02 Cardiorenal
Cardiac Failure Drugs
Digoxin

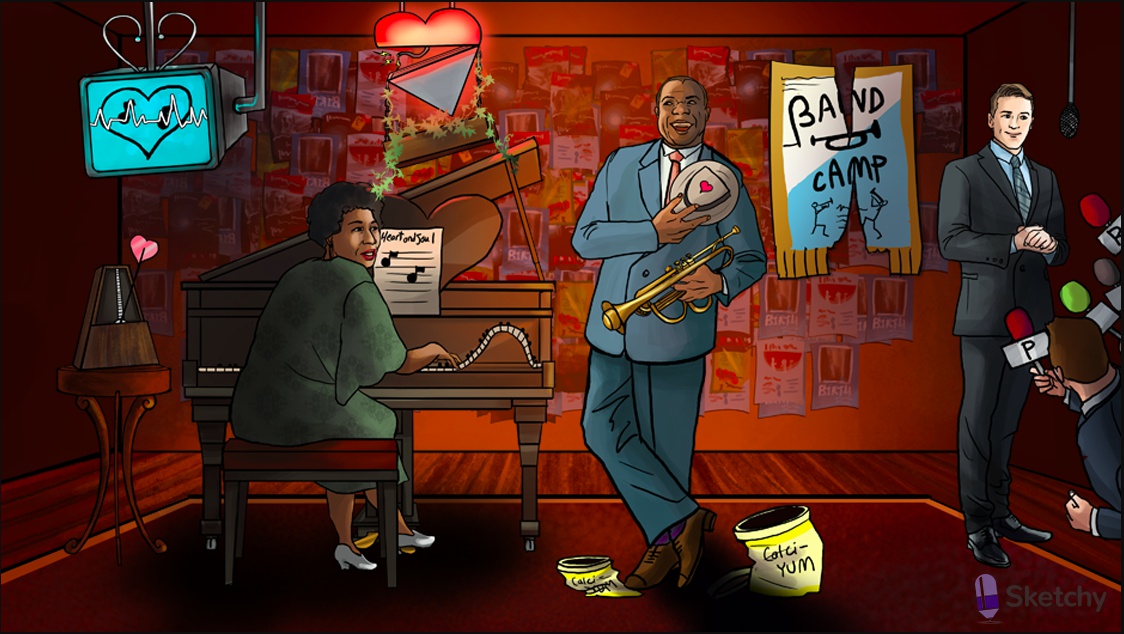
DJ Foxglove: digoxin - derived from the foxglove plant. Only one approved for chronic HF
Knocked over banana vending machine: inhibition of Na+/K+ ATPase
Three P batteries: ATPase
Obstructed salty sodium peanuts: increased intracellular sodium as a result of Na+/K+ ATPase inhibition
Salty peanuts sneaking in the calci-yum icecream: increased intracellular sodium promotes calcium influx at the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger
Flexed arm: increased cardiac contractility due to increased sarcoplasmic calcium stores

Deflated heart balloon: symptomatic treatment of chronic systolic heart failure
Las Vegas: direct stimulation of the vagus nerve allows treatment of certain arrhythmias. SA/AV, Atria more than V
Rhythm-inducing record: antiarrhythmic

Pile of bananas: side effect of hyperkalemia
Various dances on the heart shaped dancefloor: digoxin may induce various arrhythmias
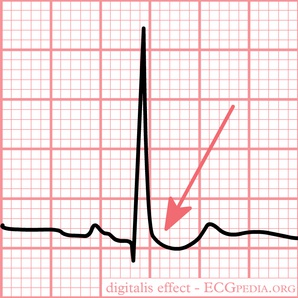
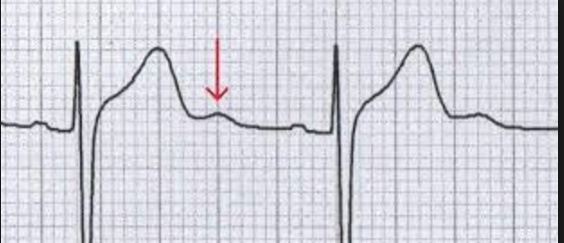
TaSTy scoop: chronic digoxin use may cause "scooped" concave ST segments on ECG
Dangling heart watch: side effect of bradycardia
SA music note: side effect of bradycardia due to parasympathetic activity at SA node
Heart shield: side effect heart block
AV music note: side effect of heart block due to parasympathetic activity at AV node
Gi side effects include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
Yellow spotlight: side effect of xanthopsia (objects appear yellow)
Remain unblocked: digoxin is contraindicated in heart block, CI with BB

Kid stuffed inside banana depleted vending machine: hypokalemia exacerbates digitalis toxicity, more binding with less K competing
Long tapering decay flag on cracked kidney: renal insufficiency increases the serum half life of digoxin, increasing susceptibility to toxicity
Records in kidney jukebox: many antiarrhythmics inhibit renal clearance of digoxin, increasing susceptibility to toxicity

Fabulous: digoxin immune Fab reverses digoxin toxicity

Acute issues: milrinone and nesiritide treat acute heart failure
One in a million: milrinone
Turn the tide: nesiritide

One in a million: milrinone
Don't phoster disinterest: milrinone inhibits phosphodiesterase
CAMPaign: milrinone decreases breakdown of cAMP
Flexing arm: milrinone increases cardiac contractility
Dilated red donkey ears: milrinone causes arteriolar dilation and decreased afterload. Hypotension SE

Turn the tide: nesiritide
BuMP: nesiritide is a synthetic form of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP)
GruMP: nesiritide increases cGMP in smooth muscle
Dilated red ears and blue legs: nesiritide causes arteriolar and venous dilation, reducing afterload and preload
Salty peanut stream: nesiritide causes natriuresis
ACE Inhibitors

Rain umbrella: renin
The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) is the site of synthesis, storage, and release of renin
Loose red tie: angiotensinogen
1 Tense red tie: renin converts angiotensinogen into angiotensin I
Lung vest and Ace card: ACE is located in the vascular endothelium of the lungs
Two tense red suspenders with the winning ace: angiotensin II is converted from angiotensin I by ACE in the lungs

Tense red suspenders: angiotensin II causes vasoconstriction
Grounds filtration rate increased: angiotensin II increases GFR
Pinched efferent end of straw: angiotensin II constricts the efferent arteriole
Low volume glass coffee: Ang II important in low volume state in preserving GFR
Pro Cart Track: proximal convoluted tubule
Salty sodium peanuts at the Pro Cart Track: angiotensin II acts at the proximal convoluted tubule to increase sodium bicarb reabsorption
Suspenders at Mineral Bar: angiotensin II increases aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid) release from the adrenal cortex
Banana peels at the Mineral Bar: the mineralocorticoid aldosterone acts on the collecting duct to increase Na+ and fluid retention at the expense of K+, hypokalemia

April: -pril suffix common to all ACE inhibitors
Pocketed ace: ACE inhibitor
Suspenders with the losing hand: ACE inhibitors prevent conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II
Floppy red suspenders: ACE inhibitors counteract the pressor effects of angiotensin II
ACE Inhibitors effects: decrease GFR, dilate efferent, decrease PCT Na/Bicarb absorption, decrease aldosterone secretion

Credit card: ACE inhibitors can cause an expected bump in creatinine
fainting: ACE inhibitors can cause significant hypotension and syncope in patients with high renin levels (e.g. heart failure)
Raised banana daiquiri: ACE inhibitors can cause hyperkalemia due to decreased aldosterone levels
Cheering single tense neck tie: ACE inhibitors increase levels of angiotensin 1 and renin
Coughing dealer: ACE inhibitors can cause a dry cough
Braids: ACE inhibitors can increase bradykinins causing lung irritation (avoid by using ARBs)

Failing heart balloon: ACE inhibitors are first line agents in the treatment of chronic heart failure (reduce peripheral resistance, afterload, and blood volume, preload; less Ang II, less sympathetic activity on heart )
Angel: ACE inhibitors reduce mortality in heart failure and MI
ACE inhibitors decrease angiotensin II mediated cardiac remodeling
Broken heart strings: ACE inhibitors are used in myocardial infarction (MI)
High pressure pipes: ACE inhibitors are first line agents in the treatment of hypertension
Kidney candy: ACE inhibitors slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Album: diabetic patients with albuminuria and blood pressure greater than 130/80 are started on an ACE inhibitor

"C" shaped ring on fat lip: ACE inhibitors are contraindicated in hereditary angioedema (due to C1 esterase deficiency) (face, lips, tongue)
Tarantula: ACE inhibitors are teratogenic (fetal hypotension, renal failure, low urine)
Fire extinguisher in cracked kidney glass: coadministration of ACE inhibitors with NSAIDs can precipitate acute kidney injury. NSAIDS decrease PGE responsible for dilation of afferent
Constricted kidney purse straps: ACE inhibitors are contraindicated in bilateral renal artery stenosis (case: pt with longterm HTN and history of angina/MI)
Credit card: ACE inhibitors can precipitate acute renal failure in bilateral renal artery stenosis as indicated by a persistent increase in creatinine

SoRry TAkeN: -sartan suffix common to all angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
Raised banana daiquiri: ARBs can increase K+ retention causing hyperkalemia due to decreased aldosterone levels

Losing at the high risk slots: aliskiren - a direct renin inhibitor
Bananas: aliskiren can cause hyperkalemia due to decreased aldosterone levels
Diuretics
Acetazolamide, mannitol

Pro Cart Track: proximal convoluted tubule
Yellow track: tubular lumen
Gray track: intracellular compartment
Banana vending machine: Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral membrane
Mom take away peanuts, give banana: 3 Na out, 2 K in, low intracellular Na composition to make room for reabsorption later
Three P batteries: ATPase
Track worker distributing peanuts inside and letting H+ helmets out: Na+/H+ exchanger located on the apical membrane

biCARb race car: bicarb (HCO3-) in the lumen of the PCT
Rider with H+ helmet sitting in biCARb: secreted H+ combines with bicarb in the tubular lumen to form carbonic acid (H2CO3)
Car battery anhydrase on the inside track: luminal carbonic anhydrase (CA)
Battery powered car producing H2O and CO2 exhaust: luminal CA converts carbonic acid (H2CO3) into H2O and CO2
H2O and CO2 exhaust on the outside track: H2O and CO2 enters the intracellular space via diffusion
Water sprayed over the wall: water is reabsorbed with solutes at the PCT (high permeability), osmolality maintained
Car battery anhydrase on the outside track: intracellular CA converts H2O and CO2 back into carbonic acid (H2CO3)
H+ helmet leaving the biCARb: Intracellular carbonic acid (H2CO3) dissociates back into H+ and bicarb (HCO3-)
Recycled H+ helmet: H+ transported back into the lumen by the Na+/H+ exchanger
biCARb taken away: intracellular bicarb is absorbed via a basolateral transporter

Acetazolamide

Battery acid breaking car battery: acetazolamide inhibits carbonic anhydrase (preventing reabsorption of bicarb)
Proximal convoluted tubule (site of action of acetazolamide and mannitol)
Spilled alkaline substance on inside track: CA inhibitors (e.g. acetazolamide) cause bicarb to stay in the tubular lumen leading to urine alkalinization
Dropping salty peanuts on the inside track: CA inhibitors prevent the reabsorption of sodium (with bicarb) causing natriuresis
"Close that gap!": CA inhibitors (e.g. acetazolamide) cause a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis (increased Cl production )

leaves enhanced Na absorption by later nephron, efficacy decreases chronically
Spilled eyeball cups: CA inhibitors (e.g. acetazolamide) decreased production of aqueous humor (useful in the management of glaucoma)
High pressure head balloon: CA inhibitors (e.g. acetazolamide) decreased production of CSF (useful in the management of idiopathic intracranial hypertension) (pseudotumor cerebri)
High altitude: CA inhibitors (e.g. acetazolamide) are useful in the treatment and prevention of mountain sickness (weakness, dizziness, nausea, pulmonary/cerebral edema)
increased pH leads to increased solubility of uric acid and cysteine, prevent stone formation and gout formation

Banana peel: CA inhibitors (e.g. acetazolamide) can cause hypokalemia (potassium wasting) (reabsorption of Na at CD)
biCARb taken away: CA inhibitors cause excretion of bicarb
Two tubes of acid: CA inhibitors cause a type 2 renal tubular acidosis (defect in proximal bicarb reabsorption)
Rocks on the inside track: CA inhibitors promote the formation of calcium phosphate stones (insoluble at high pH)
Rotten sulfur eggs: CA inhibitors (e.g. acetazolamide) are sulfa drugs, allergy
Mannitol

Tall man: mannitol (an osmotic diuretic) acts at the PCT and descending limb of the loop of Henle. Non absorbable, promoting diuresis
High pressure head balloon: mannitol draws free water out of the CNS (useful in the treatment of elevated intracranial pressure)
Spilled eyeball cups: mannitol draws free water out of the eye (decreases intraocular pressure)

Tall man causing wet lungs: mannitol induced expanded extracellular volume can cause pulmonary edema
Spilled salty peanuts: mannitol induced expanded extracellular volume can cause hyponatremia
Tall man dousing failing heart balloon: mannitol induced expanded extracellular volume can exacerbate heart failure
Elevated salty peanuts: excessive mannitol induced water depletion can cause hypernatremia
Loop Diuretics
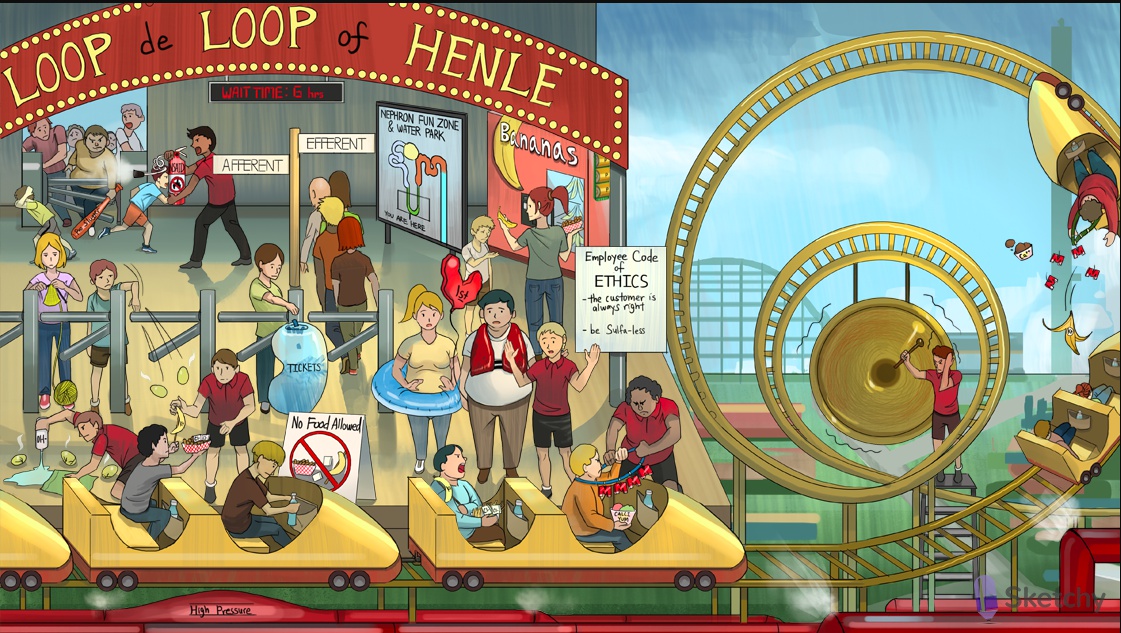

Loop de loop of Henle: loop of Henle
Yellow track: tubular lumen
Platform: intracellular compartment
Backwall: interstitium
Na/Cl actively reabsorbed
Banana vending machine: Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral membrane
Three P batteries: ATPase
Track worker taking peanuts, bananas, and 2 chloride packets: Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter (NKCC) reabsorbs these ions at the luminal membrane of the TAL
Water secured in car: the TAL is impermeable to water ("diluting segment")


Thick ascending limb (TAL) of the loop of Henle (site of action of loop diuretics)]
Furious kid: furosemide (a loop diuretic)
Furious kid clinging to food: furosemide blocks the NKCC on the luminal membrane of the TAL


Ethics: ethacrynic acid (a loop diuretic)
Sulfa-less ethics: ethacrynic acid is not a sulfa drug

Pro-slugger: prostaglandins
Furious kid wielding pro-slugger: loop diuretics induce the expression of COX-2, synthesizing prostaglandins that enhance salt excretion and dilate the afferent arteriole. More blood flow = more diuresis. Enhancing loop diuretics
Fire extinguisher inhibiting the pro-slugger: NSAIDs decrease prostaglandin synthesis, interfering with the actions of loop diuretics

Failing heart balloon: loop diuretics are 1st line for the symptomatic treatment of acute decompensated heart failure with fluid overload
Wet lungs: loop diuretics treat symptoms of pulmonary edema in an acute heart failure exacerbation
Yellow inner tube: loop diuretics treat ascites in liver failure
High pressure pipes: loop diuretics can be useful in the treatment of hypertension

Furious kid clinging to magnets and calci-yum icecream: by blocking the NKCC, loop diuretics reduce the lumen positive potential, promoting the excretion of Mg2+ and Ca2+ (K usually diffuses out to create positive potential)
Falling magnets: loop diuretics can cause hypomagnesemia
Falling calci-yum icecream: loop diuretics can cause hypocalcemia (rare)
Banana peel: loop diuretics can cause hypokalemia (potassium wasting)
Contracted bleach OH bottle: loop diuretics can cause contraction alkalosis. Increased renin, increased aldosterone, more K excretion, increased Ang II (Na absorption at PCT, H secretion)


Loud gong: loop diuretics can be ototoxic
Stinky sulfur eggs: most loop diuretics (e.g. furosemide) are sulfa drugs
Kidney filled with blue tickets: loop diuretics can cause interstitial nephritis (blue cells on histology )
Knitting needles: loop diuretics can cause hyperuricemia, needle shaped crystals. Uric acid reabsorption in PCT enhanced in hypovolemia
Contracted bleach OH bottle: loop diuretics can cause contraction alkalosis. Increased renin, increased aldosterone, more K excretion, increased Ang II (Na absorption at PCT, H secretion)


Thiazides
Distal convoluted tube slide: distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Yellow tube slide: tubular lumen
Area outside slide: intracellular compartment
Banana vending machine: Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral membrane
Three P batteries: ATPase
impermeable to water, make urine even more dilute
Sodium chloride salt scraper: NaCl cotransporter reabsorbs these ions at the apical membrane of the DCT
Active slider dropping calci-yum icecream: calcium is actively reabsorbed at the DCT (regulated by PTH)

pale Chloro-thighs: hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone (thiazide diuretics, longer duration)
Distal convoluted tubule (site of action of thiazide diuretics)
Sodium chloride dumping into pool: thiazide diuretics inhibit NaCl reabsorption by blocking the NaCl cotransporter on the apical membrane (causing natriuresis)
Chloro-thighs kid dropping calci-yum: thiazide diuretics enhance calcium reabsorption (PCT water depletion = more absorption)


High pressure pipes: thiazide diuretics are one of the first line treatments for mild or moderate hypertension
Failing heart balloon: thiazide diuretics can be useful in the symptomatic treatment of heart failure (loop diuretics are first line)
Insipidus fountain: thiazide diuretics treat nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Reduced volume induce PCT reabsorption of Na and water, less reliance on CD
Removing tube slide stones: thiazide diuretics can be used to prevent calcium stones (increased calcium reabsorption causes hypocalciuria)
New calcium chalk: thiazide diuretics may benefit patients with osteoporosis (due to increased calcium reabsorption)

Elevated calci-yum ice cream: thiazide diuretics can cause hypercalcemia
Banana peel: thiazide diuretics can cause hypokalemia (potassium wasting)
Contracted bleach bottle: thiazides can cause contraction alkalosis
Elevated stick of butter: thiazide diuretics can cause hyperlipidemia, increase serum cholesterol/LDL
Elevated candy jar: thiazide diuretics can cause hyperglycemia, less insulin secretion and glucose utilization
Yellow knitting needles: thiazide diuretics can cause hyperuricemia (can precipitate gout). Hypovolemia associated uric acid absorption
"Lift"ium balloons: thiazide diuretics can cause increased lithium levels (bipolar disorder treatment)
Spilled peanut shells: thiazide diuretics can cause hyponatremia
Rotten sulfur eggs: thiazide diuretics are sulfa drugs
K sparing
Central gutter: collecting duct
Food court ground: intracellular compartment
Water in gutter: tubular lumen
Collecting duct (site of action of the K+ sparing diuretics)
Principal court: principal cell of the collecting duct (major site of Na+, K+, and water transport)
Banana vending machine: Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral membrane
Three P batteries: ATPase
Salt-E sNaC cart: epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC) reabsorb Na+ across the luminal membrane of the collecting duct
Banana stand dumping bananas: : K+ channels allow the excretion of K+ across the luminal membrane of the collecting duct
Salt-E sNaC cart toppling banana stand: reabsorption of Na+ creates a negative luminal potential that facilitates K+ excretion
a intercontinental: a intercalated cell of the collecting duct (major site of H+ secretion)
Battery powered acid pump: H+ATPase on the apical membrane of the a intercalated pumps H+ into the lumen



Mineral - O - Food Court: mineralocorticoids (i.e. aldosterone) exert their effects at the collecting duct
Mineral key: aldosterone (a mineralocorticoid)
Mineral court services: intracellular mineralocorticoid (i.e. aldosterone) receptor
Mineral key activating the Salt-E sNaC cart: aldosterone upregulates ENaCs on the apical membrane, increasing Na+ reabsorption
Mineral key activating the banana stand: aldosterone upregulates K+ channels on the apical membrane, increasing K+ excretion
Mineral key activating the banana vending machine: aldosterone upregulates Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral membrane
Mineral key activating the acid pump: aldosterone upregulates H+ATPase on the apical membrane, increasing H+ excretion

Almonds: amiloride (a K+ sparing diuretic)
Almonds blocking the Salt-E sNaC cart: amiloride inhibits Na+ reabsorption through ENaC
Salty sodium peanuts falling into duct: K+ sparing diuretics inhibit Na+ reabsorption at the collecting duct, promoting natriuresis. Increased positive ion spared K excretion


Tangerines: triamterene (a K+ sparing diuretic)
Tangerines blocking the Salt-E sNaC cart: triamterene inhibits Na+ reabsorption through ENaC
Salty sodium peanuts falling into duct: K+ sparing diuretics inhibit Na+ reabsorption at the collecting duct, promoting natriuresis. Increased positive ion spared K excretion


Apple: eplerenone (a K+ sparing diuretic)
Teacher with apple antagonizing the mineral court services man: eplerenone antagonizes the mineralocorticoid receptor


Crumbling mineral mountain: K+ diuretics (e.g. spironolactone, eplerenone) are useful in the treatment of 1 and 2 hyperaldosteronism (high BP, low K, metabolic alkalosis)
Failing heart balloon: K+ diuretics (e.g. spironolactone, eplerenone) are useful in the treatment of heart failure
Remodeling: mineralocorticoid antagonists (e.g. spironolactone, eplerenone) prevent myocardial remodeling induced by high levels of aldosterone
Angel: mineralocorticoid antagonists (e.g. spironolactone, eplerenone) decrease mortality in heart failure
insipidus fountain: amiloride is useful in the treatment of Li+ induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, block Li reabsorption
Little gnome blocked by almonds and tangerines: amiloride and triamterene are useful in the treatment of Liddle's syndrome (overactive ENaCs)

Elevated bananas: K+ sparing diuretics can cause hyperkalemia
Acid spill into intracellular space: K+ sparing diuretics cause a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis (by decreasing the function of the H+ATPase)
4 acid tubes: K+ sparing diuretics inhibit the effects of aldosterone in the collecting duct causing a type 4 renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
Big K: type 4 RTA is associated with hyperkalemia

Spiral-bound notebook: spironolactone (a K+ sparing diuretic)
Health inspector antagonizing the mineral court services man: spironolactone antagonizes the mineralocorticoid receptor
Fried male symbol: testosterone produced from cholesterol
Health inspector inhibiting 17-a-"fry"droxylase: spironolactone inhibits 17a-hydroxylase (an enzyme in the testosterone synthesis pathway)


Bubbling ovary shaped vats: spironolactone treats the symptoms of androgen excess in polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
Bushy beard: symptoms of androgen excess (e.g. hirsutism) in PCOS (treat with spironolactone)
Preventing boy from receiving onion ring: spironolactone directly antagonizes the androgen receptor
Lids on chest: spironolactone can cause gynecomastia
Droopy churro: spironolactone can cause impotence and decreased libido
Antihypertensive
CCB
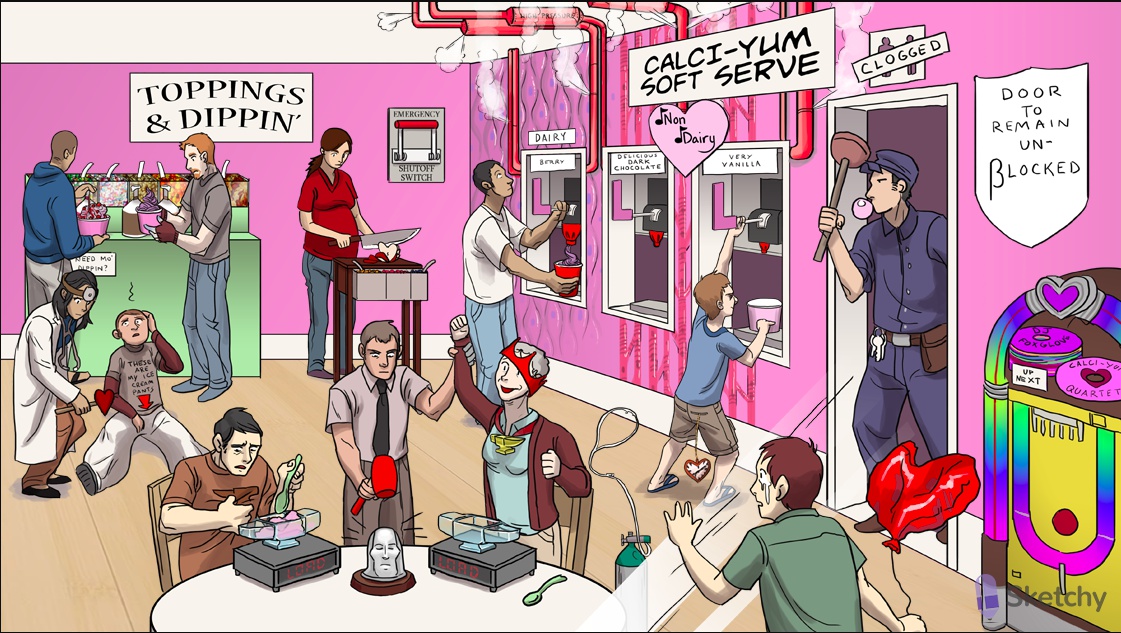

Calci yum: CCB
L-shaped handle: calcium channel blockers target voltage gated L-type calcium channels
Dairy: dihydropyridines
Non-dairy: nondihydropyridines
Smooth muscle tile: dihydropyridines block L-type calcium channels in smooth muscle
Cardiac muscle tile: non-dihydropyridines block L-type calcium channels in cardiac muscle

Dippin' station: -dipine suffix of dihydropyridines (e.g. nifedipine, amlodipine, nicardipine)

Dilated dairy nozzle: dihydropyridines cause vasodilation
Dilated coronary crown: dihydropyridines (e.g. amlodipine, felodipine) dilate coronary arteries
Reduced load: dihydropyridines reduce afterload

Very vanilla: verapamil (a non-dihydropyridine)
Delicious dark chocolate: diltiazem (a non-dihydropyridine)

Medium sized nozzle: diltiazem has some vasodilatory activity
Weak kid at the non-dairy: non-dihydropyridines decrease cardiac contractility
Music notes: non-dihydropyridines decrease activity at the SA and AV nodes
Low dangling heart watch: inhibition of the SA node by non-dihydropyridines causes bradycardia
Discarded oxygen: non-dihydropyridines decrease myocardial oxygen demand

Emergency shut off: an IV dihydropyridine (e.g. clevidipine, nicardipine) can treat hypertensive emergency
Large knife: nifedipine (a dihydropyridine)
Pregnant knife lady: nifedipine is used to treat hypertension in pregnancy
"Blue fingertips: dihydropyridines treat Raynaud's syndrome"
Brain ice cream with berries: berry aneurysm (PCOS)
Strawberry syrup: subarachnoid hemorrhage
Need mo' dippin' with berry brain ice cream: nimodipine prevents vasospasm after a subarachnoid hemorrhage
CCB:
High pressure pipes: both CCBs treat hypertension
Angina anvil: CCBs treat stable angina
Anvil medal: CCBs treat Prinzmetal angina

Pounding head bell: migraine prophylaxis with verapamil
Jukebox: non-dihydropyridines have antiarrhythmic properties
CCB:
High pressure pipes: both CCBs treat hypertension
Angina anvil: CCBs treat stable angina
Anvil medal: CCBs treat Prinzmetal angina

Lightheaded patron: dihydropyridines can cause lightheadedness and headache
Baggy pants: dihydropyridines can cause peripheral edema (dilation of pre capillary vessels, arterioles, increase hydrostatic pressure)
Heart reflex hammer: dihydropyridines can cause reflex tachycardia
Knife cutting heart: nifedipine can exacerbate myocardial ischemia due to reflex tachycardia - avoid in patients with unstable angina or MI (shorter acting, higher SE)

Clogged toilet: verapamil can cause constipation
Expanding gum: verapamil can cause gingival hypertrophy
Remain un-blocked: verapamil and diltiazem are relatively contraindicated in patients with heart block
Verapamil or diltiazem combined with a beta blocker may produce excessive AV block
Failing heart balloon locked out of store: CCBs can worsen heart failure (increased sympathetic activity and decreased contractility)
Antihypertensives
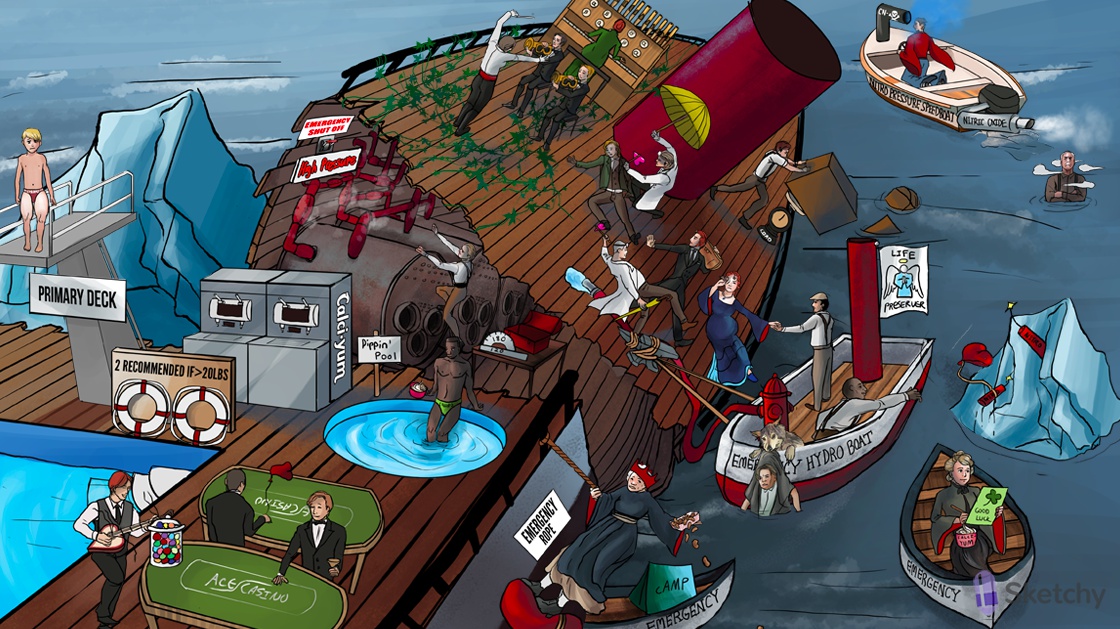

High tension, high sea: anti hypertensives
High pressure pipes: antihypertensives
Primary deck: primary (essential) hypertension treatment
Chloro-thighs: hydrochlorothiazide is a first line agent for treating primary HTN
Dippin' pool: long acting dihydropyridines (-dipine suffix) treat primary hypertension
Ace-stealing dealer: ACE inhibitors treat primary HTN

Two life preservers if > 20 lbs: two antihypertensives for BP > 20/10 mmHg above goal
Elderly black man with calci-YUM icecream: black and elderly patients respond well to a CCB for treatment of primary HTN
Chloro-thighs: black and elderly patients respond well to hydrochlorothiazide for treatment of primary HTN
ACE inhibitors are first line treatment for hypertension in patients with heart failure (failing heart balloon), MI (broken heart strings), and diabetes (candy jar)

Emergency shut-off switch: treatment for hypertensive emergency
180 degree protractor over 12 inch ruler: hypertensive emergency (SBP >180 or DBP >120)
Hole in the Titanic: hypertensive emergency is defined by end-organ damage plus elevated BP (SBP >180 or DBP >120)
Reduce pressure gradually. Reducing too quickly can lead to ischemia

Muted beta bugles: beta-1 antagonists (e.g. esmolol and metoprolol) can be used for hypertensive emergency
Ivy: IV beta blocker administration treats hypertensive emergency
Alpha and beta organ stops: labetalol (alpha and beta antagonist) can be used in hypertensive emergency
Calci-yum ice cream: IV calcium channel blockers (e.g. nicardipine, clevidipine) can be used in hypertensive emergency
Nice card: nicardipine (a dihydropyridine CCB)
Clover: clevidipine (a dihydropyridine CCB)
Hydro-boat: hydralazine treats hypertensive emergency
Nitro-pressure speedboat: nitroprusside can be used to in hypertensive emergency
Old lady Pam: fenoldopam treats hypertensive emergency

Dilated red sleeves: dihydropyridine CCBs (e.g. nicardipine and clevidipine) cause arteriolar dilation
Dilated red smokestack: many agents used in hypertensive emergencies are potent vasodilartors
Unloaded scale: vasodilation reduces afterload
Heart-shaped reflex hammer and rain umbrella: hypotension leads to reflex tachycardia and increased renin levels

Hydro-boat: hydralazine treats hypertensive emergency
Dilated red hose: hydralazine is a direct arteriolar vasodilator
Pregnant woman boarding hydro-boat: hydralazine is safe in pregnancy
Fainting: hydralazine can cause hypotension
Anvil anchoring hydro boat: hydralazine induced reflex tachycardia can worsen angina
Lupus wolf: hydralazine can cause drug-induced lupus
Beta-1 bugler leaving to get on hydro boat: administer beta-blocker with hydralazine to prevent reflex tachycardia
Muted beta-1 bugler deflecting reflex hammer and rain umbrella: beta blockers minimize the reflexive sympathetic activation

Dynamite: nitrate (e.g. nitroglycerine)
Failing heart balloon: hydralazine combined with a nitrate (e.g. nitroglycerine) treats heart failure (hydralazine arteriodilation, nitrate venodilation)
Guardian angel: hydralazine combined with a nitrate (e.g. nitroglycerine) provides a mortality benefit for certain patients in heart failure

Nitro-pressure speedboat: nitroprusside can be used to in hypertensive emergency
Grump: nitric oxide promotes smooth muscle relaxation by increasing cyclic GMP
Nitric oxide exhaust: nitroprusside causes vasodilation via nitric oxide
Sailor with dilated red sleeves and blue pants: nitroprusside causes arteriolar and venous dilation
Blue cyanide exhaust: cyanide poisoning is a side effect of nitroprusside, altered mental status, seizures

Old lady Pam: fenoldopam treats hypertensive emergency
Single rope: fenoldopam is a selective dopamine 1 receptor agonist
Camping tent: fenoldopam (a D1 agonist) increases cAMP, arterial dilation (renal, mesenteric, coronary)
DIlated red sleeves: fenoldopam causes arterial dilation
Dilated red crown: fenoldopam causes coronary vasodilation
Rope connected to kidney: fenoldopam dilates renal arteries, increasing renal perfusion
Salty peanuts falling into water: Fenoldopam (a D1 agonist) causes natriuresis, Na/water excretion
Antiarrythmics
Class I and III: rhythm control
Class II and IV: rate control
Class I

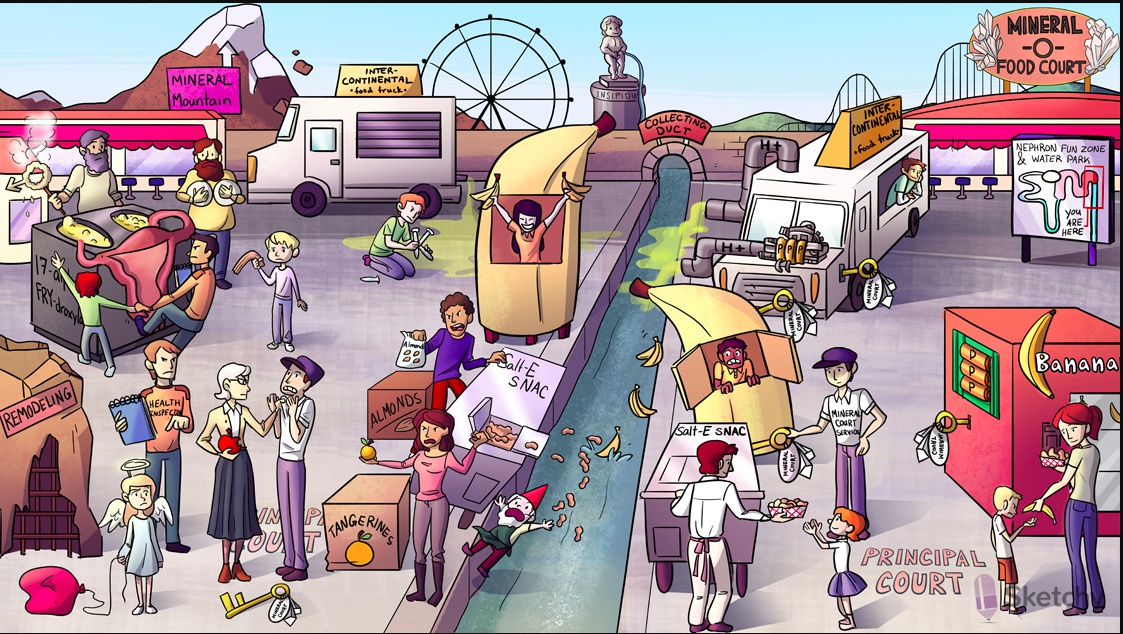
Microphone: Phase 0: upstroke dictated by Na+
Wire: Phase 2: plateau dictated by Ca2+
Wire: Phase 3: repolarization dictated by K+
Potassium banana curtain: K+ current present during phase 2 (plateau) and phase 3 (repolarization) of the cardiac action potential

Soloist: class I antiarrhythmics
Soloist holding peanut butter jar: class I antiarrhythmics block sodium channels (phase 0)
Soloist tipping mic stand: class I antiarrhythmics decrease the slope of the phase 0 upstroke (slows conduction of the cardiac AP)
Illuminated atria, ventricles, and His-Purkinje system: class I antiarrhythmics affect the Na+ dependent cardiac action potential (no action at the SA and AV nodes, upstroke by Ca channels)


Inactivating spoon in open peanut butter jar: class I antiarrhythmics bind to open or inactivated Na+ channels, poorly to channels in resting state. Cells depolarizing are in open states. Channels are in inactivated states during refractory period
Heart watch tipping mic stand: "use dependance"- class I antiarrhythmics have a greater effect on rapidly depolarizing tissues (increased heart rate causes slower phase 0 upstroke) (great for tachycardias and minimally affect normal cells)


Wide QRS shaped crack: class I antiarrhythmics widen the QRS complex on the ECG (decreased AP conduction velocity) (faster cells bind more and slow down more) (QRS widen as HR increases)
Ia

Class IA antiarrhythmics: quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide
Dining prom queen: quinidine (class IA antiarrhythmic)
Prom king: procainamide (class IA antiarrhythmic)
"Disappears!": disopyramide (class IA antiarrhythmic)

Lightly held peanut butter jar: class IA antiarrhythmics have an intermediate binding affinity for the Na+ channel (intermediate use-dependence, moderate slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Pushing away the curtain: class IA antiarrhythmics also block K+ channels, prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period

Illuminated top and bottom of heart: class IA antiarrhythmics treat supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias
White wolf pack: class IA antiarrhythmics treat Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome (a type of SVT) (extra pathway stopped)

Tin cans: quinidine toxicity can cause cinchonism (a syndrome of tinnitus, headache,dizziness)
Broken plates: quinidine can cause thrombocytopenia
Prom king's lupus wolf: procainamide can cause a lupus-like syndrome
Darts deflating failing heart balloon: disopyramide can exacerbate heart failure (negative inotropy)
Twisted torsades streamer: class IA antiarrhythmics can cause Q-T interval prolongation (precipitates torsades) (K channel prolongation)
Ib

Class IB antiarrhythmics: lidocaine, mexiletine, phenytoin
"LIED": lidocaine (class IB antiarrhythmic)
Friendly Towing: phenytoin (an anti-epileptic) shows some class IB antiarrhythmic properties
Mexican flag: mexiletine (class IB antiarrhythmic)

Dropped peanut butter jar: class IB antiarrhythmics have an low binding affinity for the Na+ channel (low use-dependence, modest slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Pulling in the curtain: class IB antiarrhythmics shorten phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> shortened refractory period

Illuminated, cracked bottom of heart: class IB antiarrhythmics treat ventricular arrhythmias (especially in ischemic tissue) (rapid binding and unbinding selects for tissues with Na in open/inactive states. Ventricles/HIS has longer AP compared to atrium)
"DEAD": class IB antiarrhythmics treat ischemia induced ventricular arrhythmias (dead tissues have reduced AP with delayed Na channel transition from inactivated to resting)

Brain trucker hat: class IB antiarrhythmics cause neurological side effects (e.g.paresthesias, tremor, convulsions)
Ic

Class IC antiarrhythmics: propafenone, flecainide
Flakes: flecainide (class IC antiarrhythmic)
purple phone: propafenone (class IC antiarrhythmic)

Tightly held peanut butter jar: class IC antiarrhythmics have an strong binding affinity for the Na+ channel (strong use-dependence, drastic slowing of the phase 0 upstroke)
Untouched potassium curtain: class IC antiarrhythmics do not affect the cardiac action potential duration

Illuminated top and bottom of heart: class IC antiarrhythmics treat supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular signal: class IC antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Converting the signal: class IC antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter

"Healthy hearts only!": class IC antiarrhythmics are contraindicated in patients with history of structural or ischemic heart disease (proarrhythmic effects) (can cause delayed in conduction speed out of proportion to prolongation of refractory period)
Class II

Phase 4: pacemaker current dictated by Na+ and other ions
Phase 0: upstroke dictated by Ca2+
Phase 3: repolarization dictated by K+

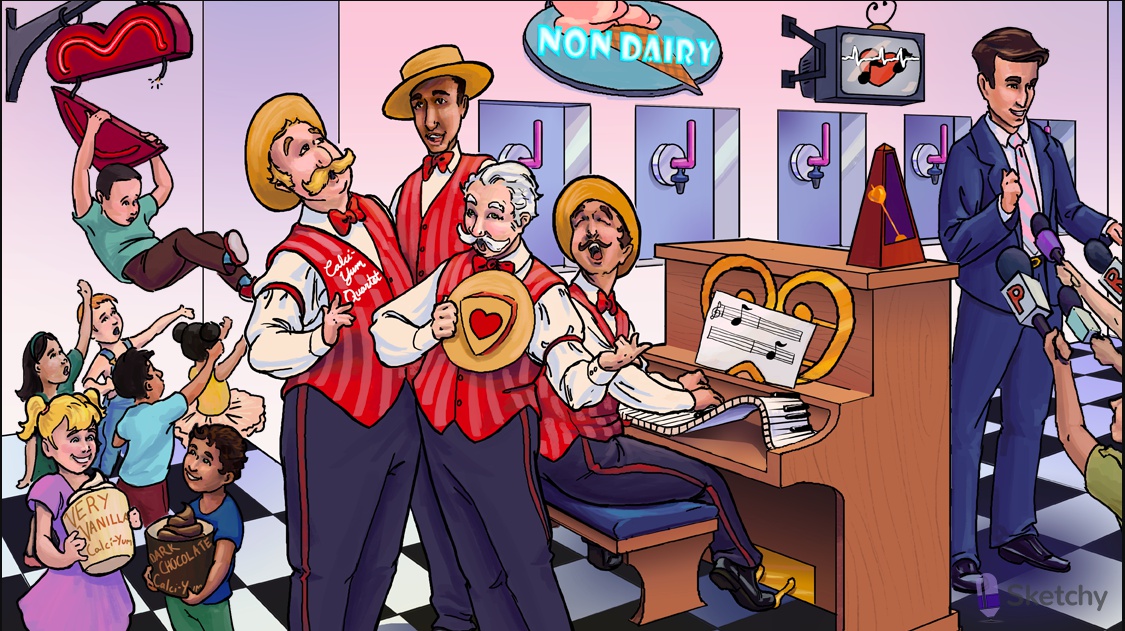
Duet: Class 2 antiarrhythmics
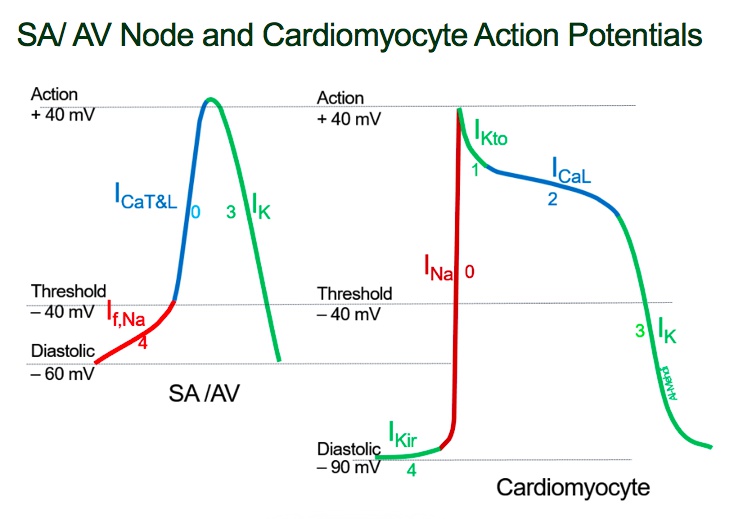
Muted beta bugle: beta blockers (class 2 antiarrhythmics)
notes: beta blockers treat arrhythmias by blocking sympathetic input to the SA and AV nodes
Torn band camp: beta blockers decrease cAMP
Crushed calci-YUM ice cream cartons: decreased cAMP leads to closure of membrane calcium channels
Sliding up the keys: beta blockers prolong phase 4 of the nodal action potential -> decreased pacemaker activity, prolonged conduction time and refractory period.


Disconnected bottom: beta blockers decrease atrioventricular conduction (AV block)
Lit up top: beta blockers treat supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. atrial fibrillation with RVR)
Ivy: IV beta blockers (e.g. esmolol) can be used for acute supraventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular static: beta blockers are useful in atrial fibrillation and flutter
Metronome: beta blockers prevent rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter ("rate control") (increase AV node refractory period, slow ventricular response rate)

Hat shielding heart: beta blockers can cause heart block
Public Relations: heart block manifests as a prolonged PR interval on ECG
Class III

Trio: class III antiarrhythmics
Phase 2: plateau dictated by Ca2+
Phase 3: repolarization dictated by K+
Potassium banana curtain: K+ current present during phase 2 (plateau) and phase 3 (repolarization) of the caria action potential
Pushing away the curtain: class III antiarrhythmics block K+ channels prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period



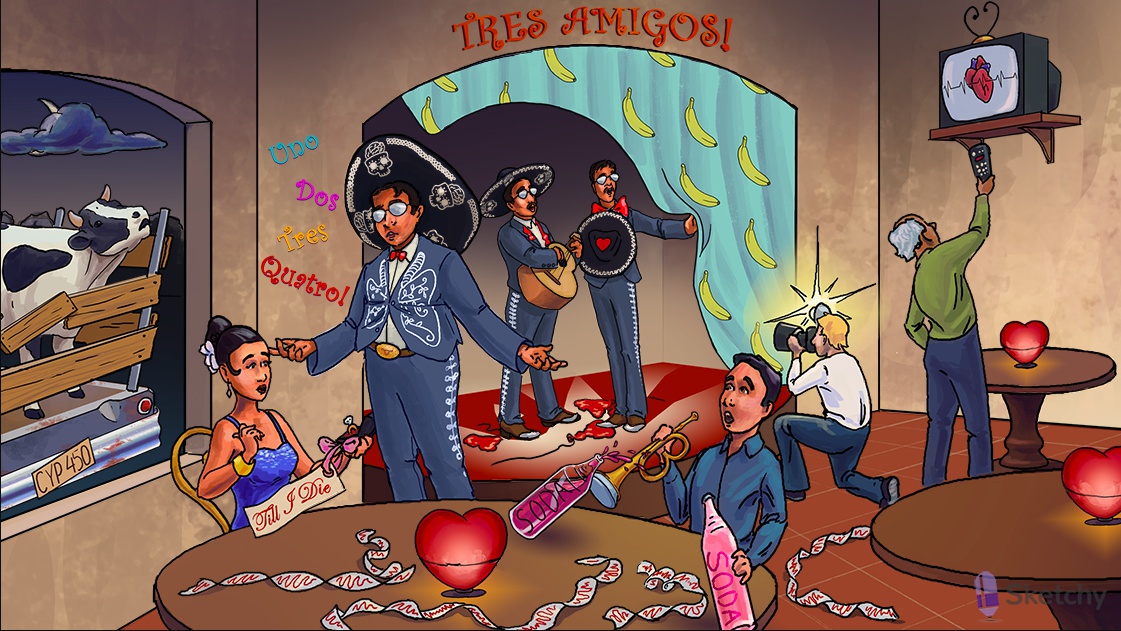
Amigo: amiodarone (class III antiarrhythmic)
"till I die": -tilide suffix shared by dofetilide and ibutilide (class III antiarrhythmics)
Soda: sotalol (class III antiarrhythmic)
Muted bugle: sotalol is also a beta blocker (-lol suffix)

Amiodarone shares properties of class I, II, III, and IV antiarrhythmics

Heart illuminated on top and bottom: class III antiarrhythmics treat both supraventricular arrhythmias and ventricular arrhythmias
Irregularly irregular signal: class III antiarrhythmics treat atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Converting the signal: class III antiarrhythmics can restore and maintain normal sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation and flutter

Skull brains: amiodarone has many neurologic side effects (e.g.tremor, ataxia, peripheral neuropathy, sleep disturbances)
Gray sunglasses: amiodarone can cause gray corneal microdeposits
Big and small bowties: amiodarone can cause hyper or hypothyroidism
Fibrotic lung embroidery: amiodarone can cause pulmonary fibrosis
Tight button: amiodarone induced lung fibrosis causes restrictive lung disease
Hat shielding heart: amiodarone can cause heart block (Class II activity)
Trampled failing heart balloon: amiodarone can induce heart failure
Liver spot: amiodarone can cause hypersensitivity hepatitis
Gray-blue outfits: amiodarone can cause gay-blue skin discoloration
Flash photo: amiodarone can cause photodermatitis
Broken chrome bumper: amiodarone inhibits the cytochrome P450 system

Twisted streamer: sotalol, dofetilide, and ibutilide can induce torsades (although all type III antiarrhythmics can widen the QT interval)
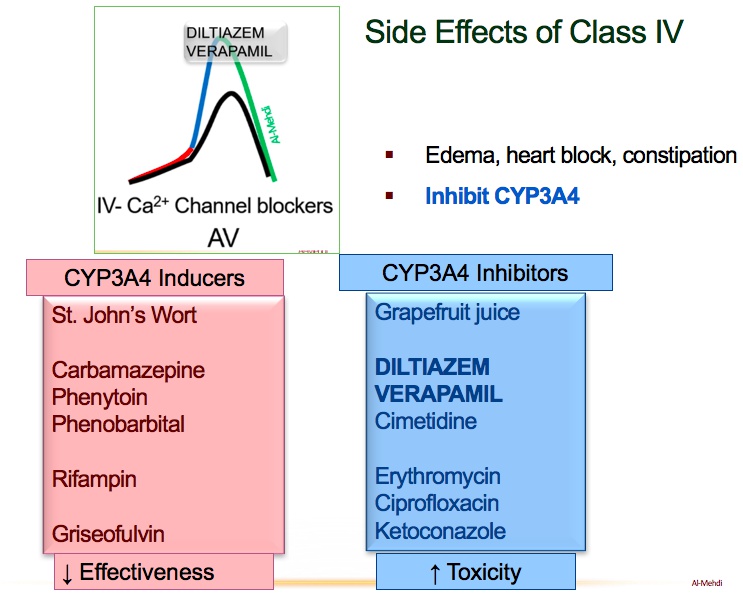
Class IV

Quartet: class IV antiarrhythmics
Nondairy: non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (type IV antiarrhythmics)
Delicious dark chocolate: diltiazem (non-dihydropyridine CCB)
Very vanilla: verapamil (non-dihydropyridine CCB)

block activated and inactivated Ca channels, not resting channels. Work more on tissues fire more frequently and exclusively activated by Ca current
Notes: non-dihydropyridines (e.g. diltiazem, verapamil) treat arrhythmias by blocking Ca2+ current in the SA and AV nodes
Disconnected bottom: non-dihydropyridine CCBs decrease atrioventricular conduction
Phase 4: pacemaker current dictated by Na+ and other ions
Phase 0: upstroke dictated by Ca2+
Phase 3: repolarization dictated by K+
Sliding up the keys: non-dihydropyridine CCBs prolong phase 4 of the nodal action potential -> decreased pacemaker activity, prolonged conduction time and refractory period



Illuminated top: non-dihydropyridine CCBs treat supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. atrial fibrillation with RVR)
Irregularly irregular signal: non-dihydropyridine CCBs are useful in atrial fibrillation (and flutter)
Metronome: non-dihydropyridines prevent rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter ("rate control")

Public Relations: non-dihydropyridine CCBs prolong the PR interval on ECG
Hat shielding heart: non-dihydropyridine CCBs can cause heart block

Class V

DJ foxglove: digoxin has antiarrhythmic properties
Vegas: digoxin exerts direct parasympathomimetic effects via direct stimulation of the vagus nerve -> (more at) AV nodal inhibition
Irregularly irregular signal: digoxin is useful in atrial fibrillation (and flutter) (1st goal is rate not rhythm)
Metronome: digoxin prevents rapid ventricular response in atrial fibrillation and flutter ("rate control")


Magnets: magnesium is useful for the treatment of certain arrhythmias (e.g. torsades)
Torn twisted torsades streamers: magnesium treats torsades de pointes

Banana dancer pointing up: hyperkalemia can induce arrhythmias
Banana dancer pointing down: hypokalemia can induce arrhythmias
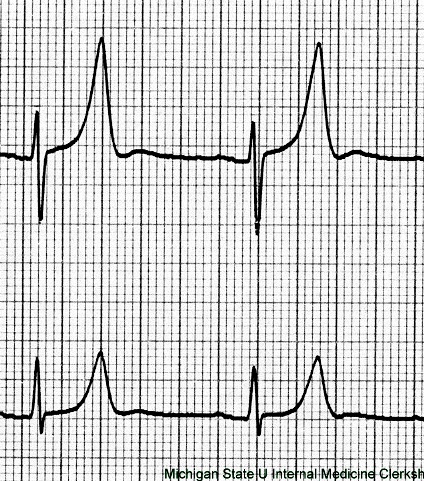
Peaked streamer: hyperkalemia can cause peaked T waves (with shortened QT interval) on ECG
Streamer with extra bump: hypokalemia can induce U waves at the end of the T wave on ECG

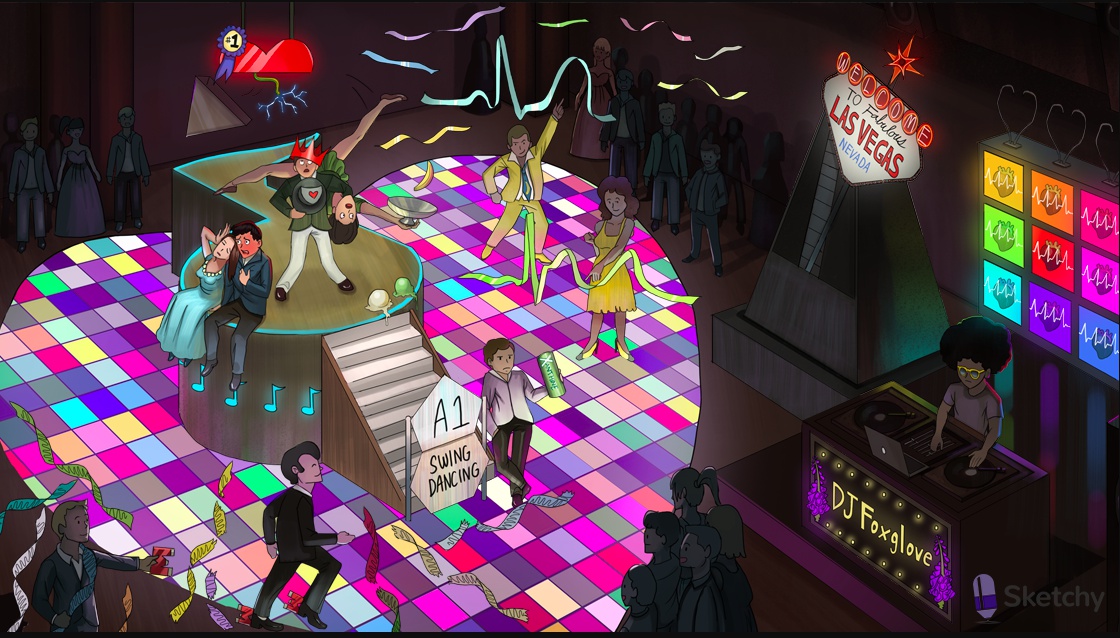
Swing dancing: adenosine (a purine nucleoside with antiarrhythmic properties)
Purine shaped gate: adenosine is a purine nucleotide
A1 Swing: adenosine activates inhibitory A1 receptors on the myocardium and at the SA and AV nodes
Falling calci-yum ice cream: activation of A1 receptors suppresses inward Ca2+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP
Banana flying out of cup: activation of A1 receptors increases outward K+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP)


Note shaped dance floor: adenosine inhibits the AV nodes (decreased AV conduction, prolonged AV refractory period)
Disconnected bottom of heart: adenosine decreases atrioventricular conduction
Dilated coronary crown: adenosine causes coronary dilation (mediated by A2 receptors)

Illuminated #1 top of heart: adenosine is a first line agent for acute treatment of supraventricular arrhythmias (e.g. PSVT)

Hat blocking heart: adenosine causes transient high grade heart block (direct AV node inhibition) (very quick half life, 10 seconds)
Flushed dancer: adenosine can cause cutaneous flushing
Dancer clutching chest: adenosine can cause shortness of breath, chest pain, and an impending sense of doom
Fainting dancer: adenosine can cause headache and hypotension

Energy drink blocking A1 gate: the actions of adenosine are inhibited by caffeine and theophylline (methylxanthines)
Last updated