09 Extrinsic Hemolysis

AIHA

antibodies coat RBC. RBC removed in spleen
RBC protect themselves from complement activation: no intravascular hemolysis
Warm
Pathogenesis and Symptoms


classic symptoms of anemia
splenomegaly: macrophages hypertrophy to consume RBCs
Diagnosis

smaller, spherical, lack central pallor
macrophage can't engulf whole RBC, just takes a bite off of it: shrink in size, more dense
also inherited disease

first see if normocytic anemia, then if RC is increased (increased production), then DAT

anti IgG antibodies bind to IgG on RBC and cause them to agglutinate

not used for AIHA
take patient serum and add sample RBC. Positive if antibodies in patient serum to RBC

used for new born hemolytic disease with mother serum against D+ RBC

Causes

all these diseases involve immune system


RBC bind antibody in absence of drug: surface of RBC altered

also cephalosporin
Treatment

severe: splenectomy
Cold

symptoms of anemia plus symptoms in extremities

large antibodies, cause RBC to agglutinate, especially in extremities
IgM fix complement, leaves bound C3 on RBC
DAT positive not for IgG but only for C3

C3 doesn't get in the way of macrophages like IgG: engulf whole
intravascular hemolysis result of complement activation

instead of add IgG, add anti-C3

IgG cold association with syphilis

MAHA

intravascular hemolysis
schistocytes: arrow, look like fragments
Mechanical
very high BP causes endothelial damage
thrombus shear RBC

narrow openings, stiff tissues
Infections
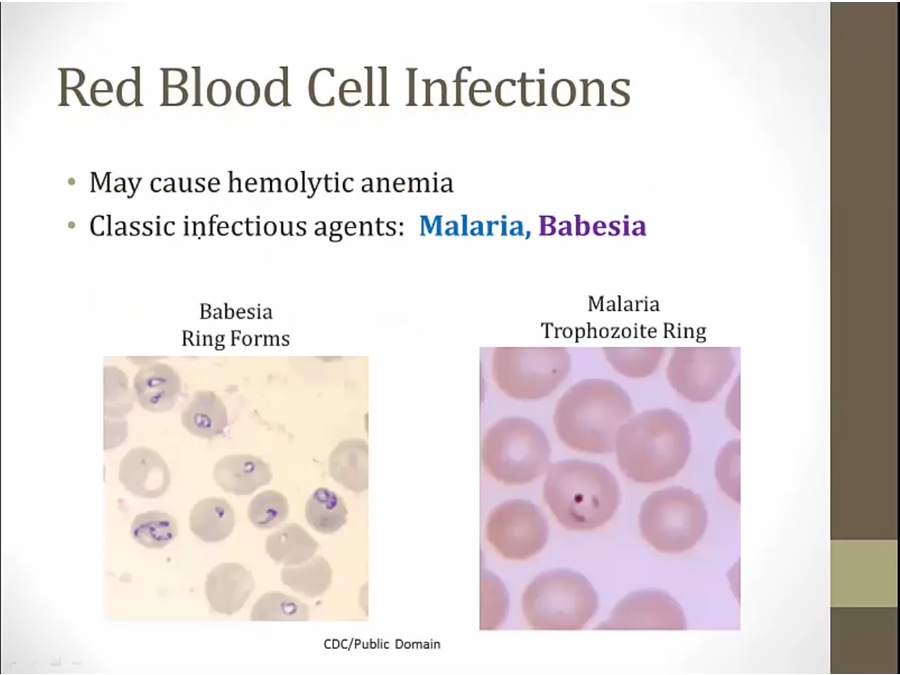
either intravascular RBC rupture or removal by spleen

sickle: Higher risk of severe disease in sickle cell disease
hole in robin's shirt: Higher risk of severe disease in asplenia
cracked blood stained windows: Hemolytic anemia
yellow babe: Jaundice
Sweating robin: fever
torn robin shirt: Irregularly cycling fevers
Last updated