
Upper Trunk



affects nerves derived from upper trunk

Lower Trunk

arm yanked outwards and upwards
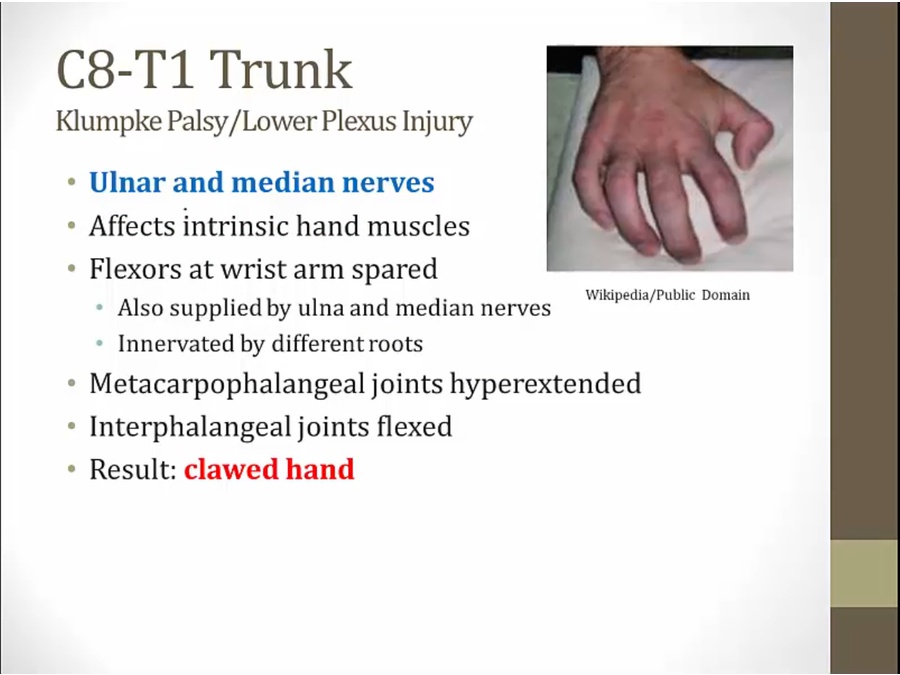
complete clawed hand

also some innervation through lateral cord
Thoracic Outlet



someone with cervical rib after whiplash

claw hand
elevation of arm/hand: compresses nerves more
elevation of arm: weak pulse
brachial plexus symptoms plus vasculature symptoms
Long Thoracic


Last updated