15 Lung Cancer
Epidemiology

Risk

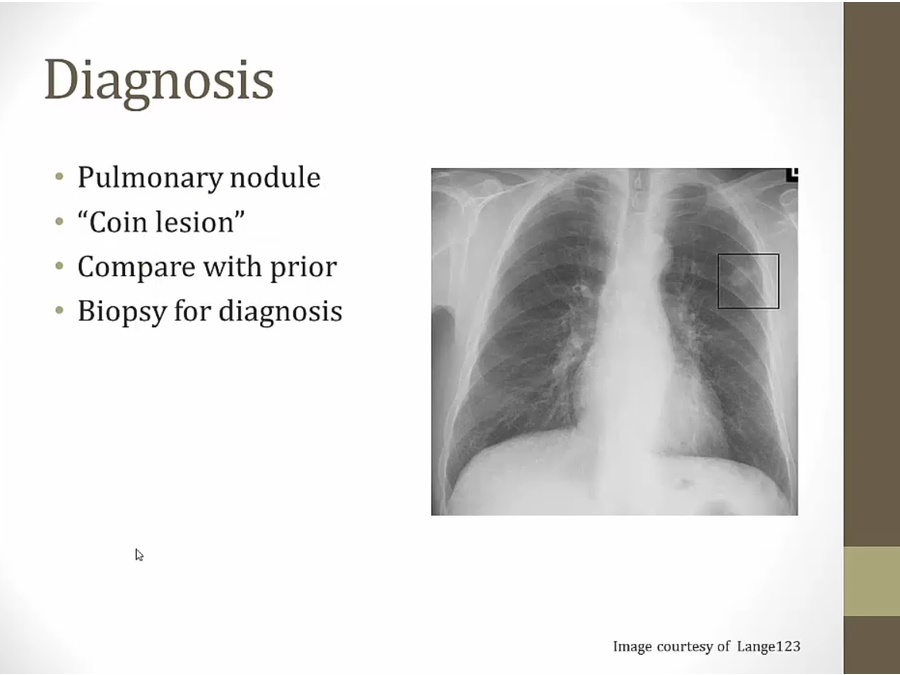
Symptoms and Diagnosis

Benign Lung Nodules


Primary Lung Cancer

Small Cell


Non Small Cell

Squamous

Adenocarcinoma

Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma

Large Cell Carcinoma

Carcinoid

Complications




Metastasis


Last updated