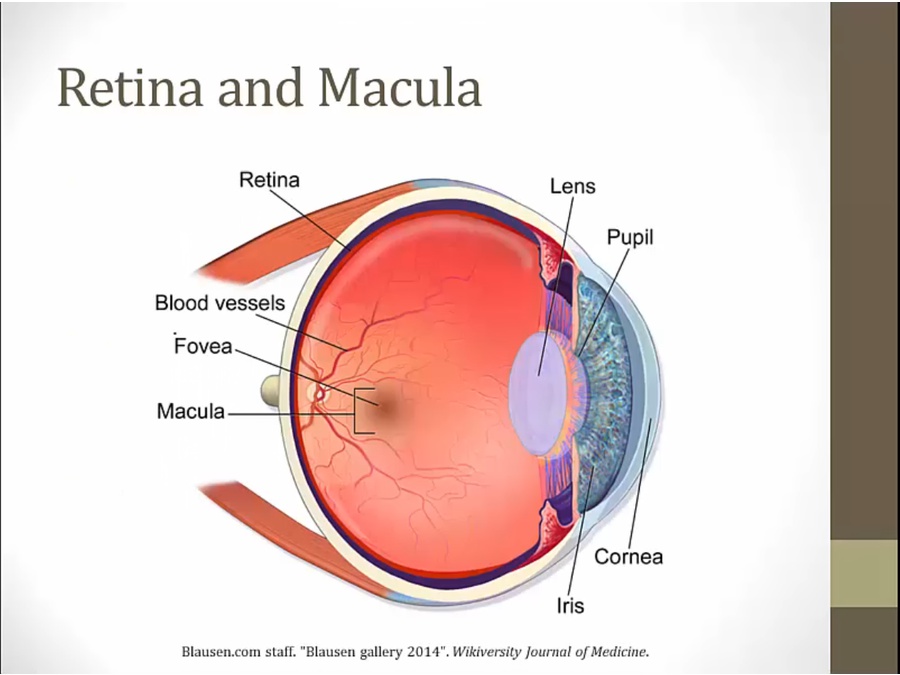
27 Retina
Structures

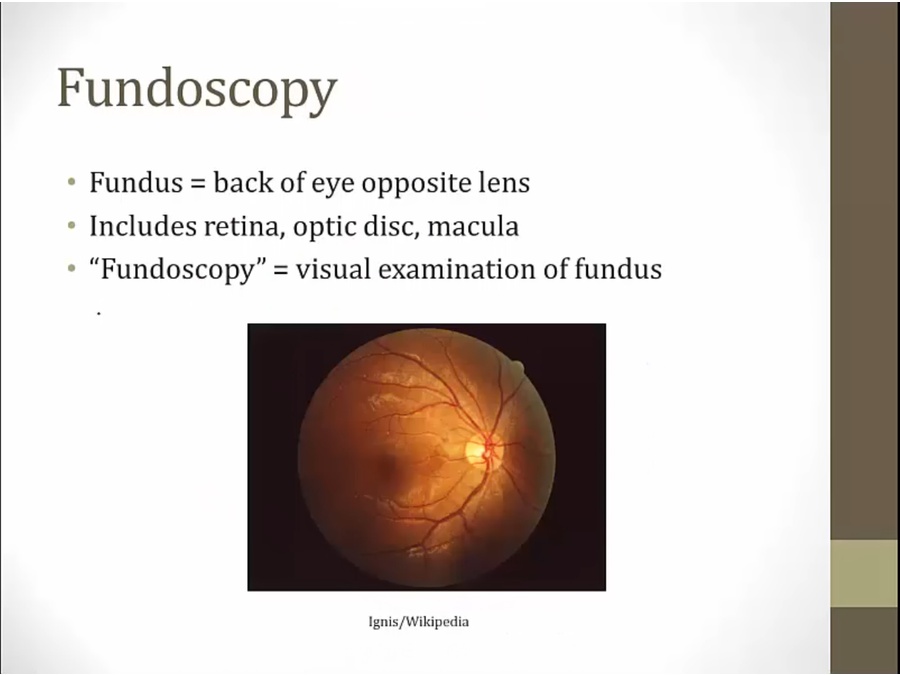
Pathology
Retinitis Pigmentosa

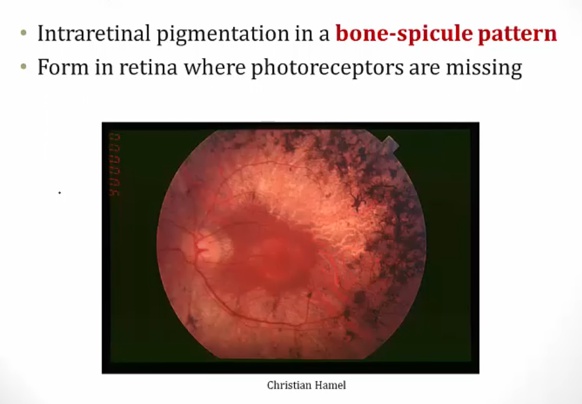
Retinitis

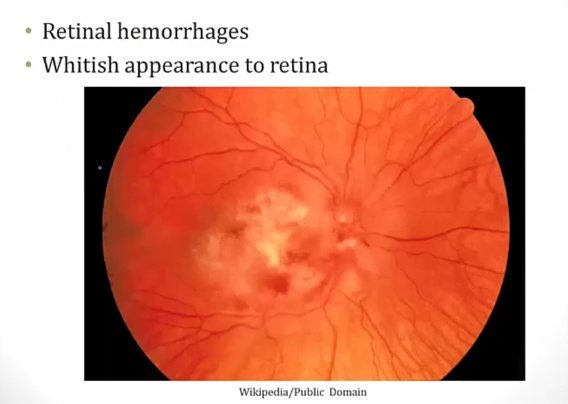
Diabetic Retinopathy

Nonproliferative

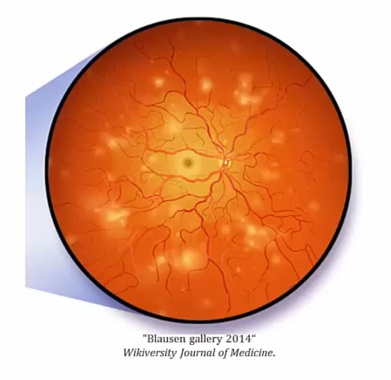
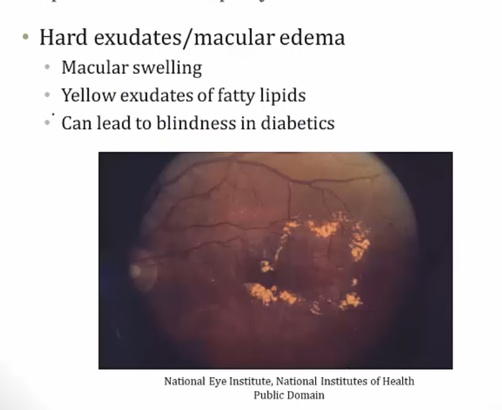
Proliferative

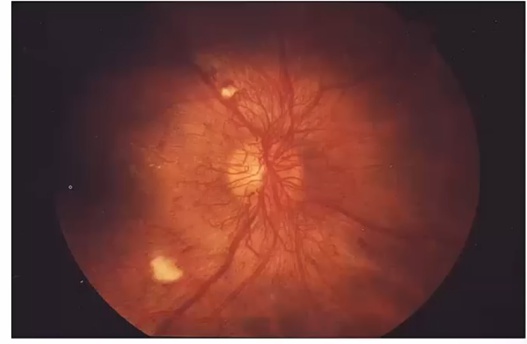

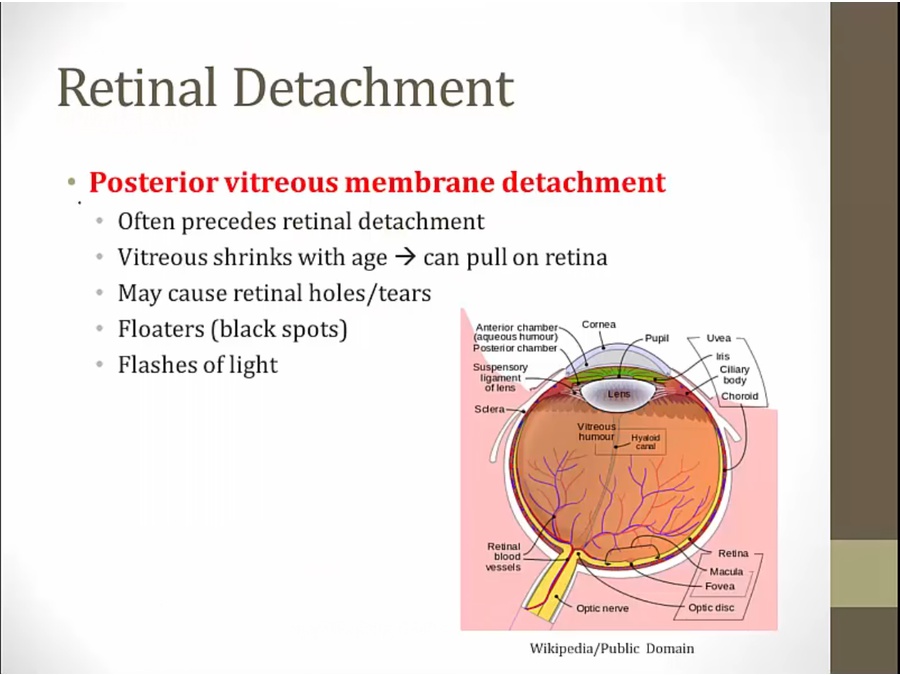
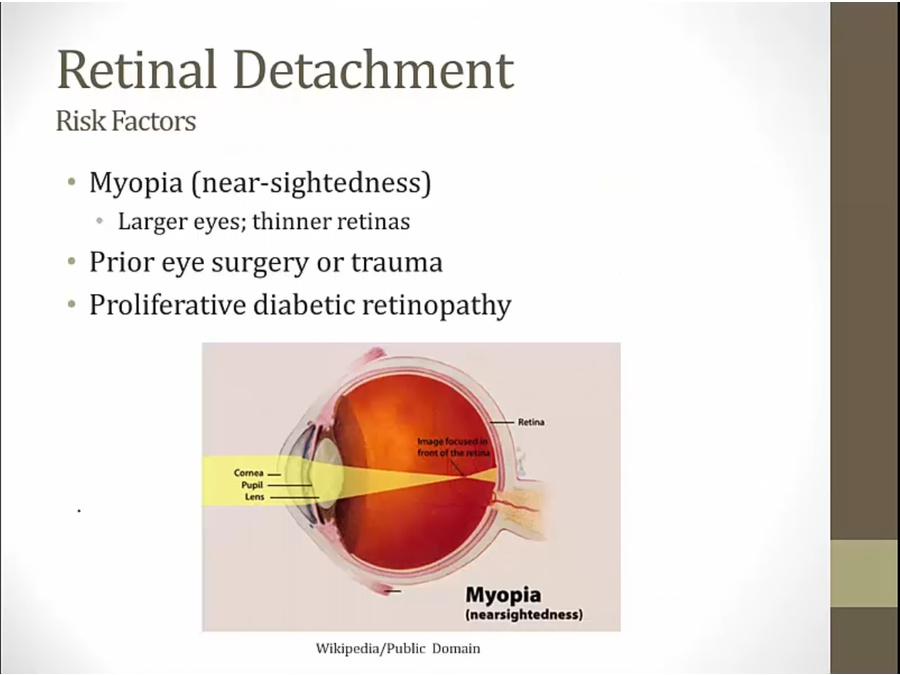
Retinal Detachment

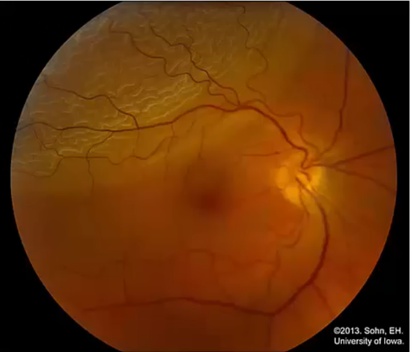
Amaurosis Fugax
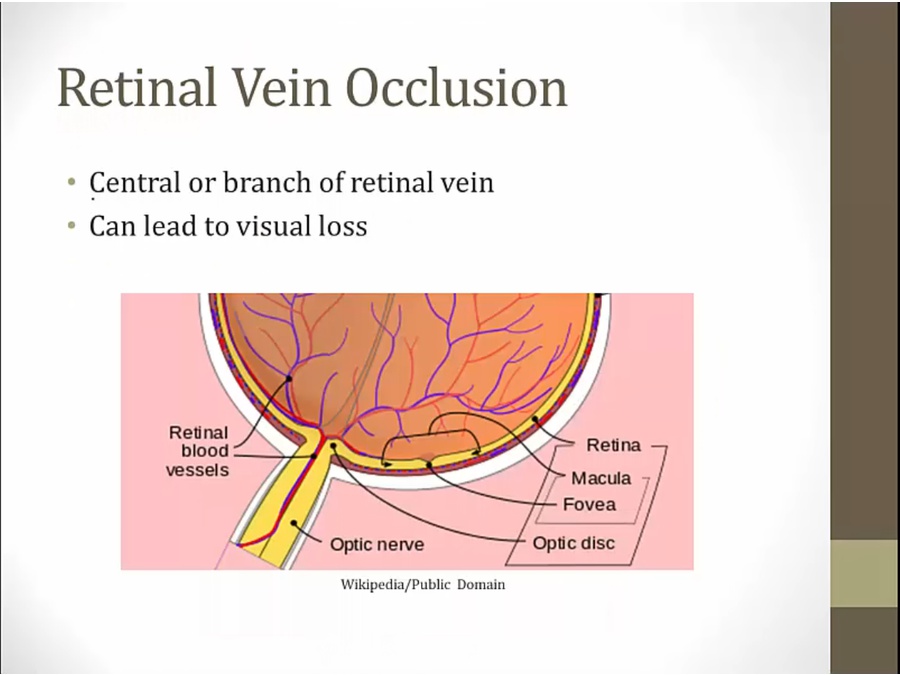
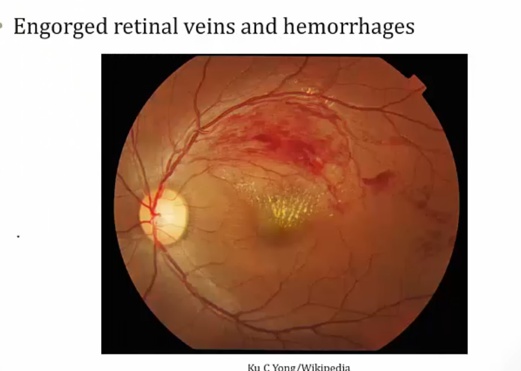
Retinal Vein Occlusion
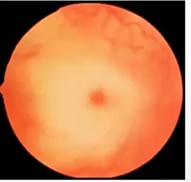
Retinal Artery Occlusion
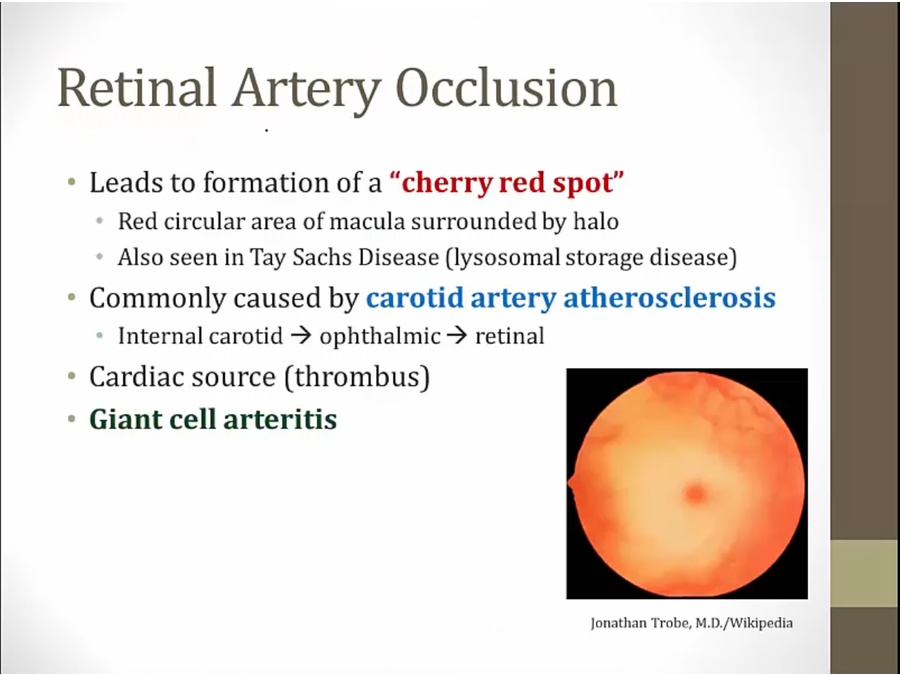
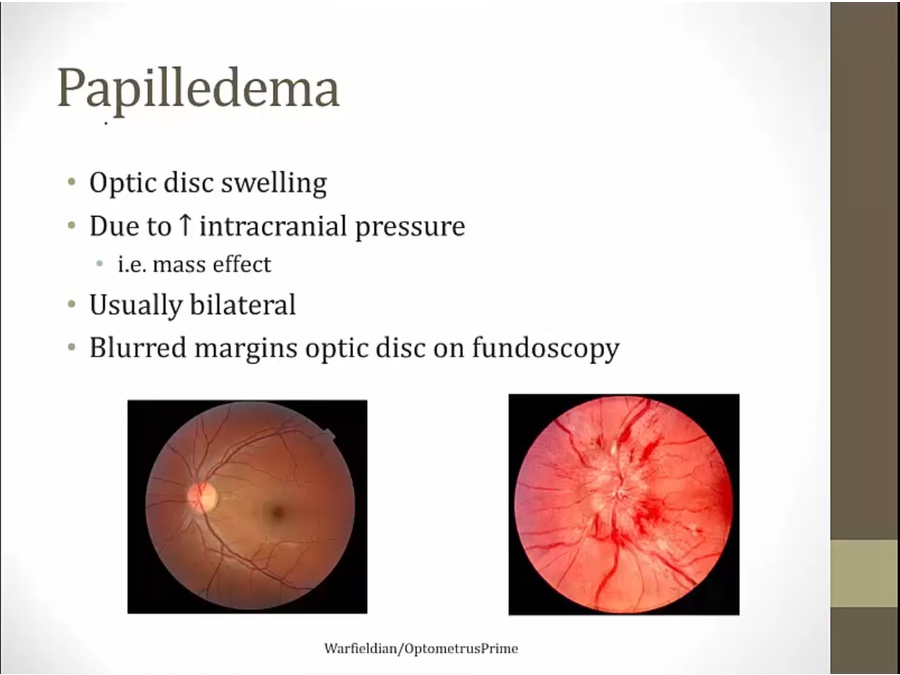
Papilledema
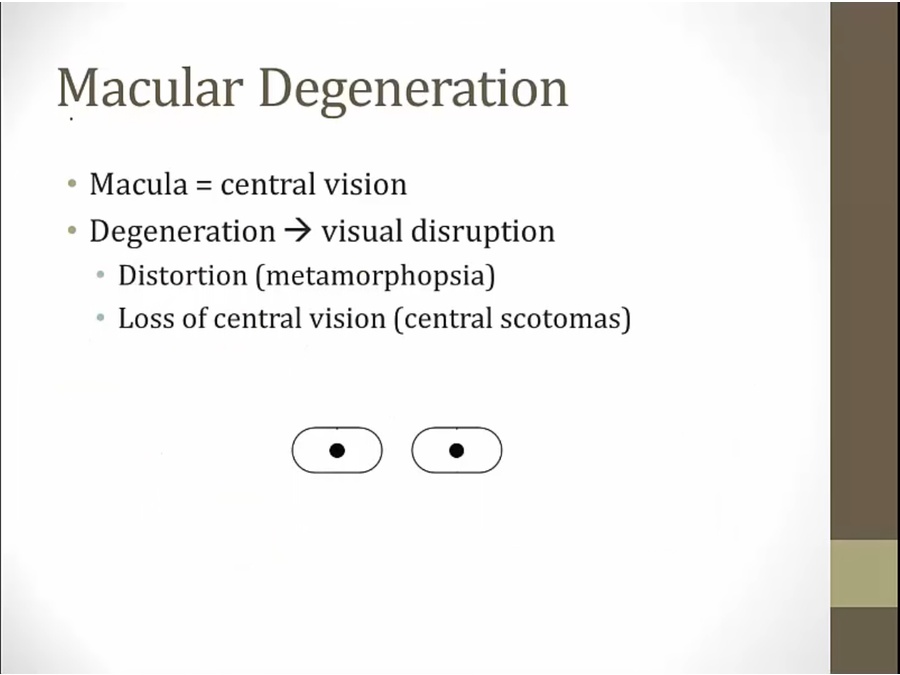
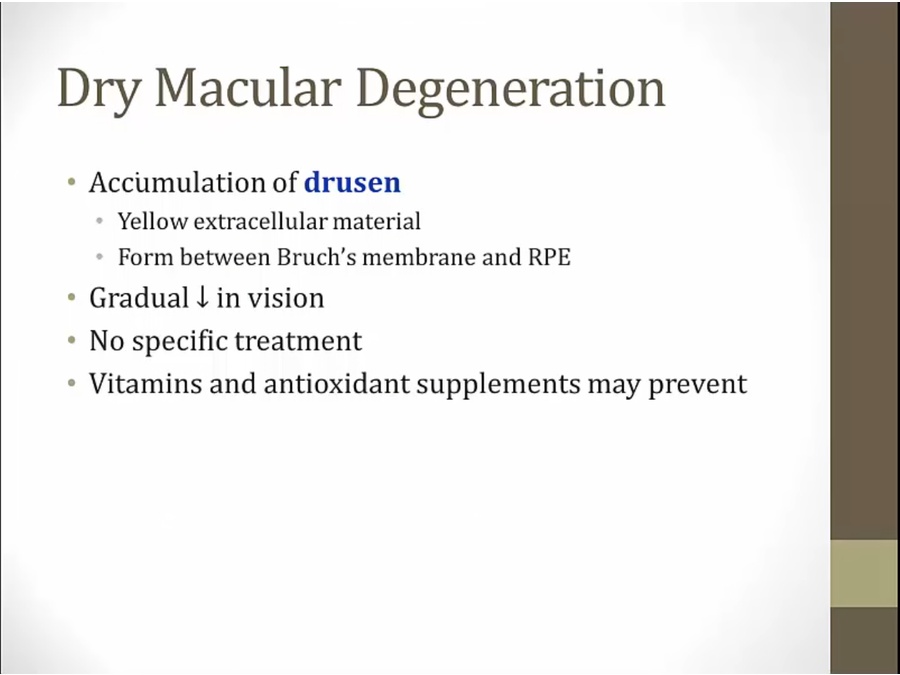
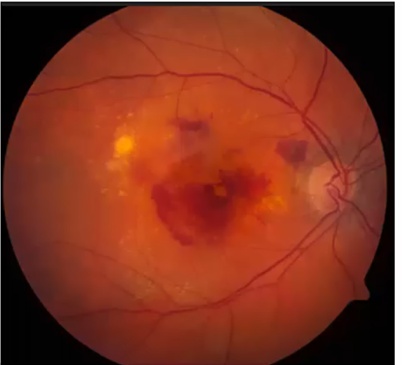
Macula Degeneration

Dry
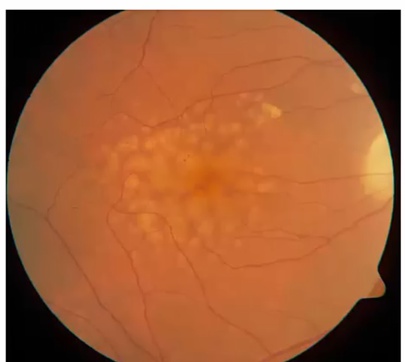
Wet

Last updated