Development
Development
_..by 3 mo _..4 mo _..by 6 mo _..by 12 mo
_..by 1 mo _.. (by 6 mo) _.. (by 8 mo) _.. (by 10 mo), _..(by 12–18 mo)
_.. (by 6 mo), _..(by 10 mo) _.. (by 12 mo)
_.. (by 2 mo) _.. (by 6 mo) _.. (by 9 mo)
_.. (by 4 mo), _..(by 9 mo) _.. (by 9 mo) _.. (by 10 mo)
_.. (by 12 mo) _.. (by 18 mo) _..number = age (yr) × 3 _.. (by 20 mo) _.. (by 24 mo) _.. (by 24–36 mo) _.. (by 24 mo) _..(by 36 mo) _..by age 2 _..2
_..3 yr _.. (by 4 yr) _.. (by 4 yr) _.. (by 5 yr) _..(by 3 yr) _.. (by 4 yr) _..age 3, 3 zeros _..by 4 yr _.. by 4 yr
_..
stranger: 6
separation: 9
_..
parallel: 2 - 3
cooperative: 4
_..
reapprochement: 2 years
away: 3 years
Reflex
_C4, myotome.,
_C5, myotome.,
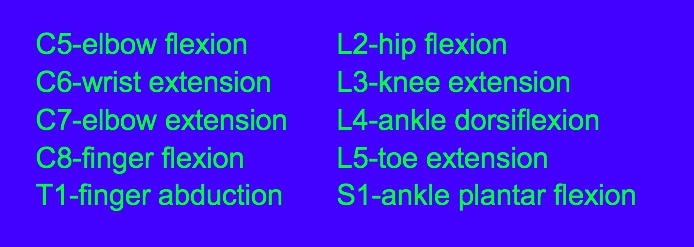
_C5, C6, myotome.,
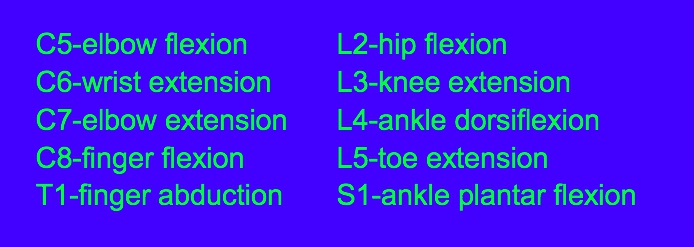
_C7, myotome.,
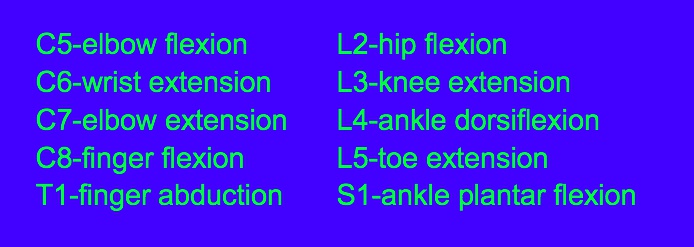
_C8, myotome.,
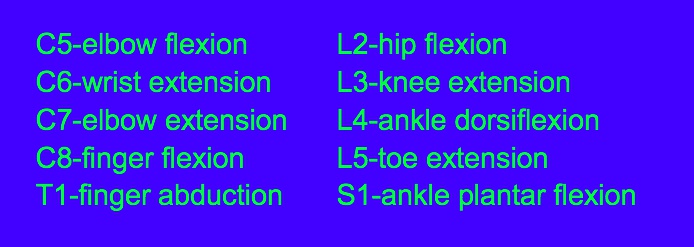
_T1, myotome.,

_C5, 6, reflex.,
_C7, 8, reflex.,
Lumbosacral
Sensory—suprapubic region
Motor—transversus abdominis and internal oblique.,
_Abdominal surgery.,
_Burning or tingling pain in surgical incision site radiating to inguinal and suprapubic region.,
Sensory—scrotum/labia majora, medial thigh
Motor—cremaster.,
_Laparoscopic surgery., _decreased anterior thigh sensation beneath inguinal ligament; absent cremasteric refex.,
Sensory—anterior and lateral thigh.,
_Tight clothing, obesity, pregnancy., _decreased thigh sensation (anterior and lateral).,
Sensory—medial thigh
Motor—obturator externus, adductor longus, adductor brevis, gracilis, pectineus, adductor magnus.,
_anterior hip fracture, Pelvic surgery., _decreased thigh sensation (medial) and adduction.,
Sensory—anterior thigh, medial leg
Motor—quadriceps, iliopsoas, pectineus, sartorius.,
_Pelvic fracture., _decreased thigh fexion and leg extension.,
Sensory—posterior thigh
Motor—semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris, adductor magnus.,
_Herniated disc .,
Sensory—dorsum of foot
Motor—biceps femoris, tibialis anterior, extensor muscles of foot.,
_Trauma or compression of lateral aspect of leg, fibular neck fracture., _
Loss of sensation on dorsum of foot
Foot drop—inverted and plantarfexed at rest, loss of eversion and dorsifexion;
“steppage gait”.,
PED = Peroneal Everts and Dorsifexes; if injured, foot dropPED
Sensory—sole of foot
Motor—triceps surae, plantaris, popliteus, fexor muscles of foot.,
_Knee trauma, Baker cyst (proximal lesion); tarsal tunnel syndrome (distal lesion)., _Inability to curl toes and loss of sensation on sole; in proximal lesions, foot everted at rest with loss of inversion and plantar fexion.,
TIP = Tibial Inverts and Plantarfexes; if injured, can’t stand on TIPtoes
Motor—gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, tensor fascia latae.,
_Iatrogenic injury during intramuscular injection to upper medial gluteal region.,
_Trendelenburg sign/gait— pelvis tilts because weightbearing leg cannot maintain alignment of pelvis through hip abduction
Lesion is contralateral to the side of the hip that drops, ipsilateral to extremity on which the patient stands.,
_Choose superolateral quadrant (ideally the anterolateral region) as intramuscular injection site to avoid superior gluteal nerve injury..
Motor—gluteus maximus .,
_Posterior hip dislocation.,
_Diffculty climbing stairs, rising from seated position; loss of hip extension.,
Sensory—perineum
Motor—external urethral and anal sphincters.,
_Stretch injury during childbirth.,
_decreased sensation in perineum and genital area; can cause fecal or urinary incontinence.,
_Pudendal nerve can be blocked with local anesthetic during childbirth using ischial spine as a landmark for injection..
Neurovascular
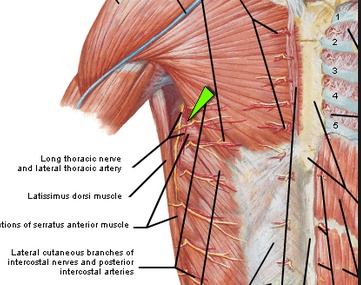
_ Long thoracic, Lateral thoracic.,
_ Axillary, Posterior circumfex.,
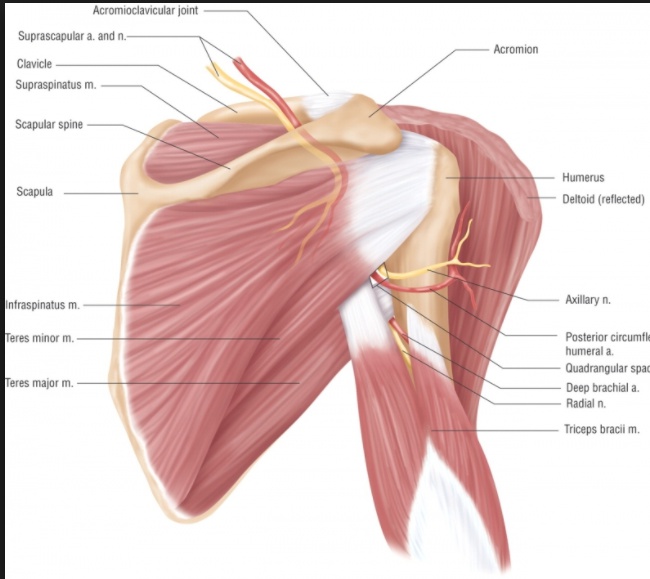
_ Radial, Deep brachial., _ Median, Brachial.,
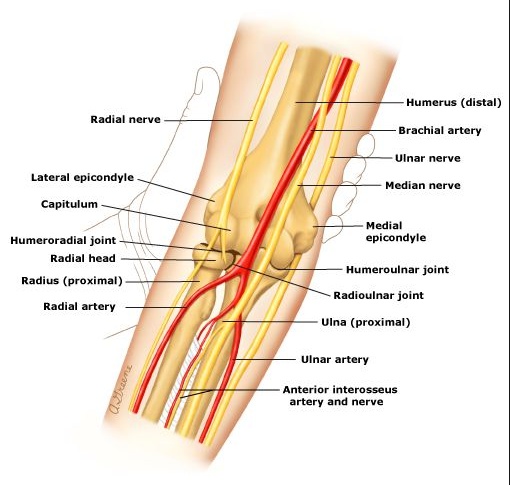
_ Tibial, Popliteal.,
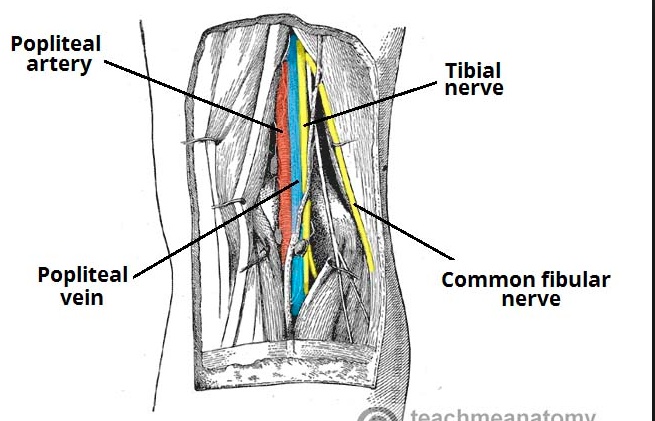
_ Tibial, Posterior tibia.,
Overuse
_golfer's elbow.,
_tennis elbow.,
_repetitive flexion, pain near medial epicondyle.,
_repetitive extension, pain near lateral epicondyle.,
Upper Extremity
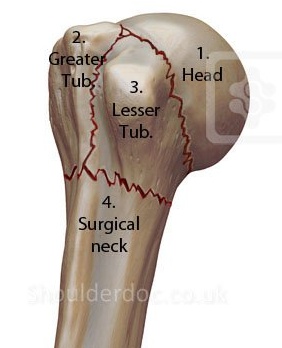
_anterior dislocation of humerus, surgical neck fracture.,
_upper trunk compression.,
_loss of flexion and supination, loss of sensation over lateral forearm.,
_radial nerve..
_radial nerve..
_radial..
_..wrist drop, decreased grip strength, loss of sensation posterior arm/forearm, dorsal hand
_ulnar, hook of hamate..
_recurrent median, loss of muscles, no loss of sensation..
_infant, lateral traction on neck during delivery. Adult, trauma.,
_infant, upward force on arm during deliver. Adult, grabbing tree branch.,
_compress lower trunk and subclavian vein..
_axillary node dissection, masectomy, stab wounds..
Radiculopathy
_L4-5, loss of dorsiflexion..
_L5-S1, loss of plantar..
Lymph Nodes
Internal iliac
_..
lower rectum above pectinate
bladder
vagina (middle third), prostate, cervix
Superficial Inguinal
_..
anal canal below pectinate
skin below umbilicus, except popliteal (anterior abdominal wall and legs)
scrotum
vulva, skin of penis
buttocks, perineum
Deep Inguinal
_..
penile urethra, glans penis
paraaortic
_..
testes, ovaries
uterus
kidney
Signaling Pathway
_FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, CRH, hCG, ADH (V2-receptor), MSH, PTH, calcitonin, GHRH, glucagon, histamine (H2-receptor).,
FLAT ChAMP
_ BNP, ANP, EDRF (NO).,
BAD GraMPa Think vasodilators
_GnRH, Oxytocin, ADH (V1-receptor), TRH, Histamine (H1-receptor), Angiotensin II, Gastrin.,
GOAT HAG _Progesterone, Estrogen, Testosterone, Cortisol, Aldosterone, T3/T4, Vitamin D.,
PET CAT on TV _Insulin, IGF-1, FGF, PDGF, EGF MAP kinase pathway.,
Think Growth Factors _ Prolactin, Immunomodulators (eg, cytokines IL-2, IL-6, IFN), GH, G-CSF, Erythropoietin, Thrombopoietin.,
JAK/STAT pathway Think acidophils and cytokines PIGGLET
Last updated