36 Pericardial Disease
_..

Pericarditis
_..


fibrinous: not immune, extension of necrosis

ischemic chest pain not positional

like sand paper
T wave association with pericarditis
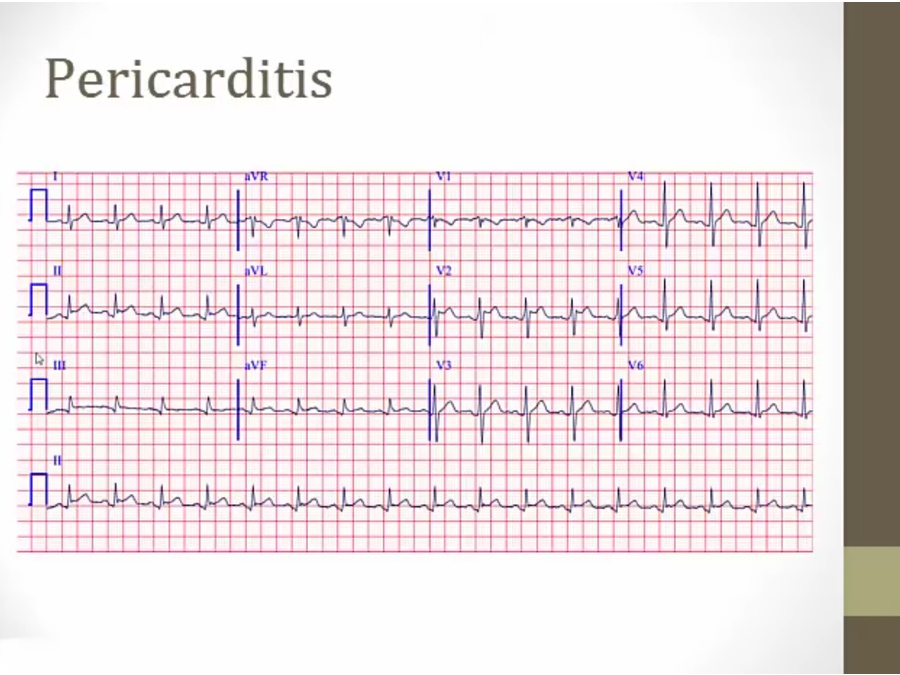
diffused ST elevation
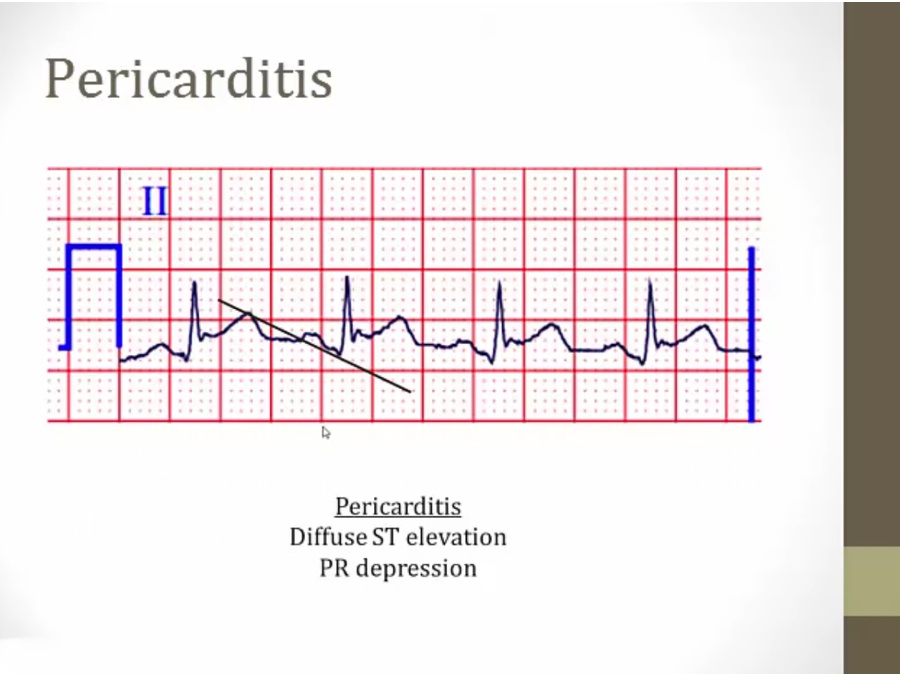
P begins at higher point than where R point ends

_..
inflammation of myocardium not from ischemia
Tamponade
_..

cancer pts developing dyspnea: tamponade

wall of fluid muffle heart sounds

usually hypotension only in acute
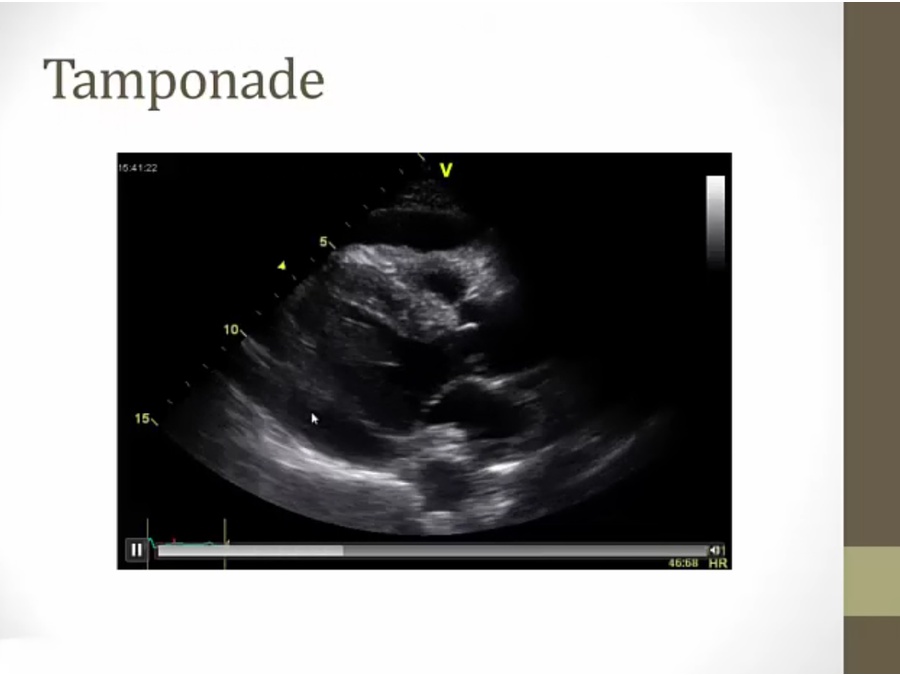
black band around infralateral wall (lower left) and in front (top)
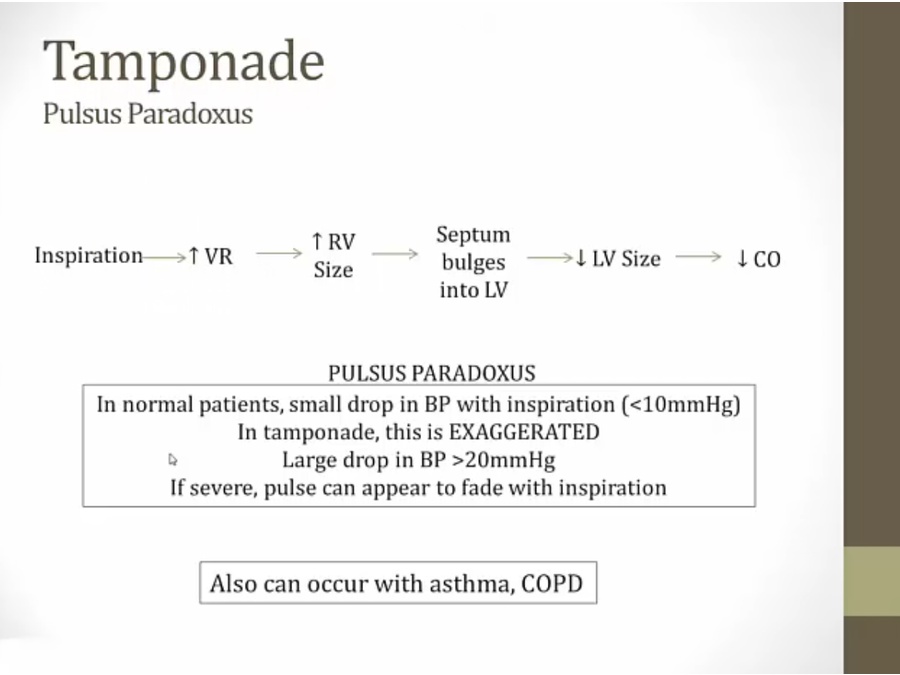
inspire, push diaphragm down, compress abdomen vessels (IVC), thorax vessels dilate, increased venous return
tamponade: RV cannot increase in size, all its increase in size bulges into LV
asthma/COPD: exaggerated changes in thoracic pressure may leads to hemodynamic changes

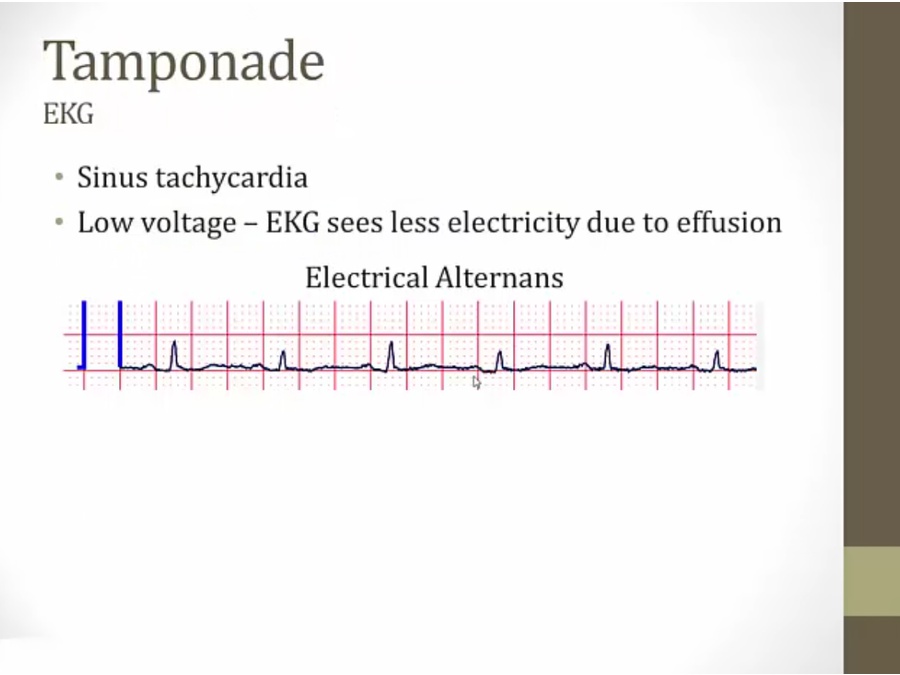
tachycardia: increased sympathetic
EKG: rare, tall and short QRS, heart swinging inside fluid
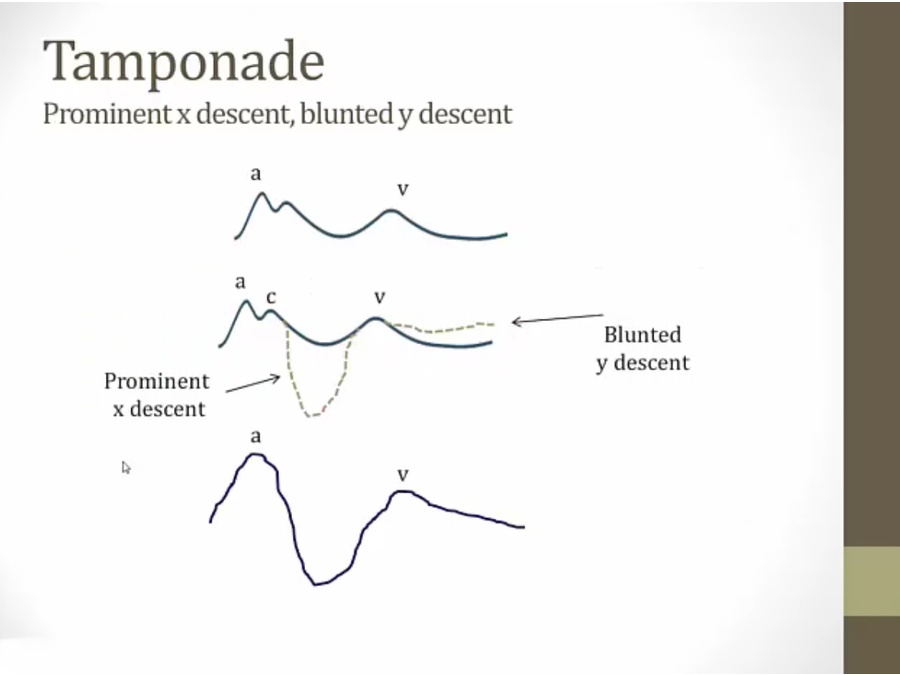
x descent: RV contraction
tamponade: RV contraction, makes room in pericardium for fluid to move away from RA to RV, allow RA to relax more, steep x descent
y descent: filling of RV impaired
late diastolic collapse of RA
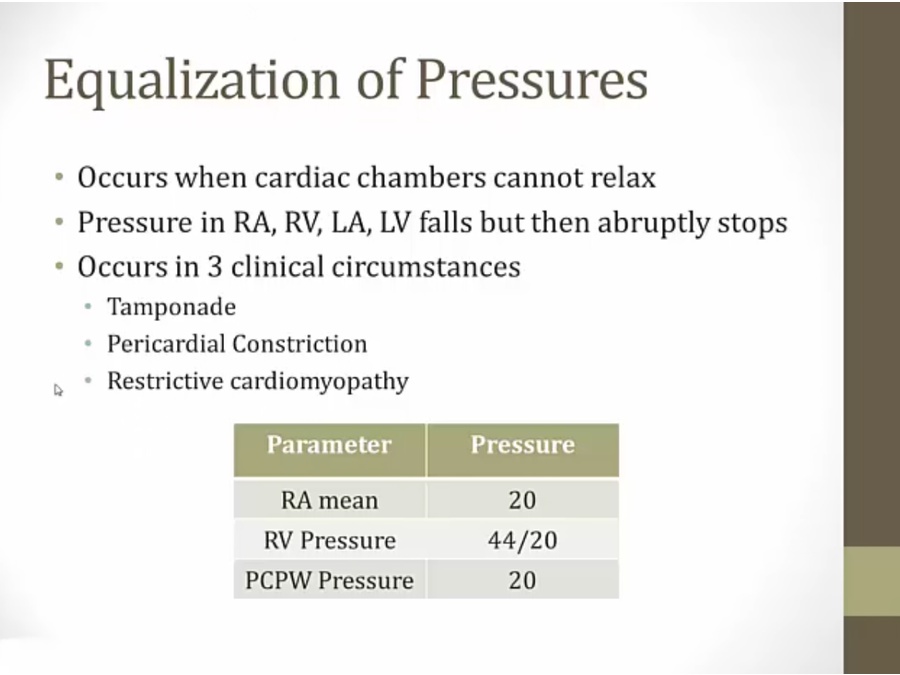
Constrictive
_..

viral carditis
RV stuck to pericardium
also caused by miliary TB (immigrant)
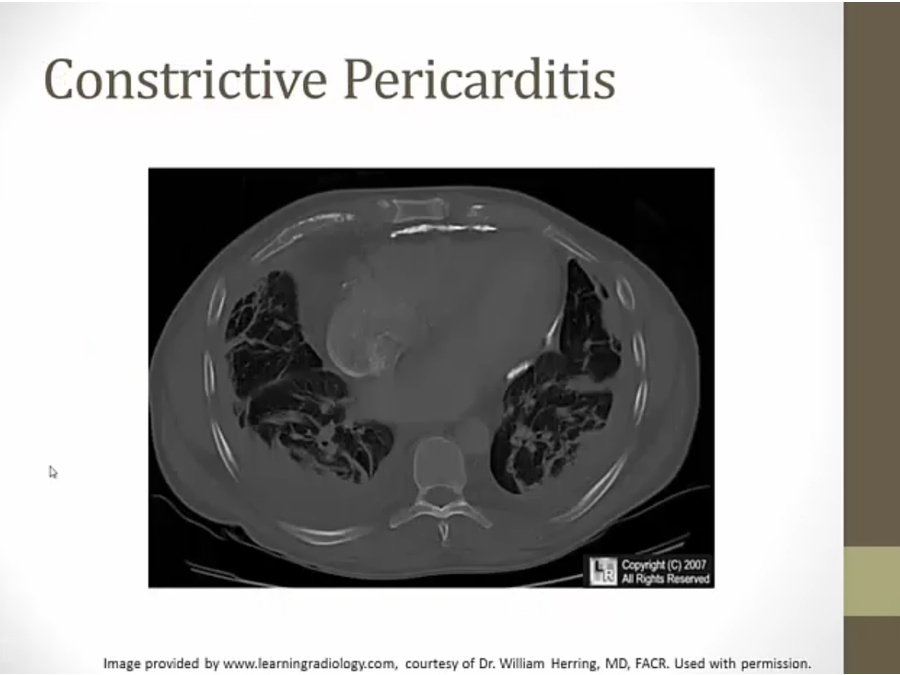
bright white material surrounding heart, Ca
long standing inflammation: calcified


any disease where can't accept venous return leads to kussmaul's sign
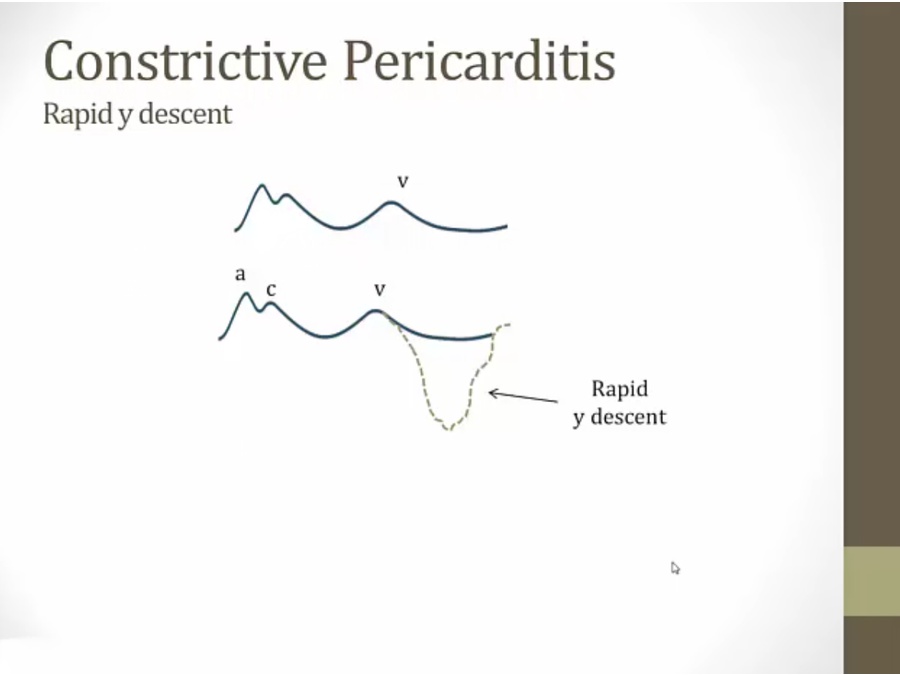
constrictive: RV adhered to pericardium, contracts in systole, and snaps back in diastole, pulled towards pericardium, then it hits the calcified shell, and pressure shoots back up
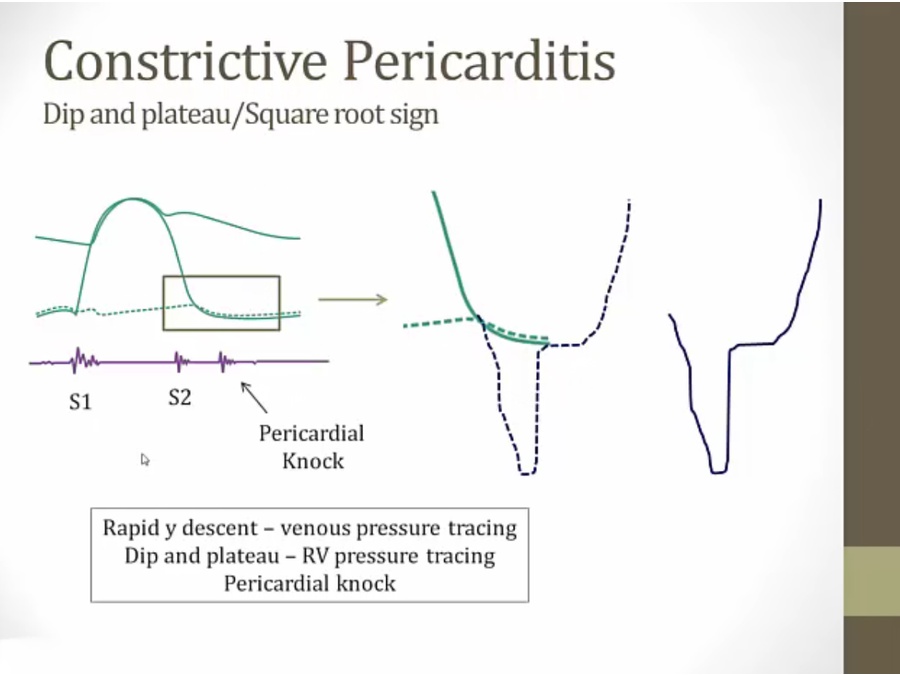
square root sign: RV falls much more rapidly and deeper than normal, same physiology as RA tracing
pericardial knock: abrupt stop and shoot up pressure, similar to S3
_..
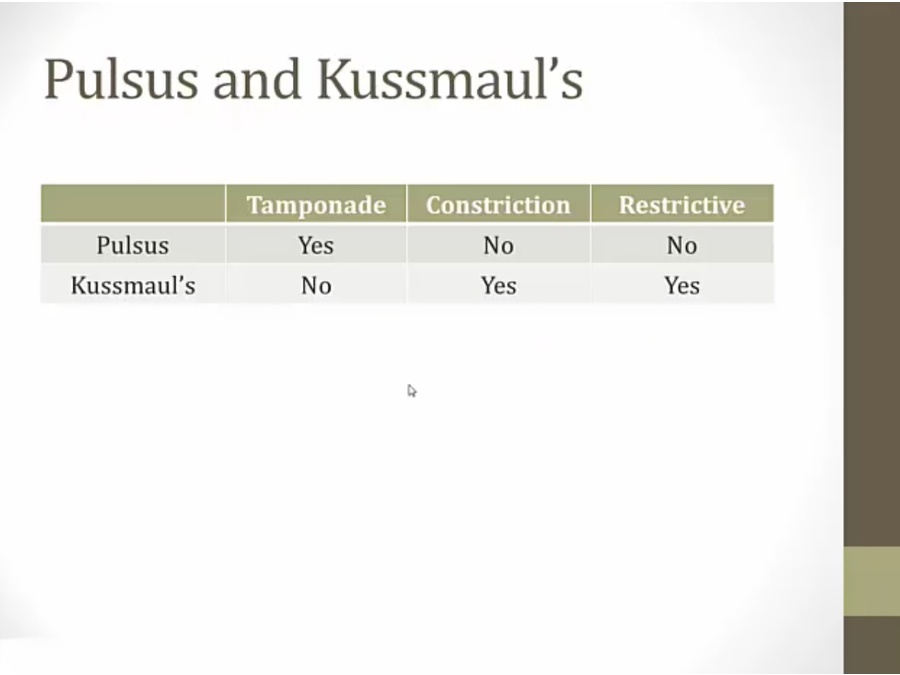
Tamponade: RV is able to distend and fill, thus no kussmaul. However, RV fills by pushing septum to LV, thus pulsus
restrictive: restricting substance, RV cannot accept venous return, and septum frozen
constriction: RAP goes up in inspiration (Kussmaul); however, increased pressure is not passed along to septum
Last updated