08 Pituitary Pathology
Anterior Pituitary Pathology
Pituitary Adenoma
 ..
..
_Symptoms
 .,
.,
Bitemporal hemianopsia
_Pathogenesis:
 .,
.,
Pituitary is next to optic chiasm. Enlargement of pituitary can cause vision problems.
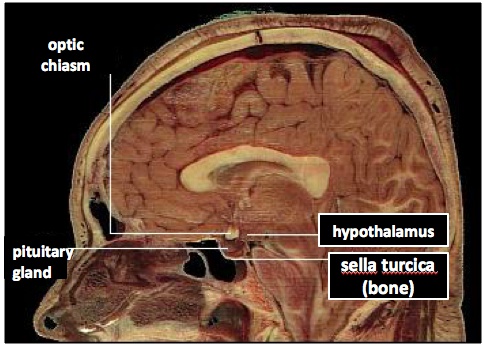
_Include:
Prolactinoma: common
GH adenoma
ACTH adenoma: Cushings
TSH, LH, FSH: rare.,
Prolactinoma
Benign tumor of lactotroph. Inhibits GnRH, thus LH/FSH
Male: no breast lobular unit for milk
 .,
.,
_Dopamine antagonists such as the antipsychotic risperidone and haloperidol. Antiemetics, metoclopramide. All of these block D2 receptors..
_Treatment
Dopamine agonists: bromocriptine or cabergoline to shrink tumor
Surgery.,
_Dopamine agonists drugs.,
GH Excess
_Causes are usually due to tumor. Presentation can be different depending on where the tumor is. If the tumor secretes GHRH and is in the hypothalamus or the sytem, there would be a high GHRH level. If the tumor is in the anterior pituitary, there would be a low GHRH and high somatostatin level.

.,
_Symptoms

.,
_Diagnosis

.,
_Treatment
pegvisomant: a GH receptor antagonist that effectively blocks IGF-1 production
 ..
..
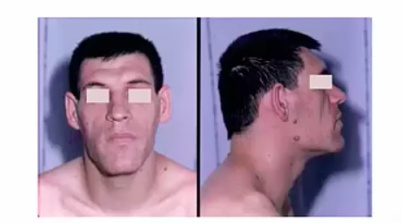
Acromegaly
Insidious onset, 12 yrs average: difficult to diagnose
Enlarged features
jaw, corse faces (enlarged nose, frontal bones)
tongue
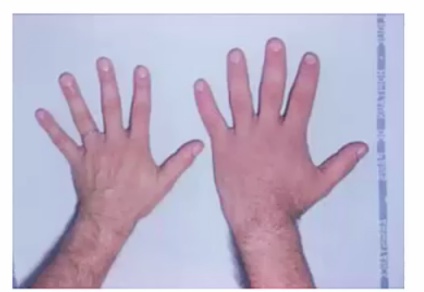
hands and feet (rings no longer fit)
larynx (voice deepens)
Enlarged visceral organs
Cardiac failure
Enlarged joints: joint pain
Secondary diabetes from GH induced liver gluconeogenesis
Increased risk of colon cancer
.,
Hypopituitarism
_Describes the insufficient secretion of pituitary hormones resulting from diseases of the hypothalamus or the pituitary. .,
_The majority of cases are secondary to destructive processes directly involving the anterior pituitary. This includes:
Tumors, such as nonfunctional pituitary adenomas (adnomas not producing hormones) or craniopharyngiomas(exert pressure on adjacent pituitary cells)
Pituitary surgery or radiation
Traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage
Pituitary apoplexy (sudden hemorrhage into the pituitary gland)
Sheehan syndrome (postpartum necrosis of the anterior pituitary secondary to infarction precipitated by obstetric hemorrhage or shock)
Empty sella syndrome (presence of an enlarged, empty sella turcica due to a condition that partially or totally destroys the pituitary gland; classically affects obese women with a history of multiple pregnancies).
 ..
..
_The clinical manifestation of hypopituitarism depends on the specific hormone(s) that are lacking. For example, a deficiency of melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) may manifest as hypopigmentation, due to MSH's stimulatory effects on melanocytes.

Aldosterone part of RAAS system, not adrenal system...
_The treatment for hypopituitarism includes hormone replacement therapy, including:
Corticosteroid
T4 (thyroxine)
Sex steroids
Human growth hormone
Pulsatile GnRH (for patients that desire fertility)..
Empty Sella Syndrome
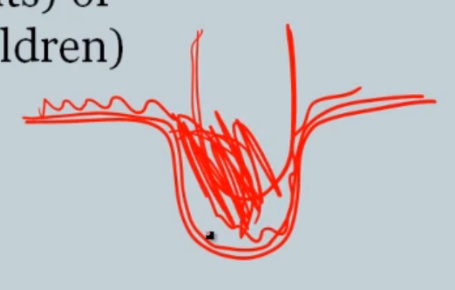
Arachnid and dura matter around sella. Pia matter around pituitary
Herniation of arachnoid and CSF into sella compresses and destroys pituitary: hypopituitarism
Sella filled with CSF, which is clear on imaging..
_  .,
.,
Pituitary Apoplexy
.,
Sheehan's Syndrome
[_](Sheehan's syndrome pathogenesis)Pituitary gland enlarged in preglancy as result of increased prolactin. However, the blood supply is not increased. In postpartum hemorrhage, pituitary is at risk of infarct from hypotension. ..
[_](Sheehan's syndrome symptoms)Can present as shock after delivery from low cortisol levels if severe. If not severe, present as failure to lactate from loss of prolactin 
Other symptoms:
Absent menstruation from low FSH/LH
Loss of pubic and axillary hair from low FSH/LH
Cold intolerance from low TSH
Fatigue from low GH
Anorexia
.,
Posterior Pituitary Pathology
DI
_Is due to:
Central DI: a lack of antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Nephrogenic DI: a lack of ADH functionality in the collecting tubules..
_Is characterized by:
Dilute urine (even after water restriction)
Intense thirst
Polyuria.,
_Labs:
hypernatremia
Urine specific gravity < 1.006
Serum osmolarity > 290 mOsm/L..
_A water restriction test is used to diagnose central and nephrogenc DI:
Water intake is restricted for 2-3 hours, and urine volume, urine osmolality, plasma Na+ concentration, and plasma osmolality are measured hourly.
In healthy individuals, water deprivation leads to a urine osmolality 2-4 times greater than plasma osmolality.
In patients with central or nephrogenic DI, urine osmolality will be less than 300 mOsm/kg after water deprivation..
Central: low ADH
Nephrogenic: high ADH
DDAVP (desmopressin, an ADH analog) is administered to differentiate between central and nephrogenic DI:
In central DI, DDAVP administration will result in a 50% or greater increase in urine osmolality.
In nephrogenic DI, DDAVP administration will lead to no change in urine osmolality..
Central Diabetes Insipidus
radiation, surgery, trauma

.,
_Treatment: Desmopressin.,
Nephrogenic Diabetes
_Is due to the inability of the kidney to respond to ADH. This may be due to an inherited mutation in the V2 receptor or secondary to:
Lithium (drug-induced nephrogenic DI)
Demeclocycline (reduces responsiveness of kidney tubules to ADH) (treats SIADH)
Hypercalcemia (causes natriuresis and water loss)
Hypokalemia (decreases responsiveness of kidney tubules to ADH)
Sickle cell disease (impairs renal response to ADH)..
_Treatment involves:
Adequate hydration
Hydrochlorothiazide (see below)
Indomethacin
Amiloride.,
Why treat a water-wasting disease with a thiazide diuretic? Thiazides increase renal Na+ excretion, which leads to extracellular fluid volume contraction. This decreased volume will decrease GFR, and increase proximal tubular reabsorption of water and Na+. Therefore, ultimately less water and Na+ are lost as urine.
SIADH
_Occurs when too much ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary. Common CNS causes of SIADH include:
Brain infections (encephalitis)
Tumors of the pituitary, or tumors that impinge on the pituitary
Head trauma
Psychiatric illness
Non-CNS causes of SIADH include:
Medications (chlorpropamide, carbamazepine, cyclophosphamide and SSRIs)
Ectopic production by lung tumors (especially small cell carcinoma)
Pulmonary infection (viral, bacterial or tuberculous pneumonia)..
_Patients will generally present with euvolemic hyponatremia. Total body water is increased, but near-normal blood volume is maintained due to the body's compensatory response (decreased thirst, suppressed aldosterone release). Peripheral edema does not develop.,
_If asymptomatic, the treatment of SIADH is free water restriction.
Treatment of SIADH includes:
Demeclocycline, an antibiotic (tetracycline) used to treat SIADH because it induces a state of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by inhibiting the actions of ADH in the kidney. This allows for diuresis and less retention of water.
Vaptans (conivaptan, tolvaptan), which are vasopressin antagonists
Hypertonic (5%) saline should also be administered if severe CNS changes (e.g. seizures) are present.
It is important that hyponatremia be corrected slowly. A rapid correction of hyponatremia can lead to central pontine myelinolysis (aka osmotic demyelination syndrome)..
_Damage to the myelin sheath of the pons leads to the patient becoming "locked in", with intact cognitive function but total muscle paralysis, with the exception of eye blinking..
_In SIADH, urine osmolarity is greater than serum osmolarity..
Last updated
