06 PCR
PCR
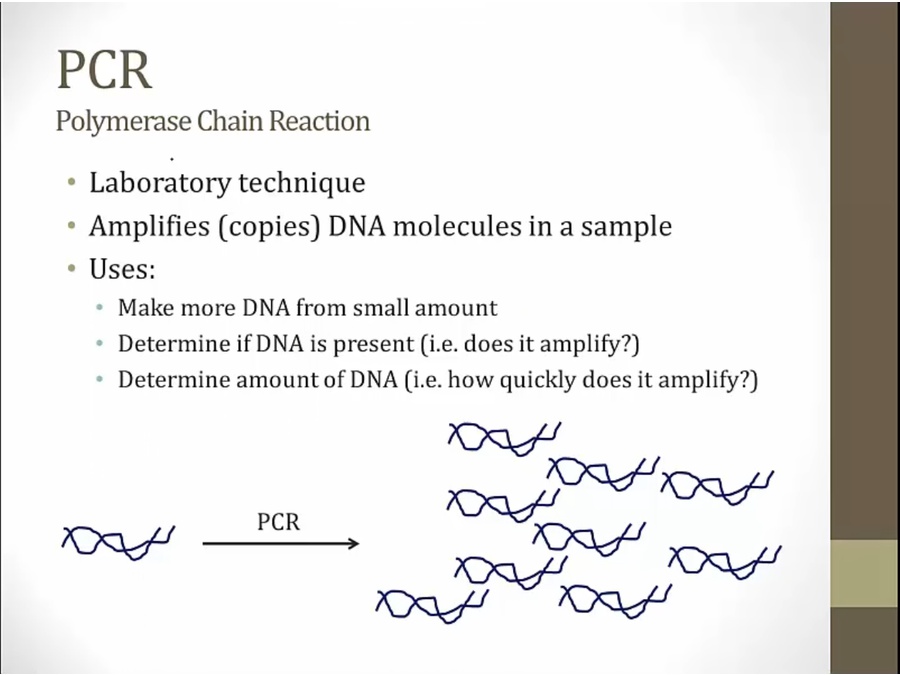

DNA polymerase requires primer

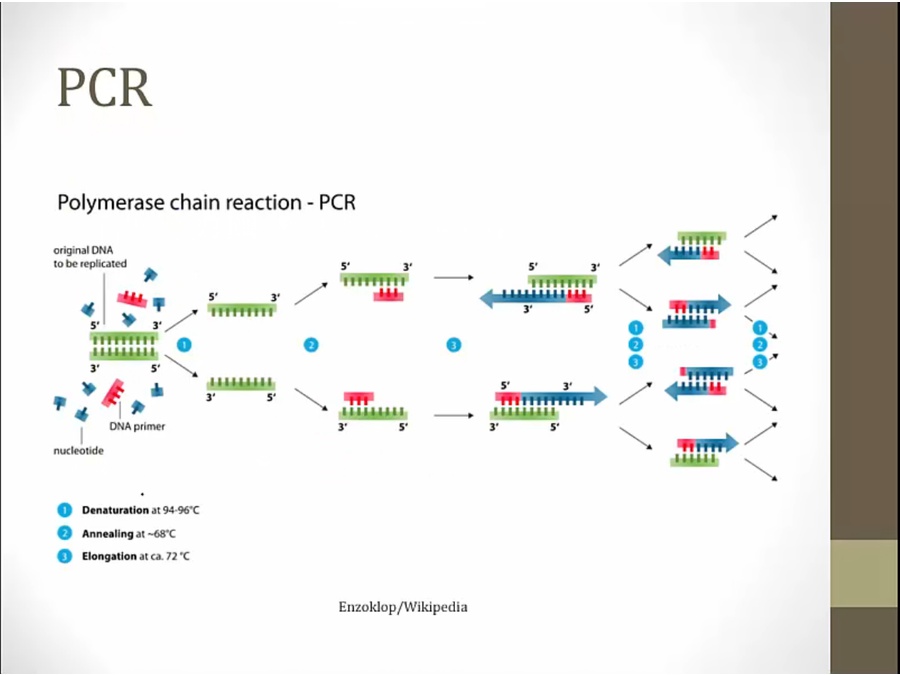

variant, quantitative

used for small amount of DNA curculating
HIV: RNA. Use reverse transcriptase to make copy of virus RNA: cDNA
Blotting


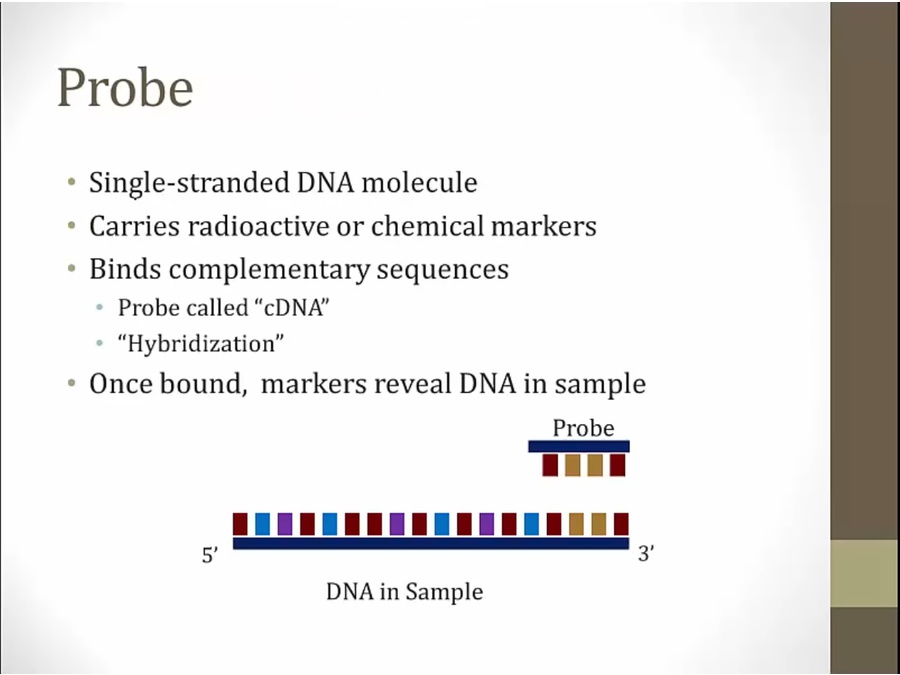
binding = hybridization
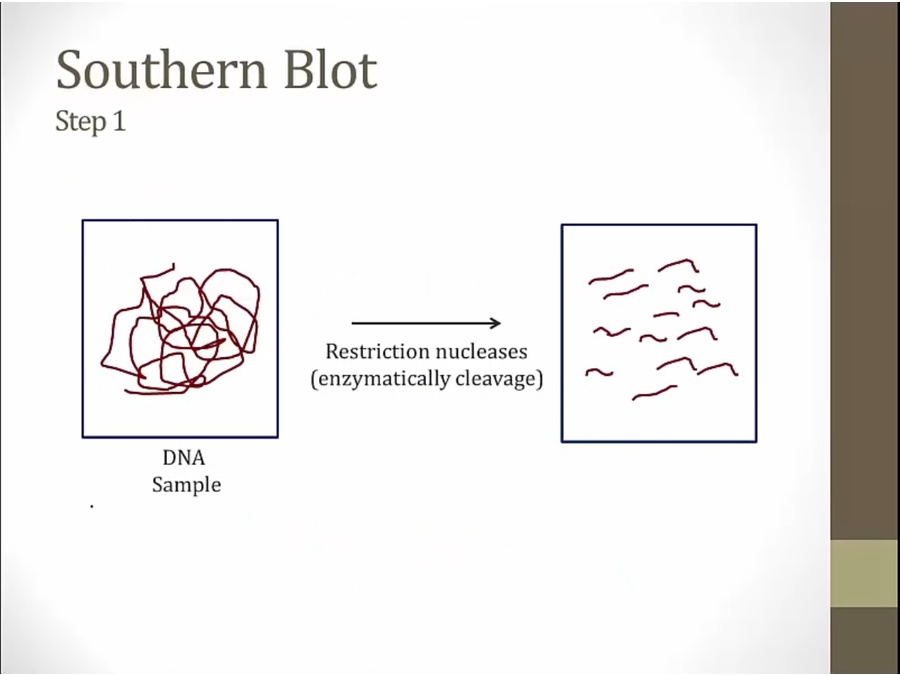
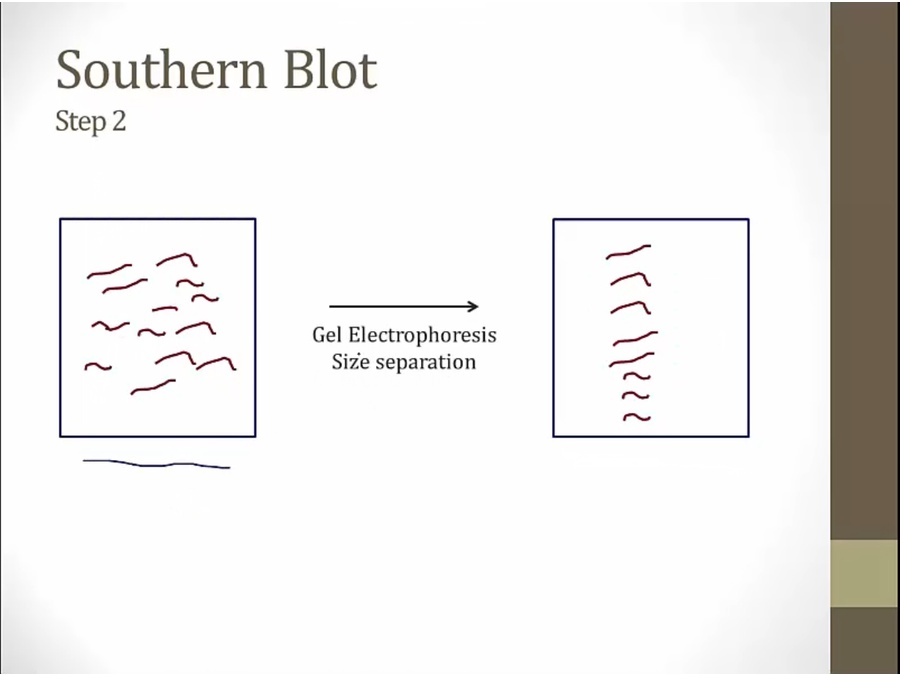

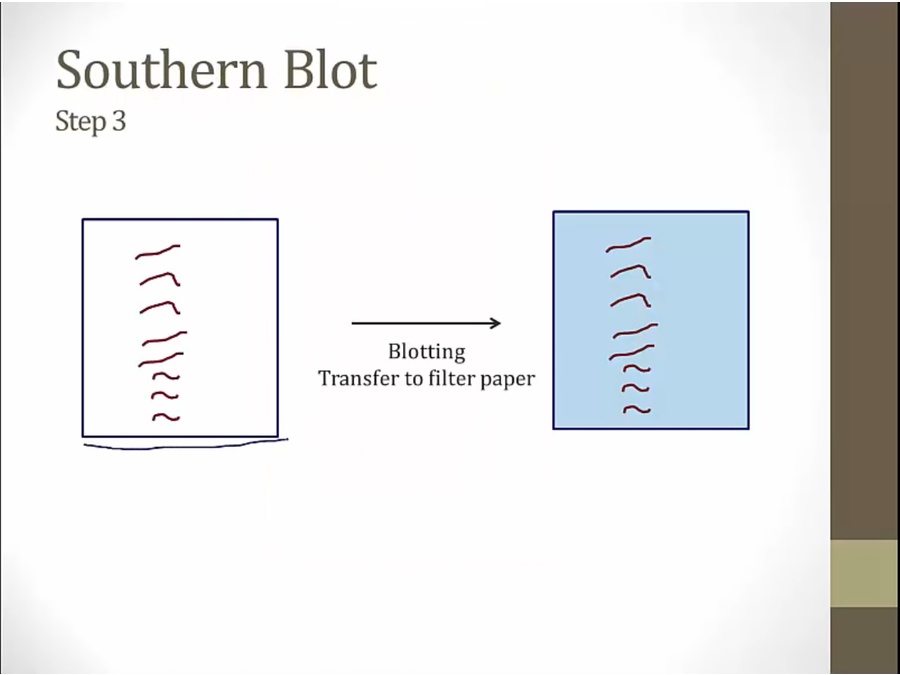
put a piece of filter paper on top. DNA stick to it

DNA left complementary to probe
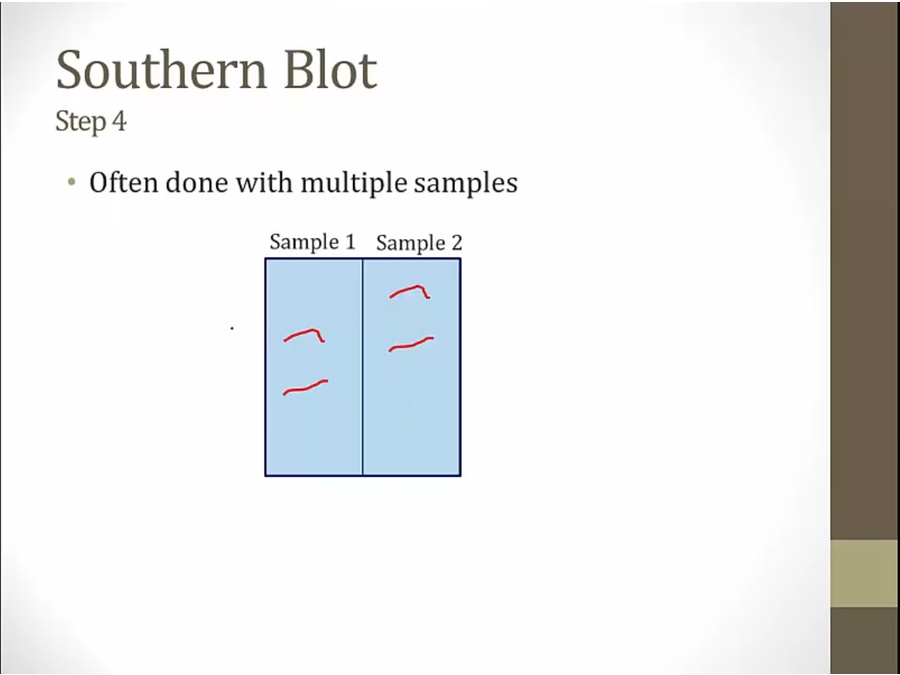
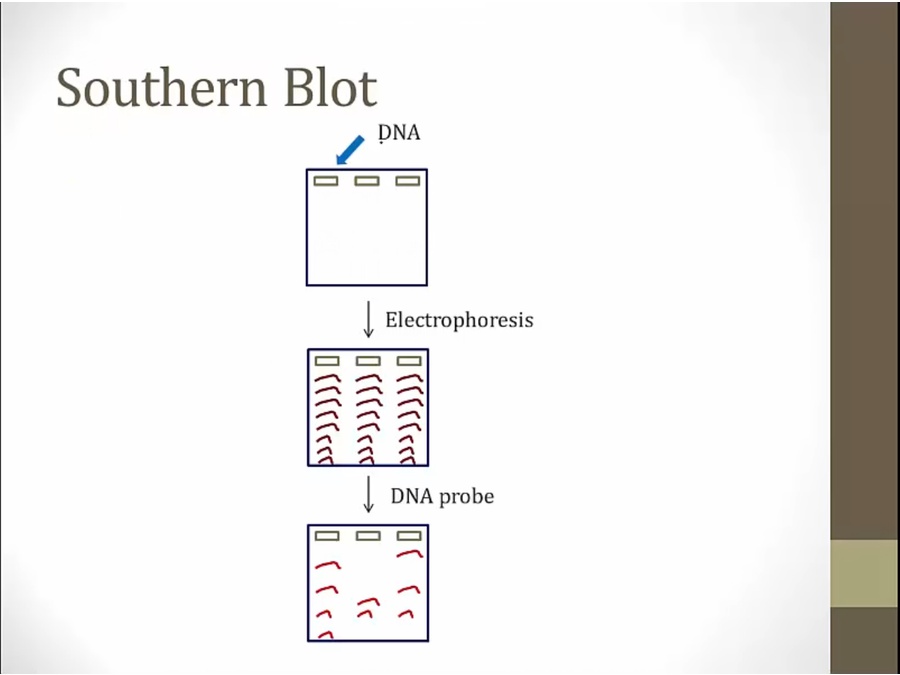

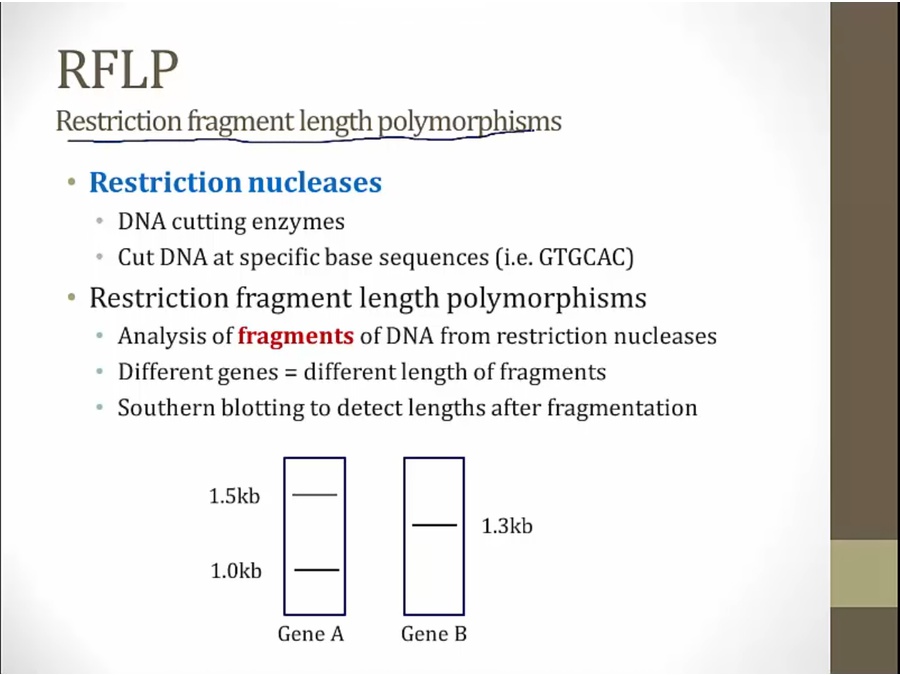
for characterizing genes
length of fragments unique to each particular gene
Restriction nuclease added to Gene A and Gene B: breaking up into different fragments
Compare unknown gene that break up to gene A or B
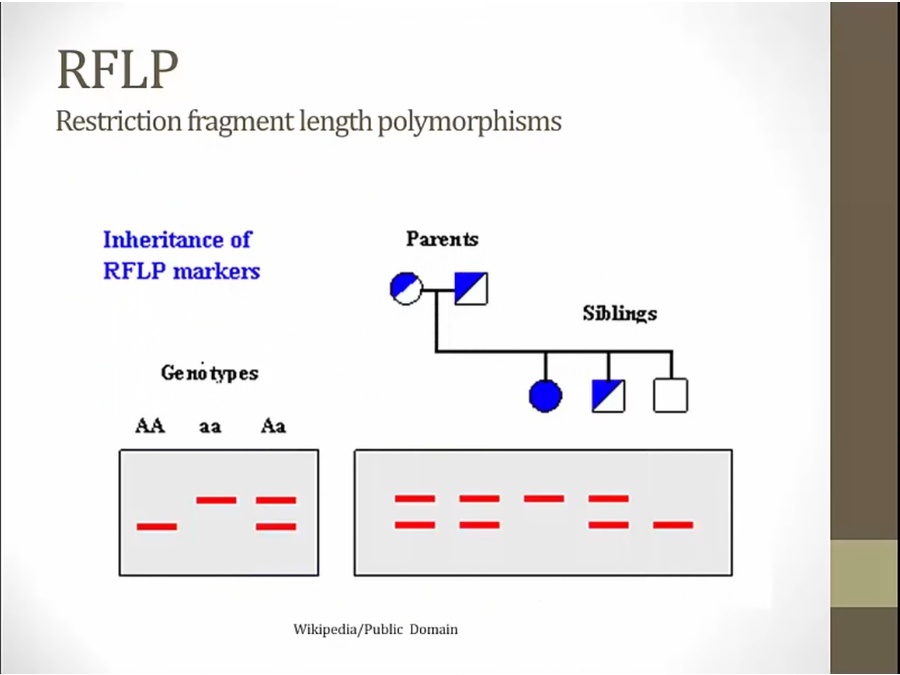
determine genotype
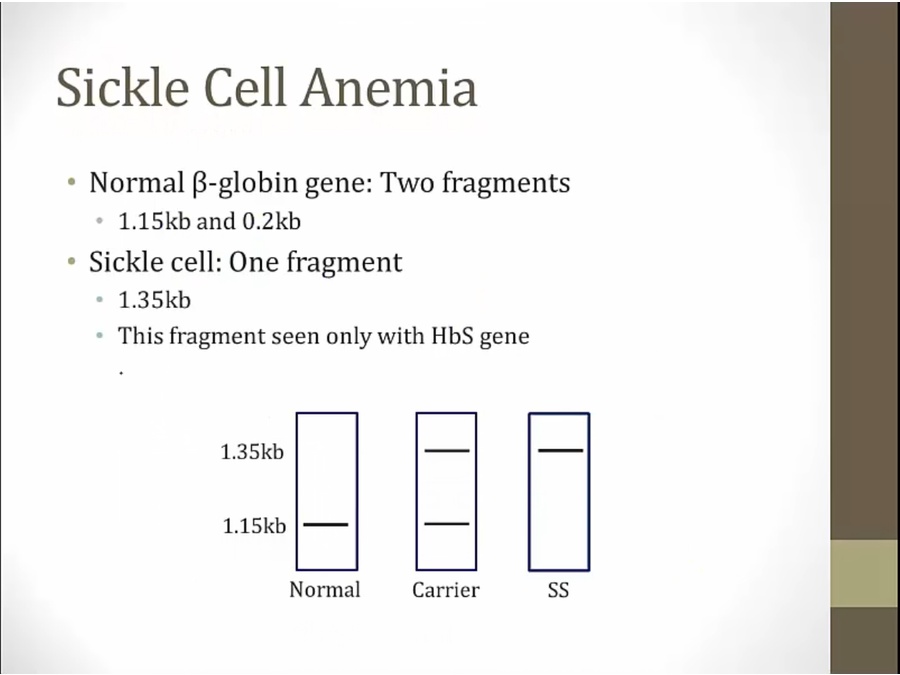
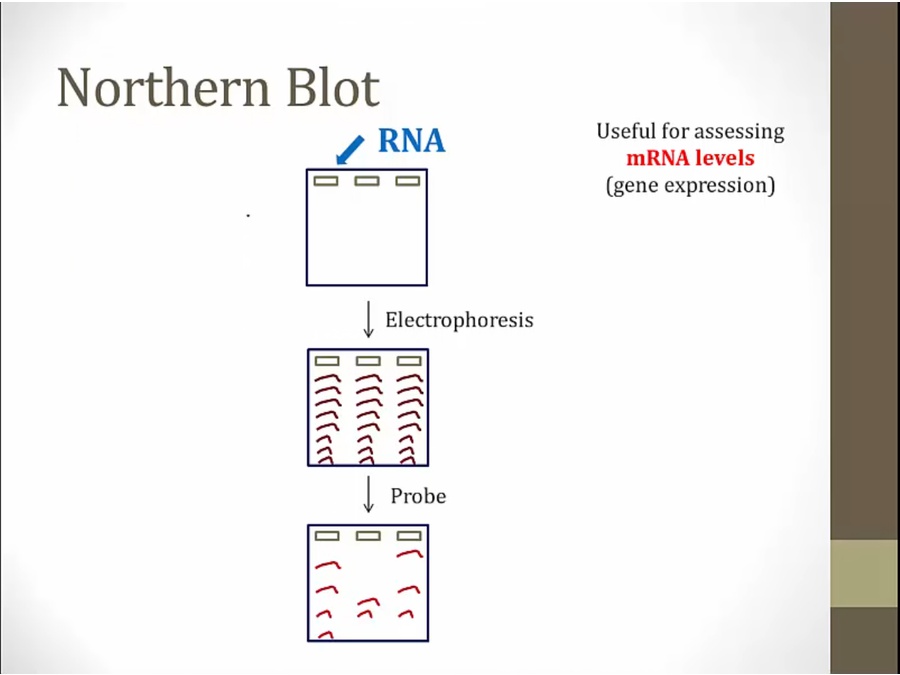
same technique for RNA
studies gene expression by finding mRNA corresponding to standard
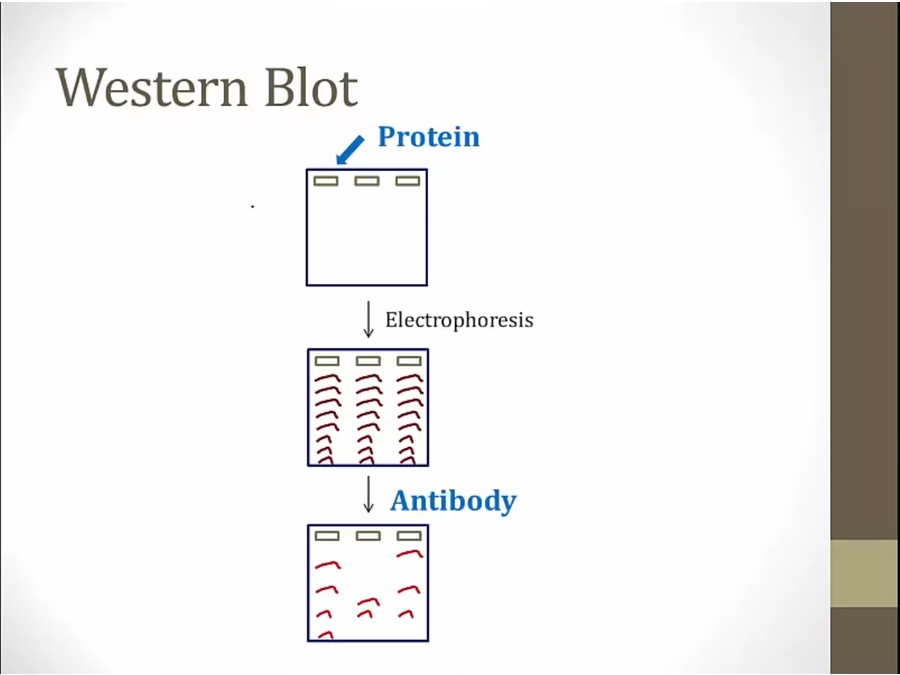
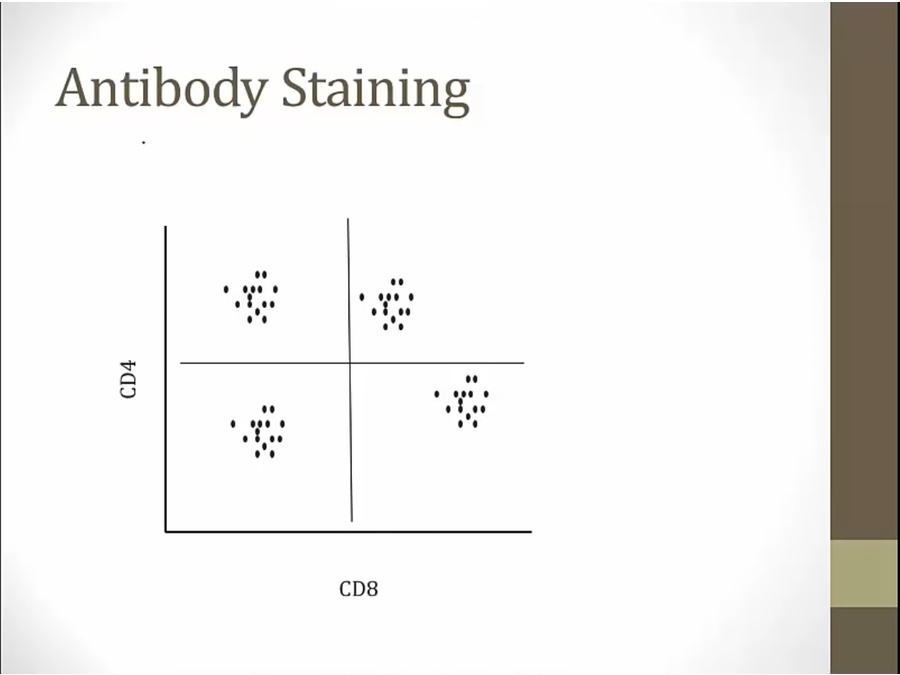
use antibody to protein instead of probe


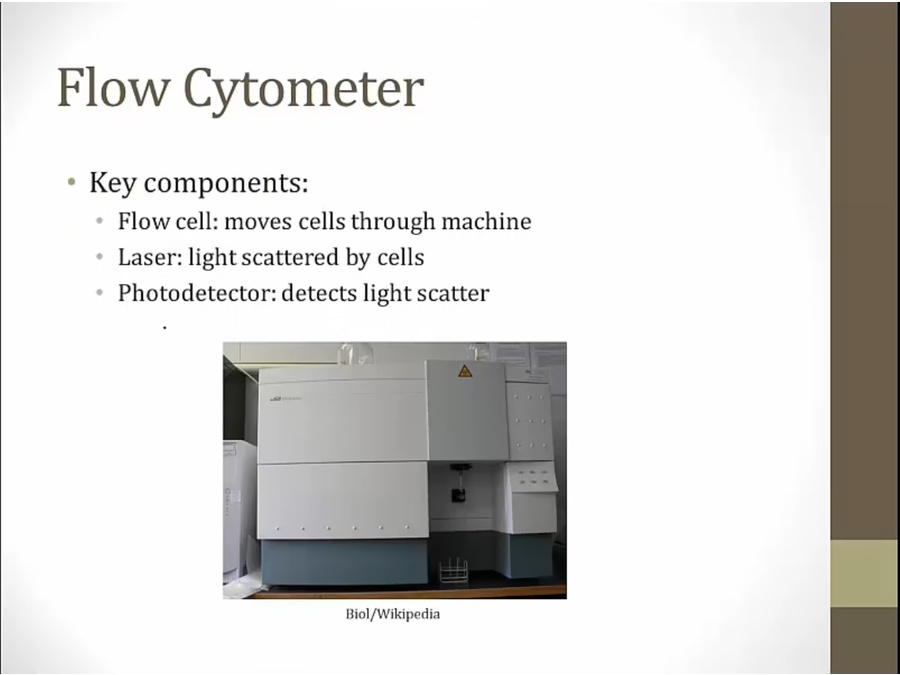
Flow Cytometry

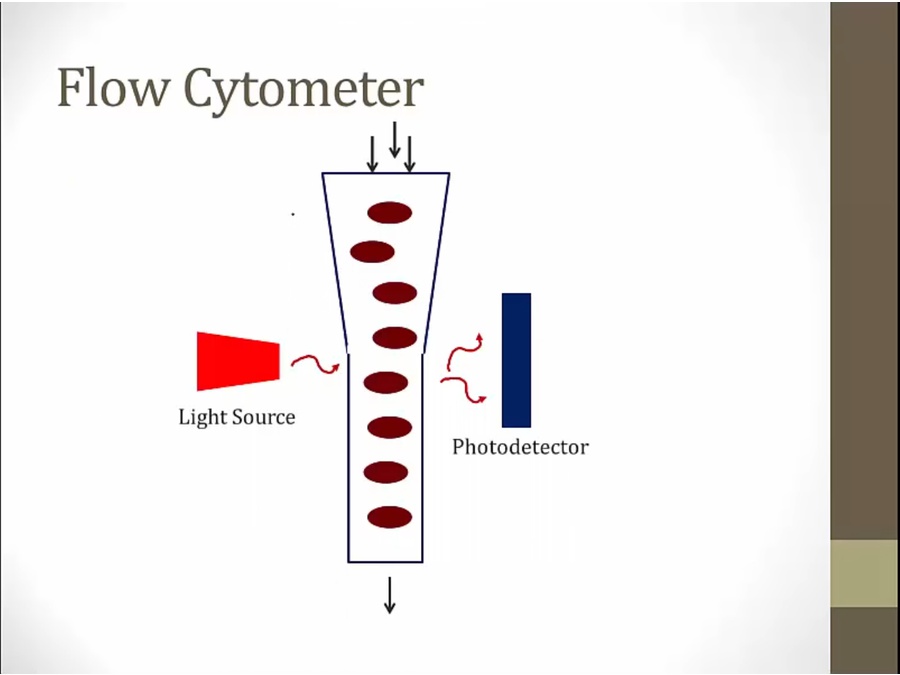
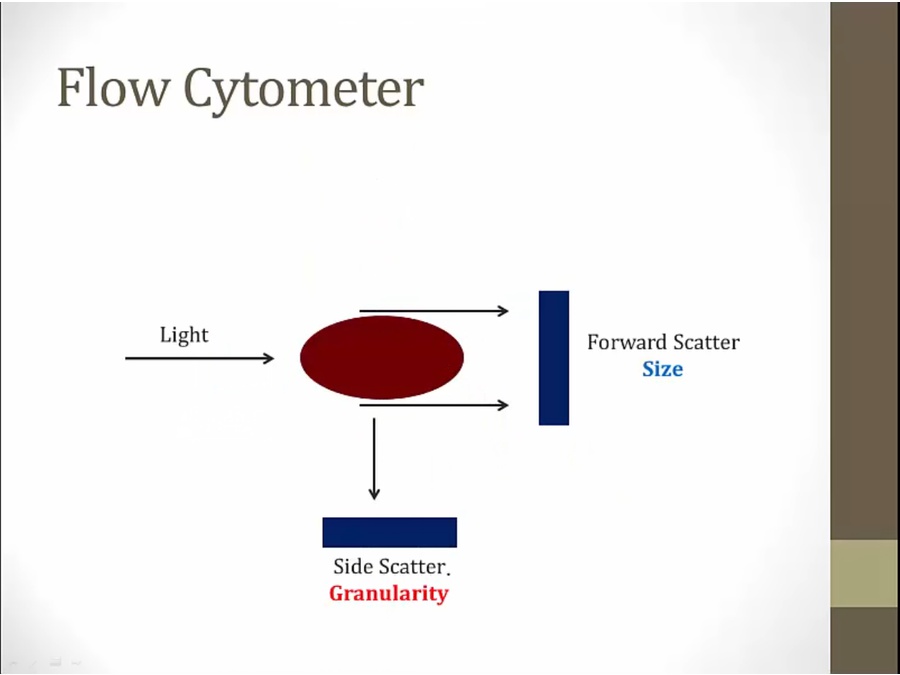
side and forward scatter
forward scatter based on cell size
side scatter based on granularity
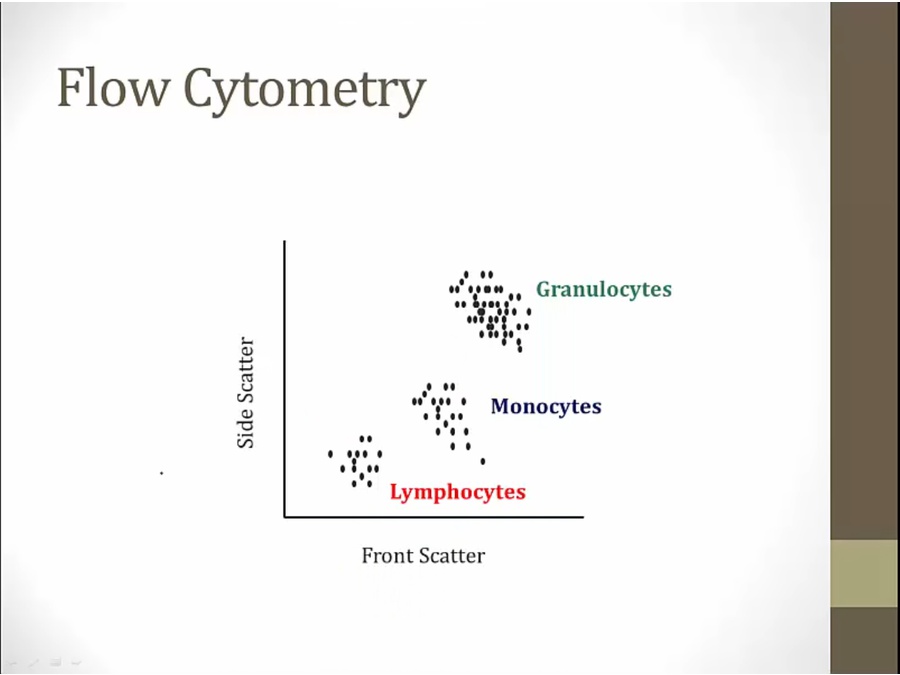
lymphocytes: small, little granules
granulocytes: big, lots of granules

determine Hb F in maternal circulation = hemorrhage
Elisa

good for detect proteins
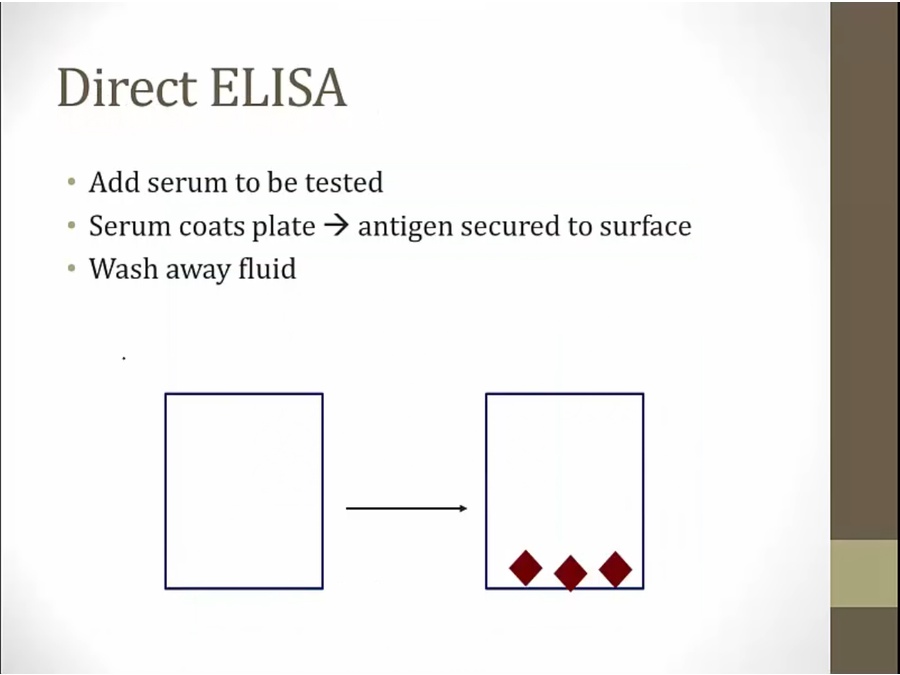
add serum to one of the wells
plate designed so antigen stick to surface
wash away serum and left with antigens bound
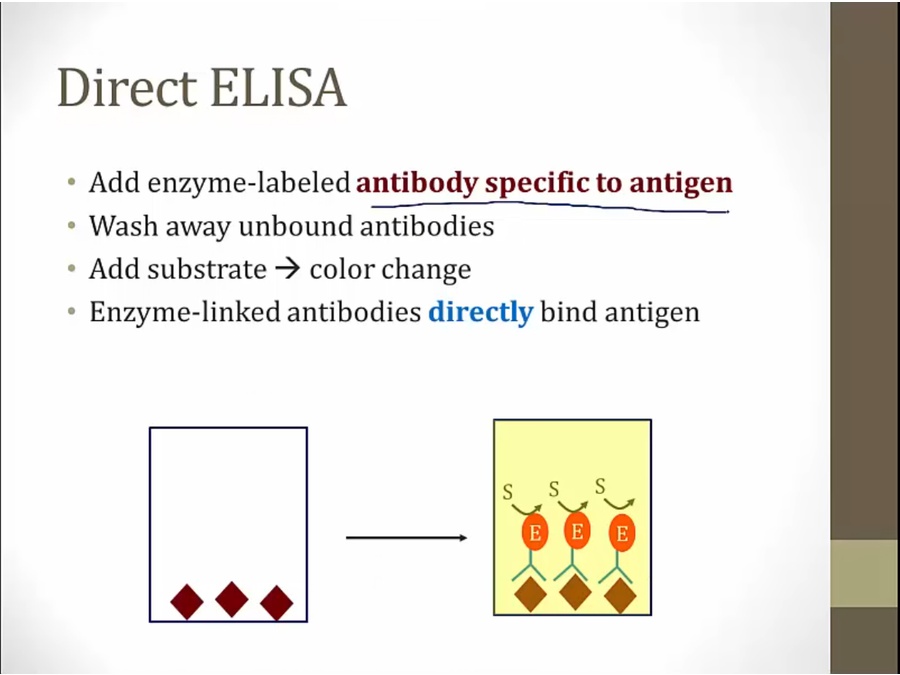
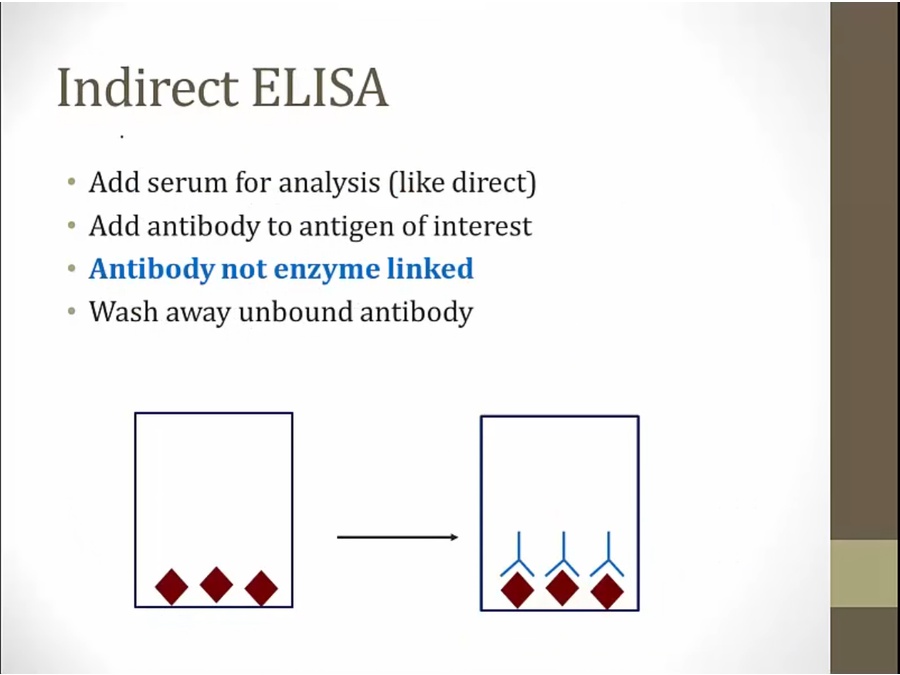
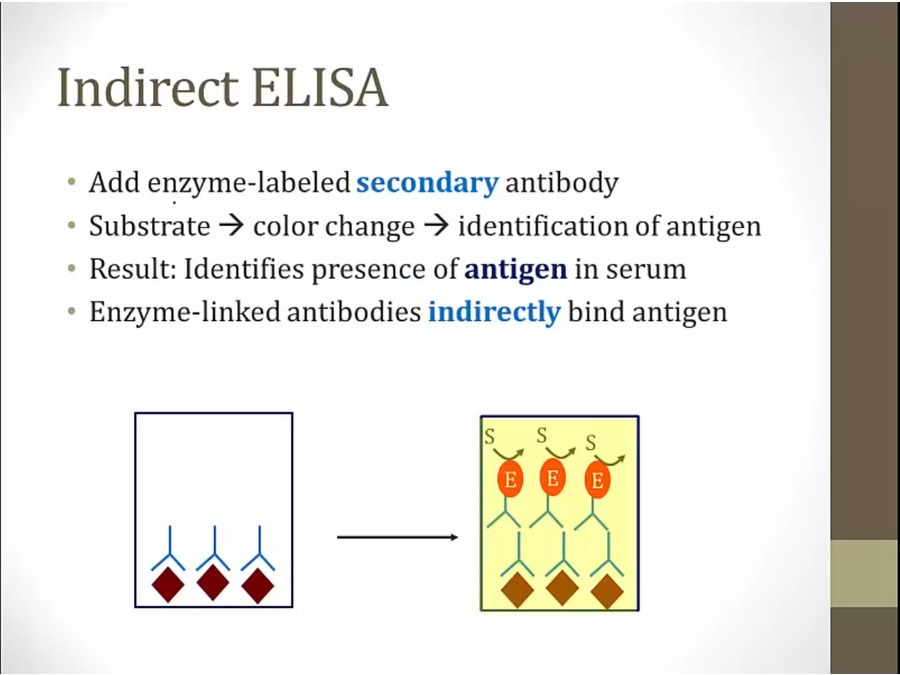

direct: for every antigen test for, must have an antibody enzyme linked
indirect: more common
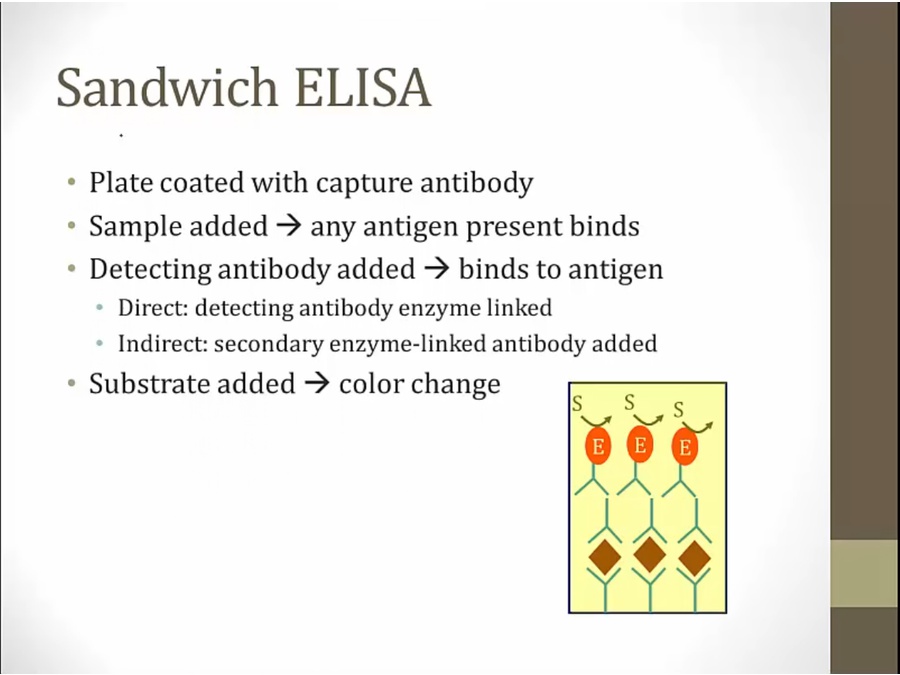



unbound antibody: free antibody from last slide
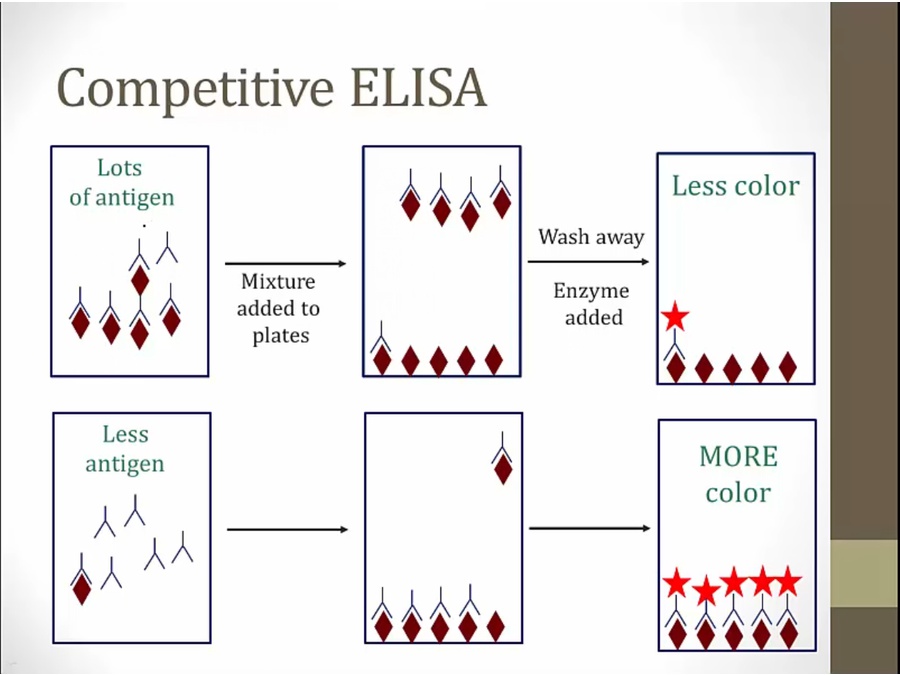
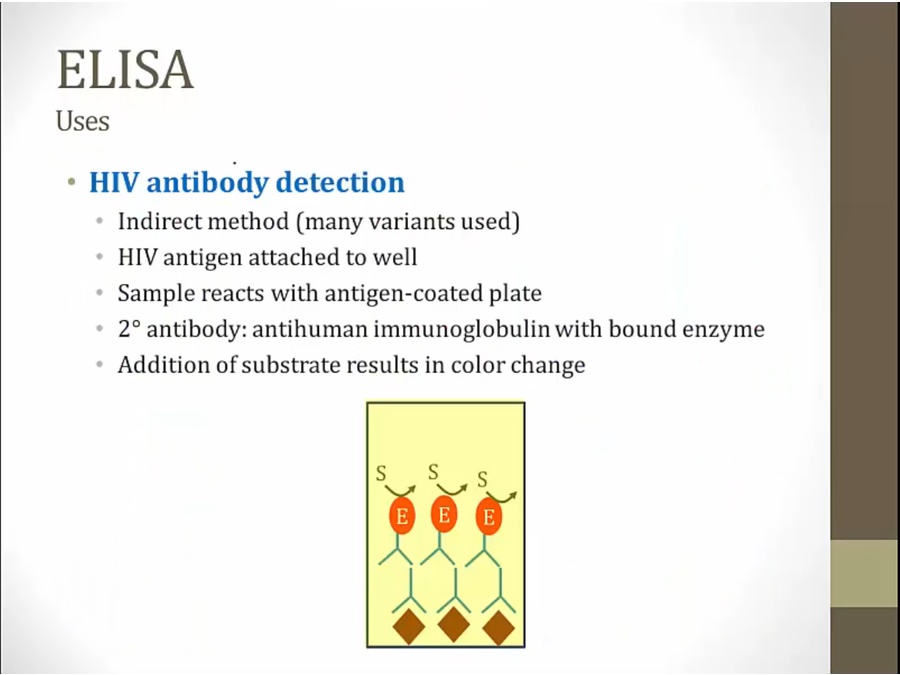
any HIV antibody in sample will bind to antigen in plate

Microassays


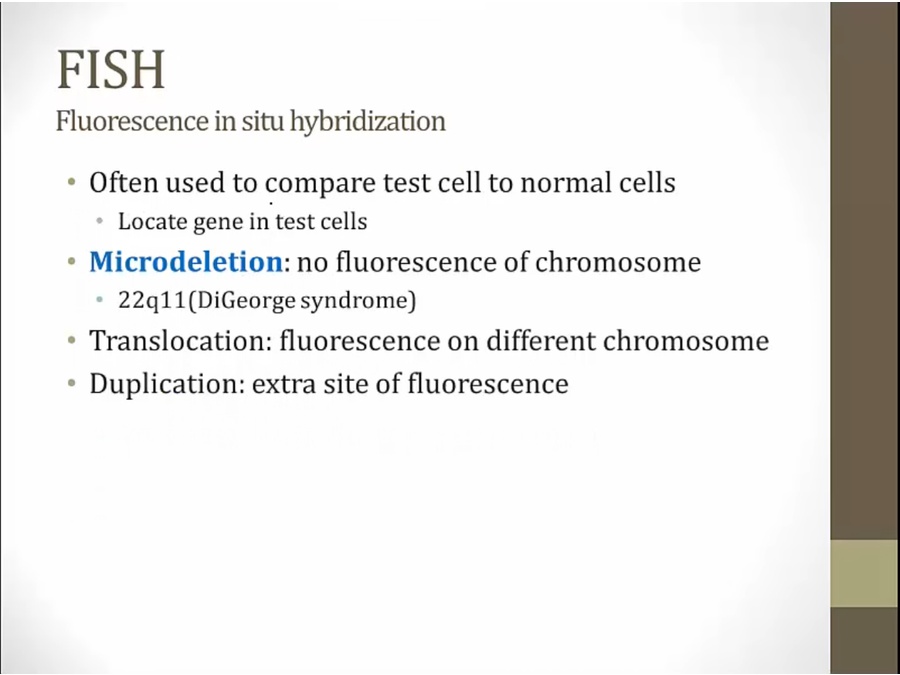
FISH

like microarray, uses fluorescent
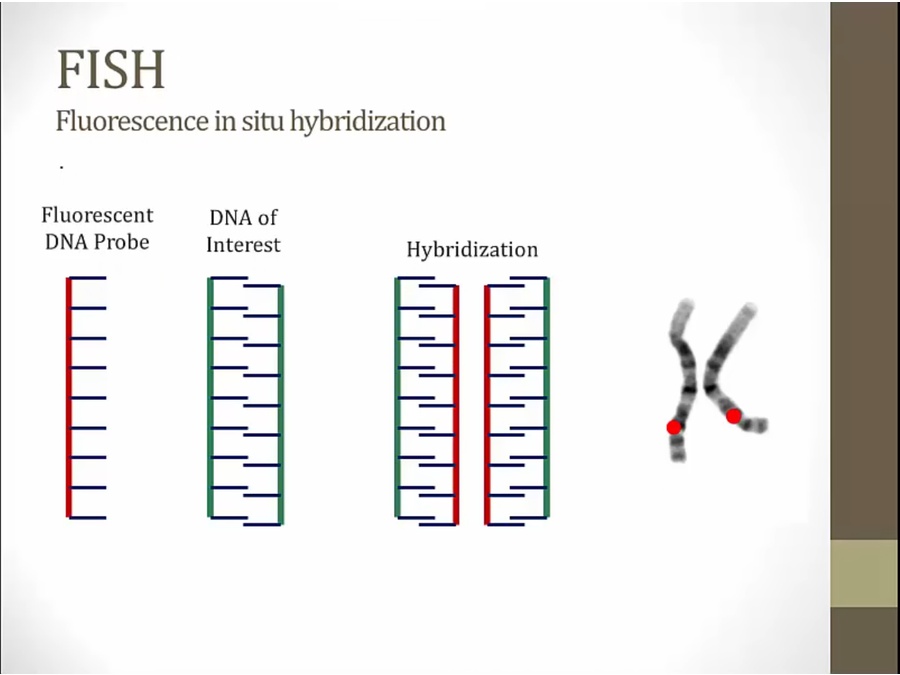
tell that gene is present on that chromosome

Last updated