12 Thalassemia
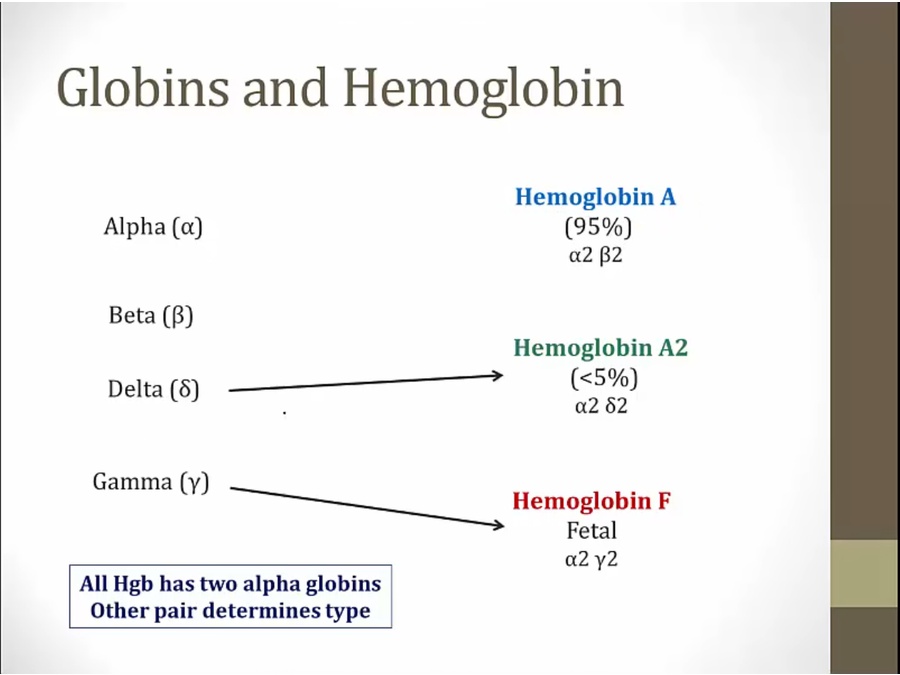
Globin
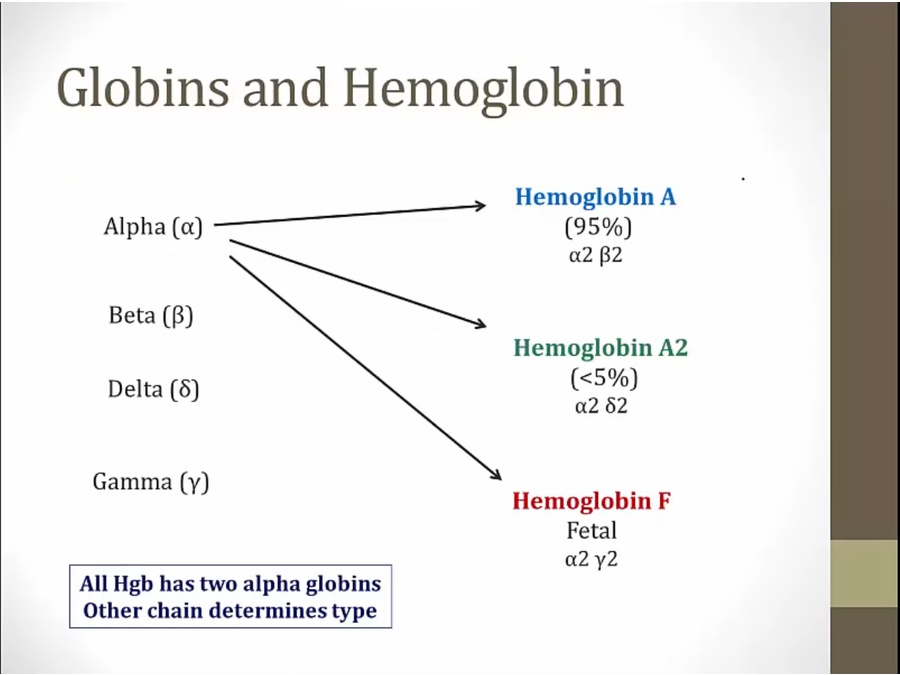
alpha chain very important: component of all 3 types
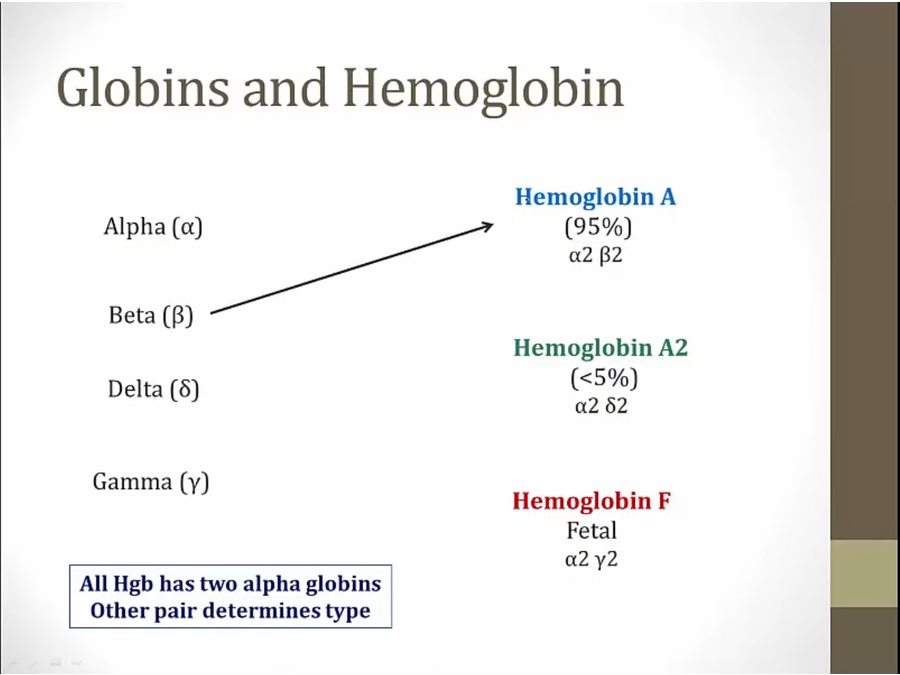
beta thalassemia only affects A
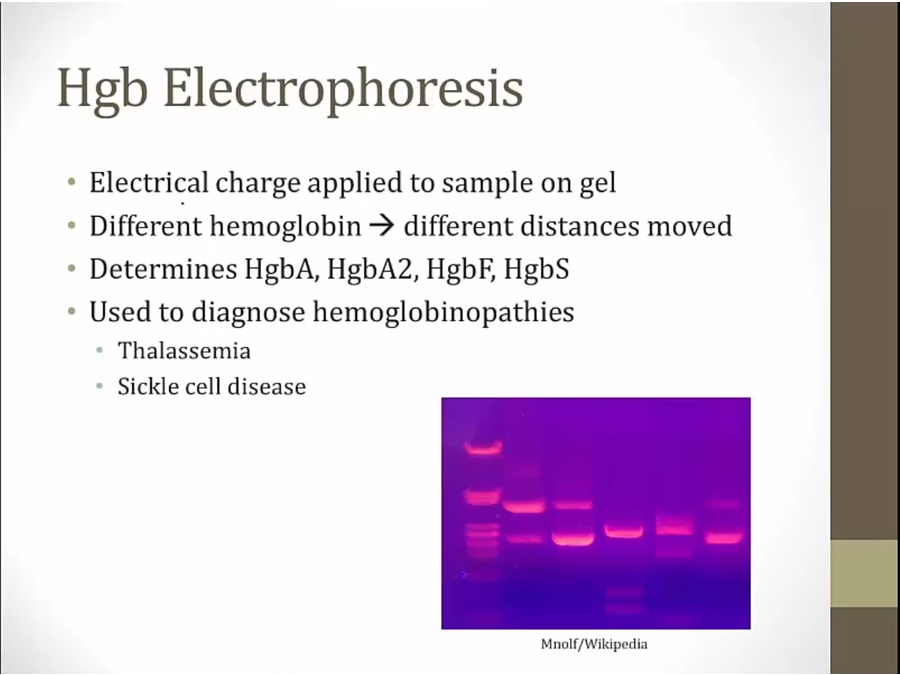
sample from patient in gel with electrical charge
Thalassemia


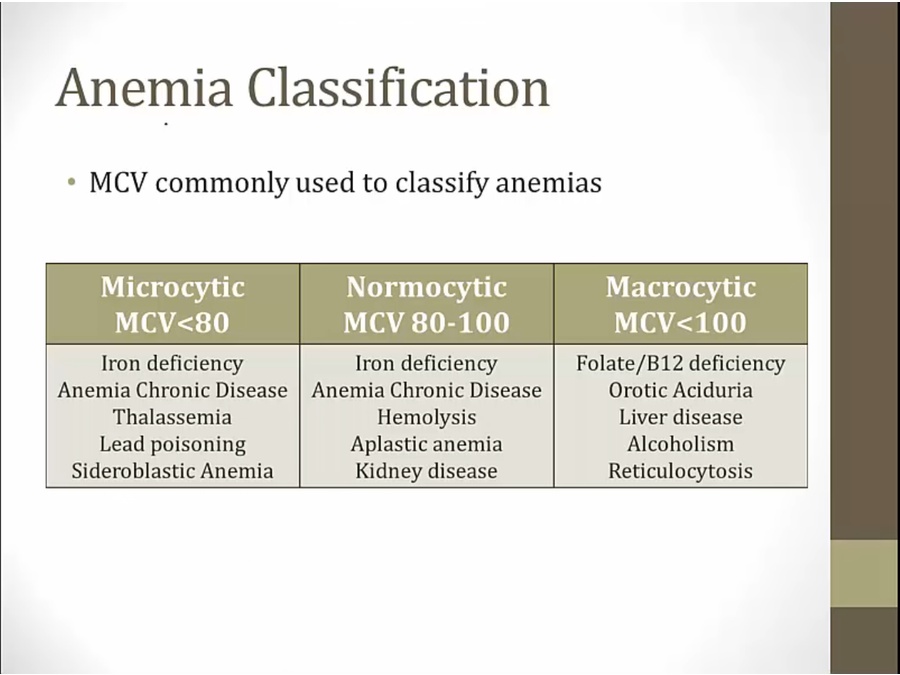
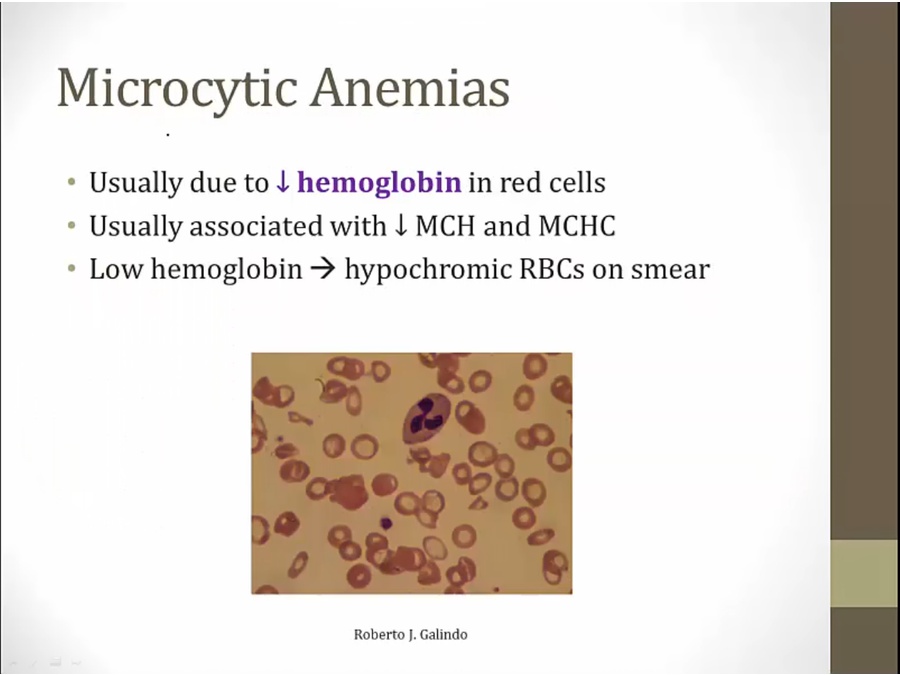
decreased hemoglobin causes thalassemia
Alpha
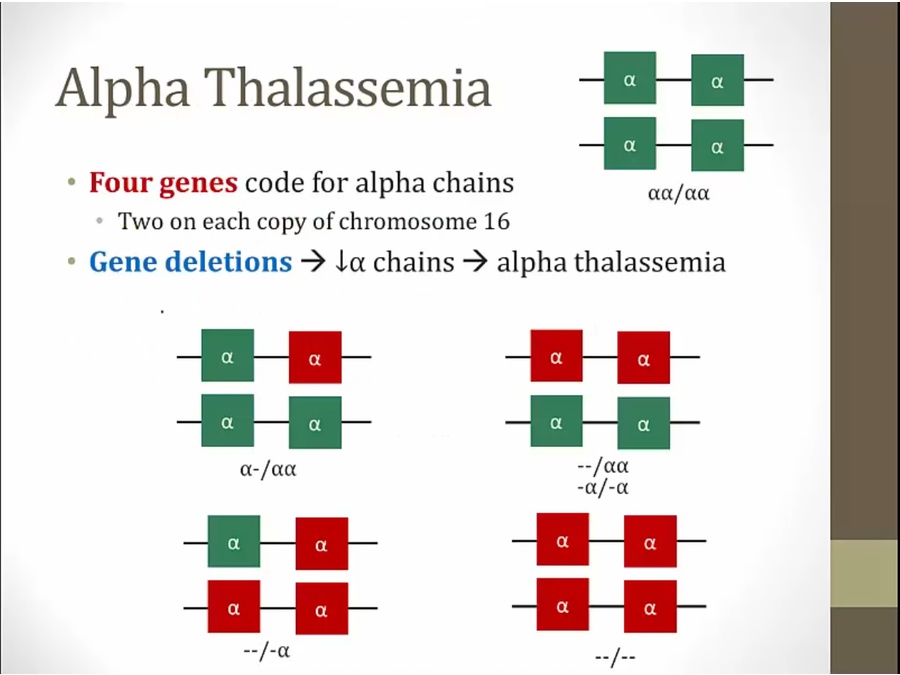
top right: normal, 2 alpha on each copy of Ch 16
alpha: gene deletion
depending on number missing, severity
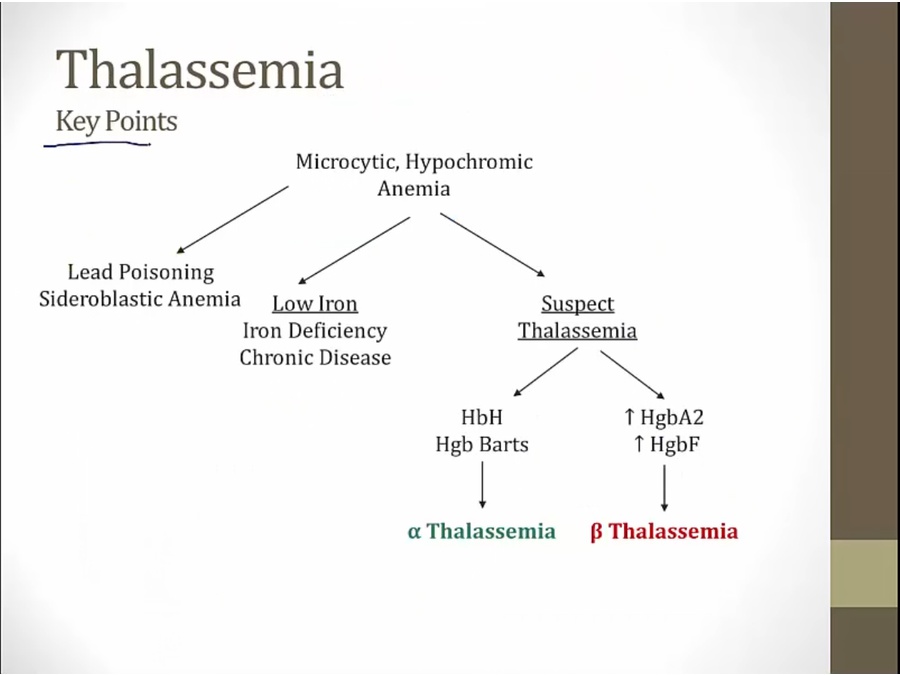
if not lead poisoning, sideroblastic, or iron, suspect thalassemia
use electrophoresis to determine alpha or beta
Minima
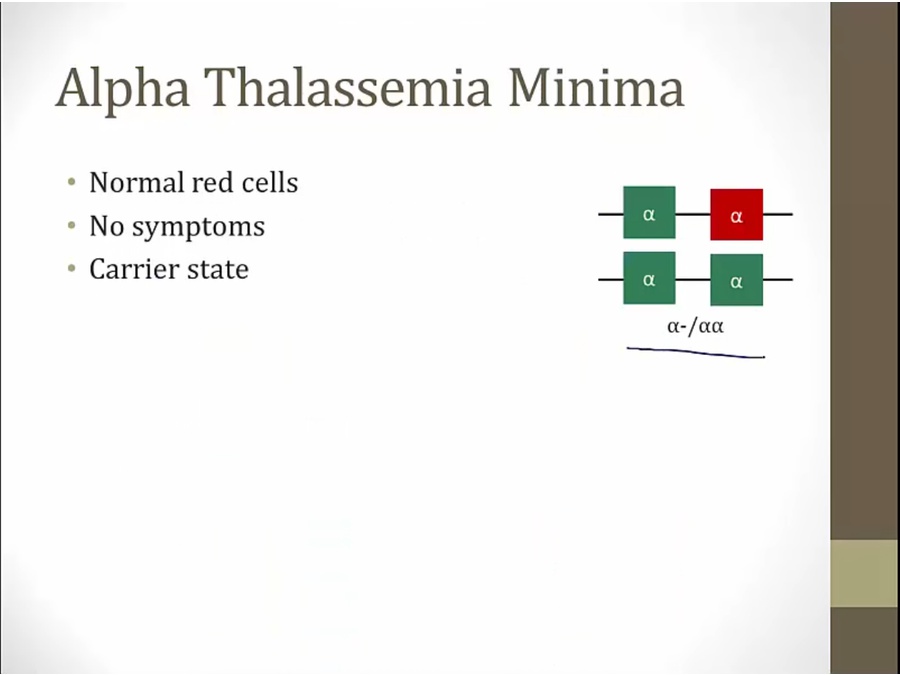
only risk is pass to offspring
Minor
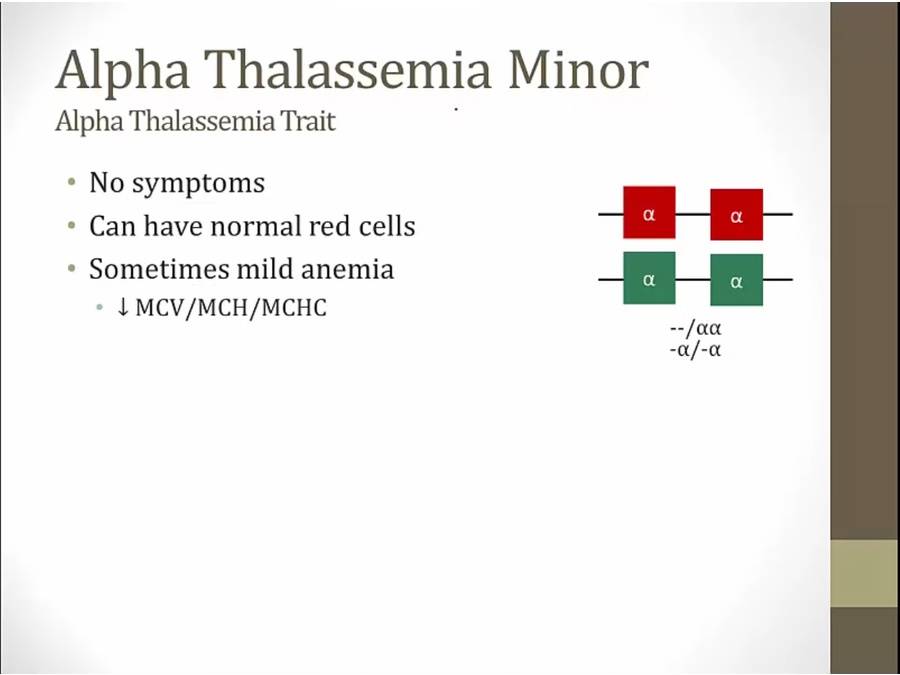
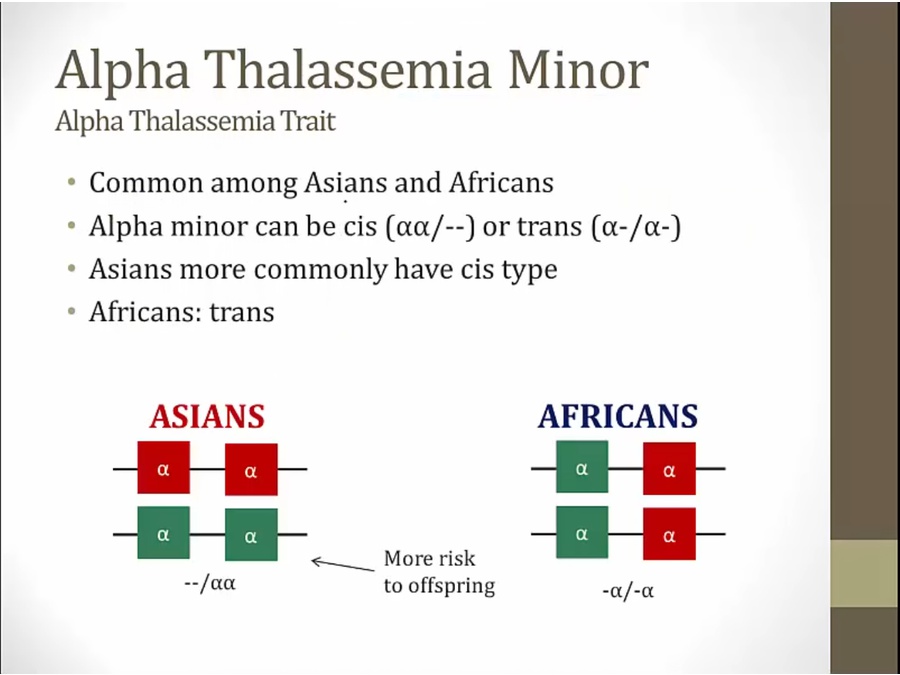
cis more risk: parent can pass 2 deleted genes to offspring
trans: can only pass on one deleted gene
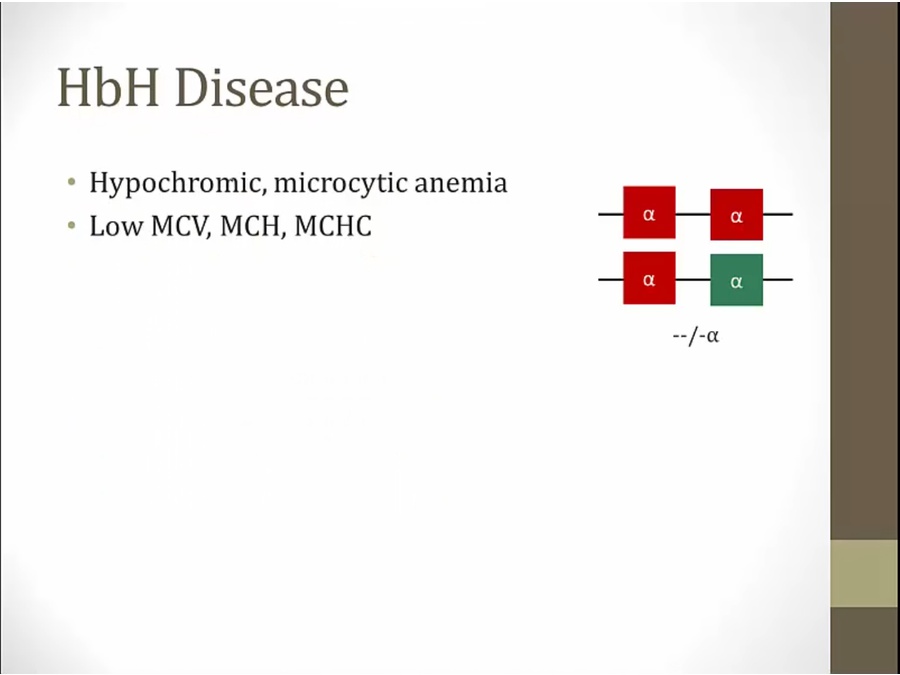
HbH Disease
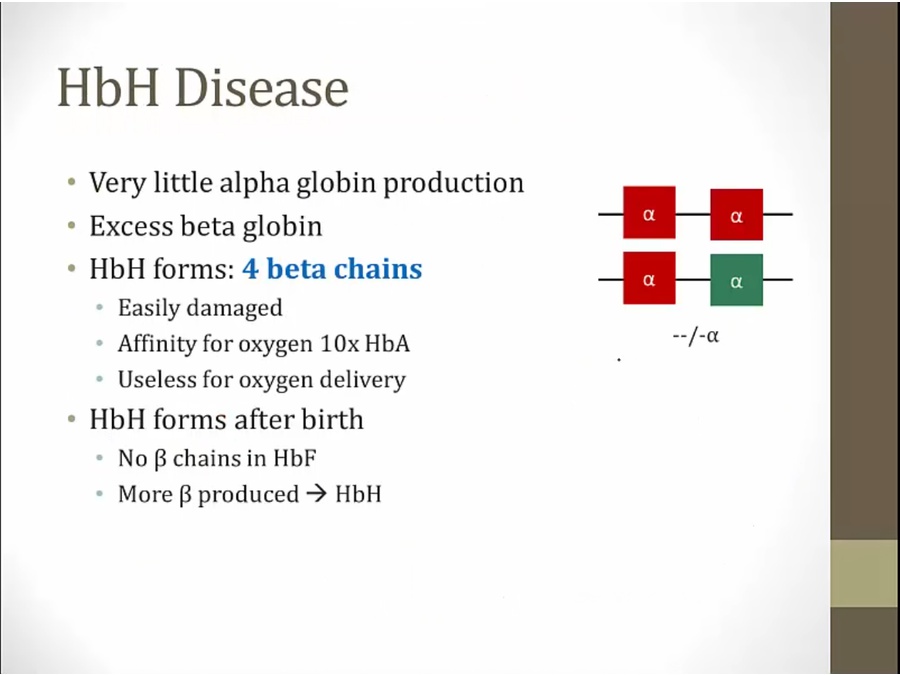
excess beta globin but can't combine with alpha globin
binds O2 but won't release
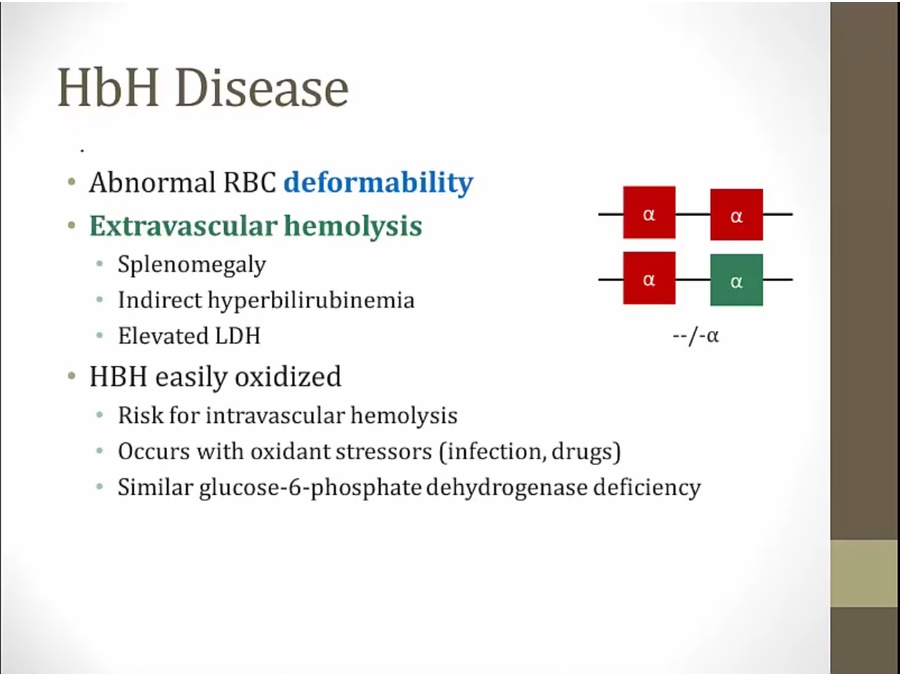
cleared by spleen
can look a lot like iron deficiency, but never see hemolysis (high bilirubin, splenomegaly) in iron deficiency

Bart
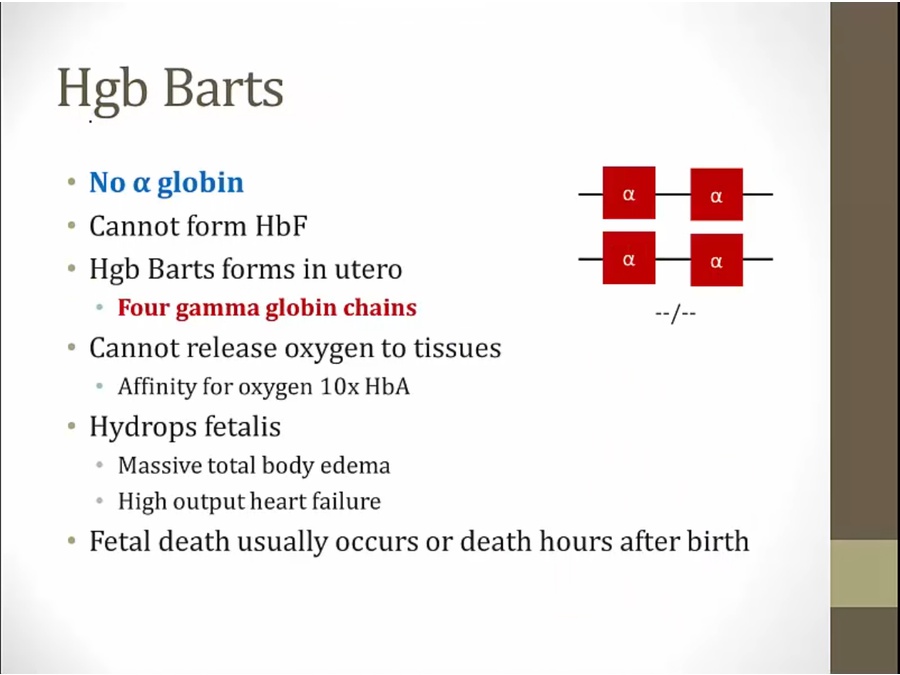
negative coombs test, compared to erythroblastosis fetalis
Beta

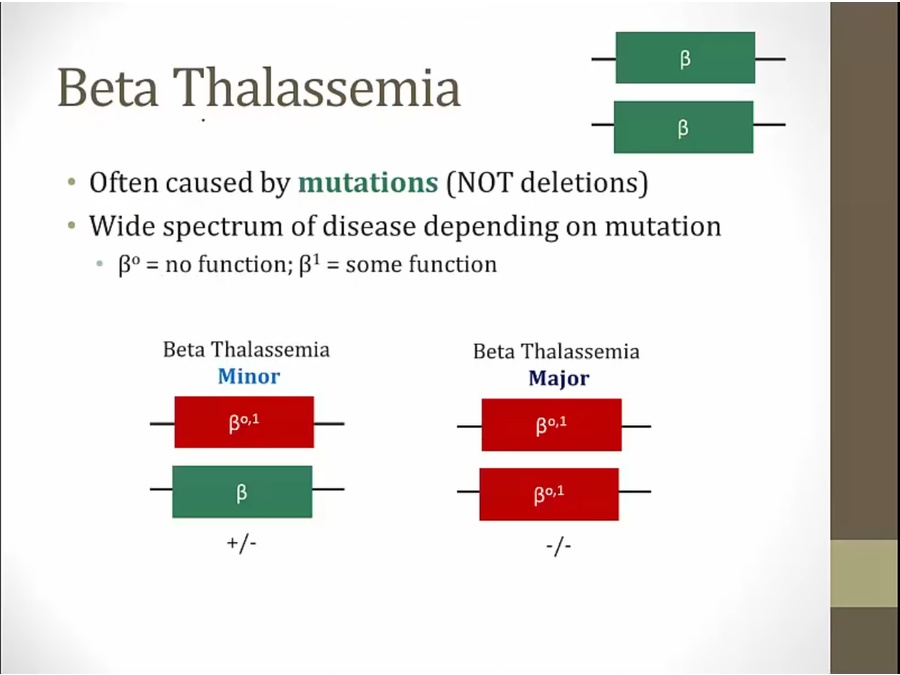
mutation can result in no function or some function
minor: 1 mutated gene
major: both genes mutated

if not lead poisoning, sideroblastic, or iron, suspect thalassemia
use electrophoresis to determine alpha or beta
mediterranean thalassemia
italy/greece.,
Minor
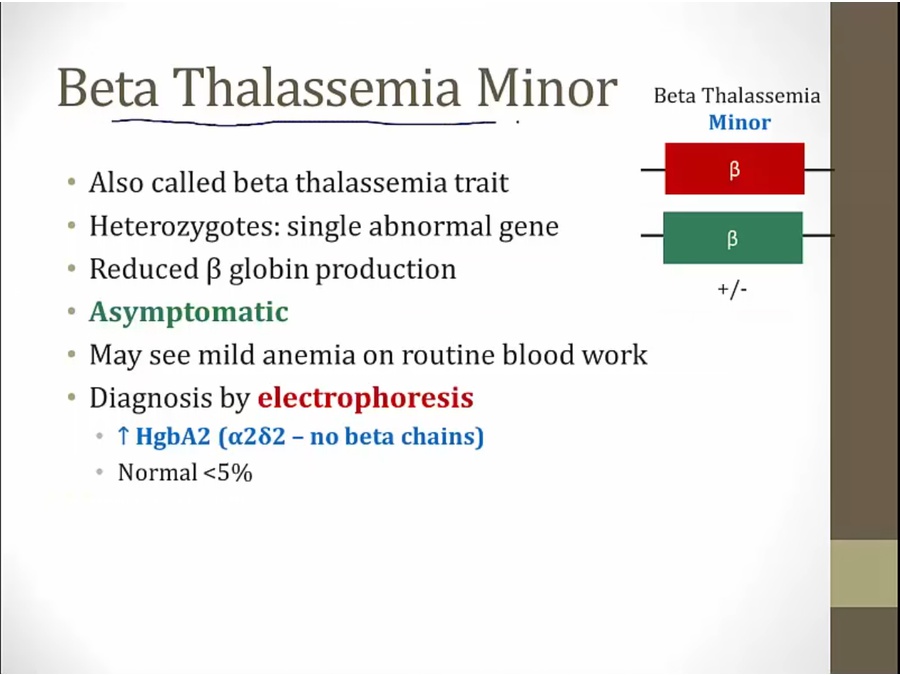
still makes enough to be asymptomatic
increased A2 is hallmark of minor
Major

severe anemia and reduced RBC count
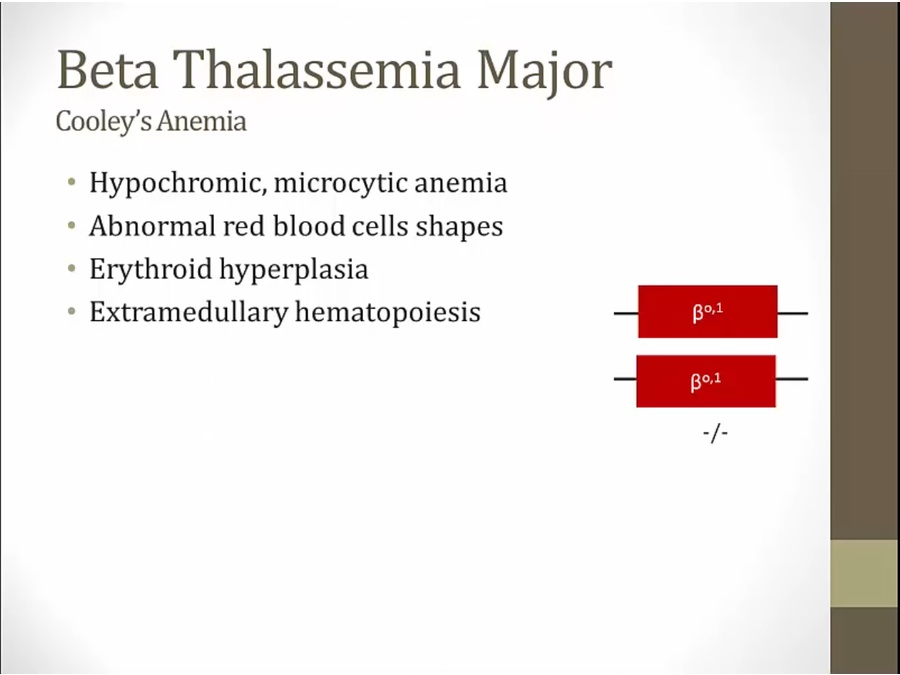
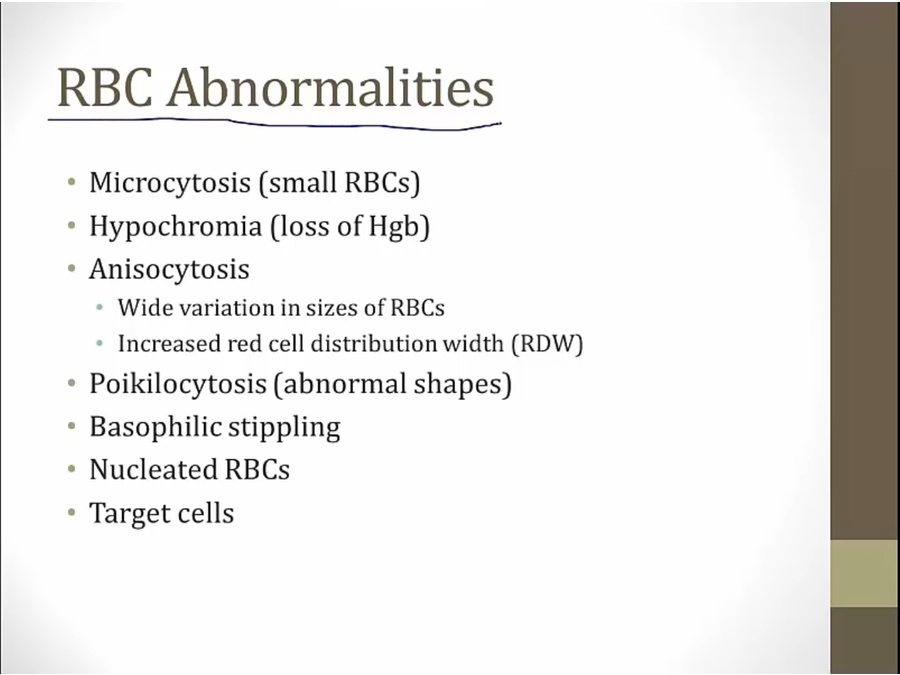
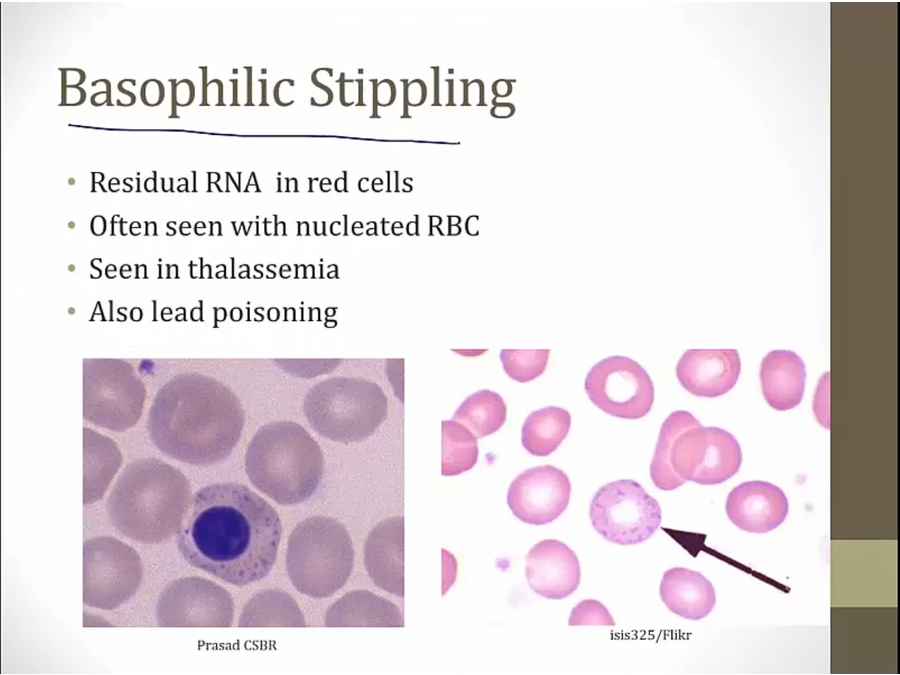
lots of abnormalities on smear
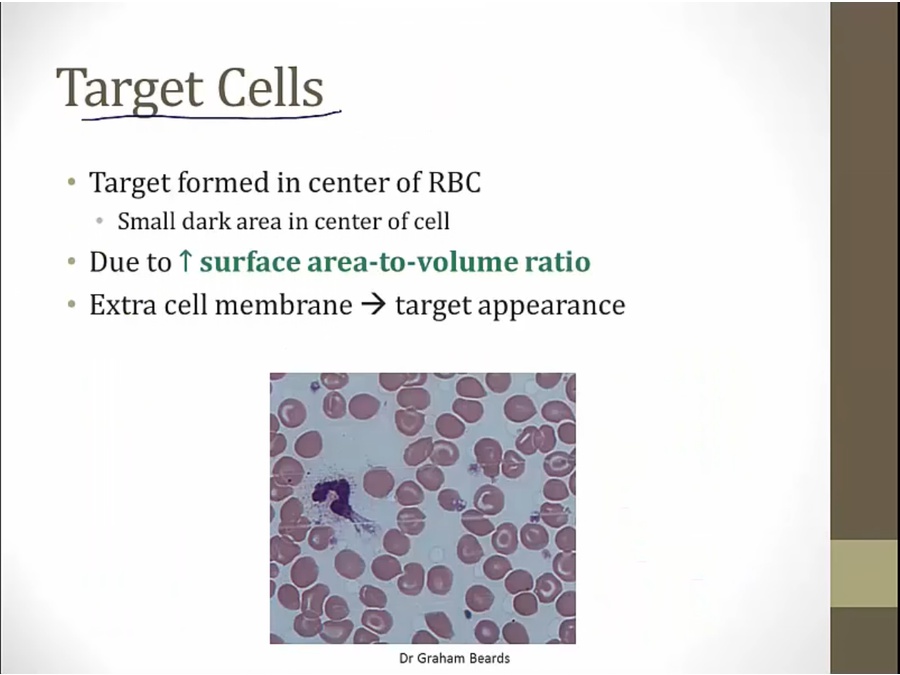
extra cell membrane or shrink volume

decreased volume with low Hb

bone marrow working so hard to make RBC: abnormal skull/face
crew cut: skull with fine points sticking out of it
liver/spleen make RBC with very high EPO


Intermedia

symptoms of anemia but not severe enough to require transfusion
Misc
just as likely to be infected as others, but less severe
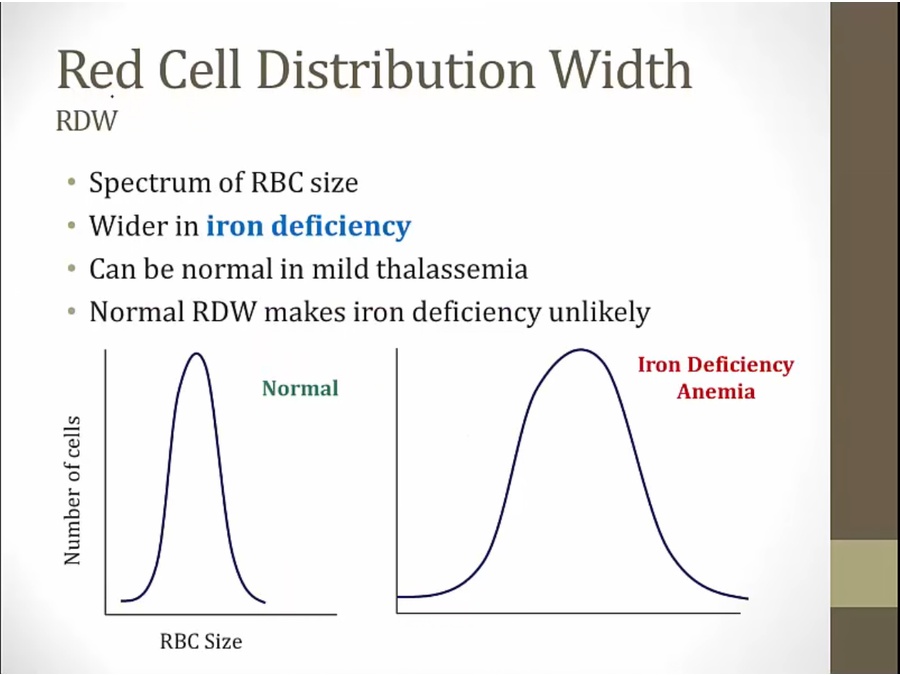
thalassemia: genetic disorder, all RBC affected
only for mild, not major
Last updated