07 Pituitary Secretions
Hypothalamus-Pituitary System
_The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland communicates with the hypothalamus by the hypothalamic–hypophysial portal system:
The hypothalamus is supplied by blood coming from the superior hypophyseal artery.
Hypothalamic hormones enter the capillary plexus near the median eminence, and travel via long portal veins to the anterior pituitary.
In the anterior pituitary, hormones exit a secondary capillary plexus to stimulate or inhibit hormone release from their specific endocrine target cells.
Endocrine cells respond by increasing or decreasing their output of tropic hormones into systemic circulation.

 Hypothalamus outlined on MRI:
Hypothalamus outlined on MRI:  ..
..
_In contrast, the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland contains the axons of neurons whose cell bodies are located in hypothalamic nuclei.
Hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus, packaged in secretory granules and transported down the nerve axons for secretion.
Upon stimulation of the hypothalamic cell bodies, hormone-containing granules are released by exocytosis into peripheral circulation, via the capillary plexus of the inferior hypophyseal artery.
 ..
..
..
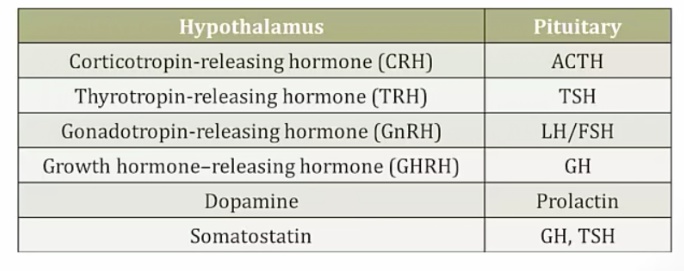
CRH
_Stimulates ACTH secretion, as well as the release of other peptides derived from proopiomelanocortin (e.g. MSH, β-endorphin).,

GnRH
_Stimulates the secretion of LH, FSH.,

Somatostatin
_Inhibits the secretion of GH and TSH.,

_Pharm uses:
 ..
..
TRH
_Stimulates the secretion of TSH and prolactin. Prolactin is under tonal dopamine inhibition, and excess TRH levels suppress dopamine. Thus, prolactin levels will increase as dopamine decreases.,

Dopamine
_Inhibits the release of prolactin.,

Melanocyte Inhibiting Factor
_Inhibits the release of MSH.,

Anterior Pituitary
_There are 6 major hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary (mnemonic: FLAT PiG):
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH; thyrotropin)
Prolactin
Growth hormone (GH)
 ..
..
FSH and LH
_Secreted by gonadotropes of the anterior pituitary.,
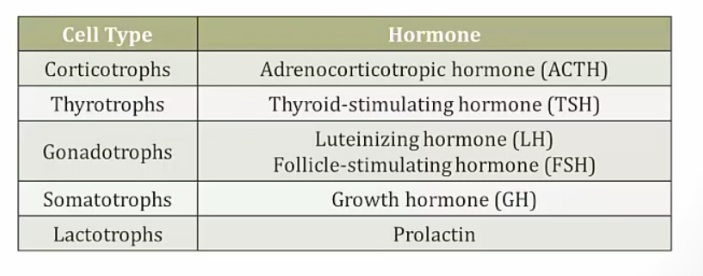
LH
FSH
Male
Leydig cell:
Sertoli Cell:
testosterone synthesis
sperm maturation
Female
Theca Cell:
Granulosa Cell:
testosterone synthesis, ovulation, corpus luteum formation
follicle growth, estrogen secretion
..
ACTH
_Secreted by corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary and stimulates adrenal growth and steroidogenesis.,

TSH
_Secreted by thyrotrophs of the anterior pituitary and stimulates thyroid hormone synthesis and release.,

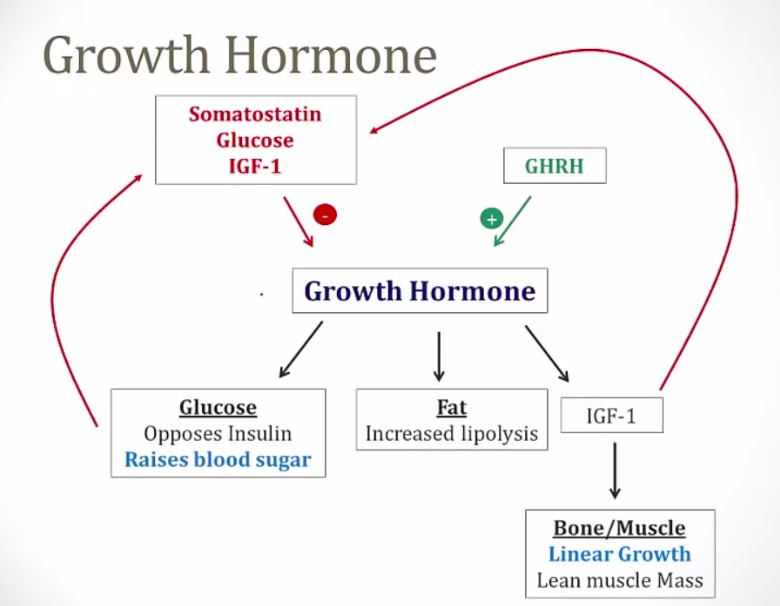
GH
_Secreted by somatotropes of the anterior pituitary and is counter-regulatory to insulin. It stimulates linear height growth via insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1), which is released by the liver in response to stimulation by GH.,

_Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH, somatocrinin) stimulates the secretion in pulsatile fashion.
Also increased by
Exercise
Sleep (very high just after onset of sleep)
Starvation (hypoglycemia)
.,
_Is decreased by:
Glucose
Somatostatin (released in response to IGF-1; GH)
IGF-1 (direct and indirect).,
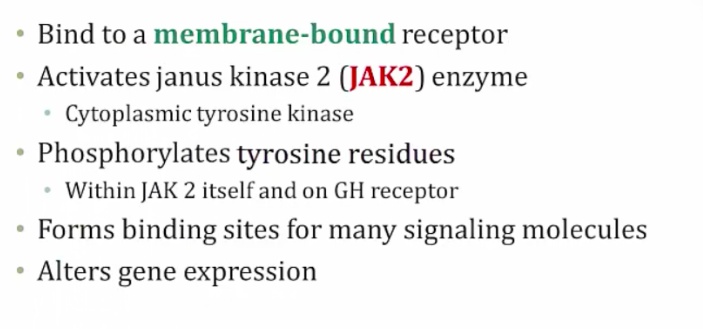
_Protein hormone and binds to surface receptors, uses JAK2-STAT pathway.,
Growth Hormone Receptor
 ..
..
IGF-1
_aka Somatomedin.,
_Many growth hormone receptors are found in the liver, and they secrete IGF-1, which mediates many of GH effects. IGF-1 is also produced in peripheral tissues and mediates its effect in paracrine fashion...
_Has following effects:
Stimulates chondrocytes, increase linear growth
Stimulates muscles, increase lean muscle mass
Stimulates organs, increase organ size
.,
_IGF-1 is measured in serum as indicator of GH function, as GH is difficult to measure with its pulsatile fashion...
GH Effects
_Has following effects:
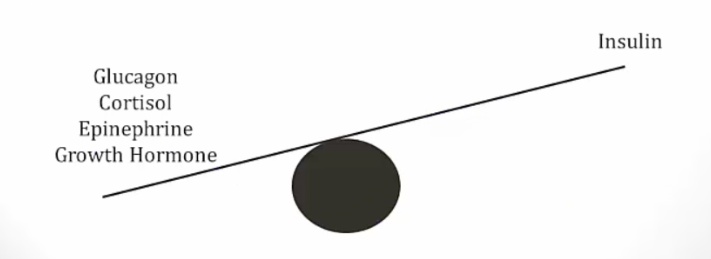
Increased insulin resistance and blood sugar
Increased lipolysis by activating hormone sensitive lipase
Increased IGF-1 that results in bone, muscle, and organ growths.,

_GH decreases blood glucose intake in to cells and will cause anti-insulin effects:
increased blood sugar (diabetogenic)
increased insulin resistance in peripheral tissues
hyperinsulinemia.,
GH Deficiency
_Most common caues is pituitary tumor from masses or as result of surgery/radiation...
_Symptoms are different for children and adults:
Children: failure to grow
Adults: increased fat, low lean body mass, low energy..
_Treatment is synthetic growth hormone and IGF-1 level monitoring..
HCG
_TSH, LH, FSH and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) share a common α-subunit, while the β-subunit of these hormones determines hormone specificity.
 ..
..
MSH
_aka melanotropin.,
_MSH, or melanotropin, stimulates melanin synthesis and is secreted from the intermediate lobe of the pituitary...
[_](MSH and Cushing's disease)In Cushing's disease, the ACTH adenoma produces both excess ACTH and MSH, causing the characteristic darkened skin...
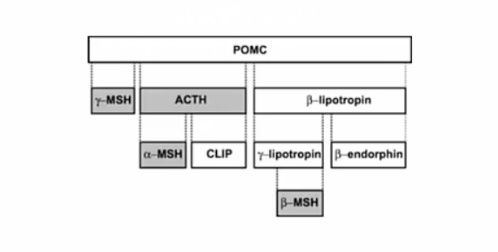
POMC
_Derived from pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC).,
Basophils and Acidophils
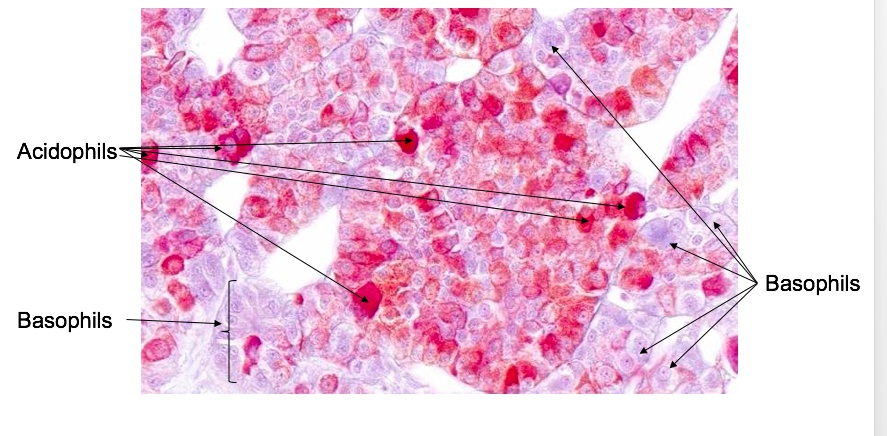
_Cells of the anterior pituitary are categorized into two groups, basophils and acidophils, based on whether they stain readily with acidic or basic dyes. To remember which type of hormone-secreting cells fall into which category, use the mnemonics “GPA” and “B FLAT”:
“GPA”: Growth hormone and Prolactin are secreted by Acidophils
“B FLAT”: Basophils secrete Follicle stimulating hormone, Lutenizing hormone, Adrenocorticotropic hormone, and Thyroid stimulating hormone...
Feedback
_Anterior pituitary hormones enter the systemic circulation and exert their effects at target glands. Eventually, the target gland response is limited by its hormonal product exerting negative feedback inhibition at the level of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus...
Posterior Pituitary
_:
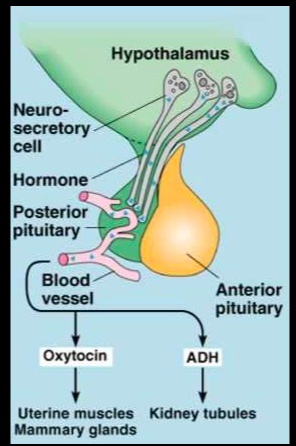
Paraventricular nuclei: Oxytocin
Supraoptic nuclei: ADH..
_Vasopressin and oxytocin are two hormones that are secreted from the posterior pituitary. Note that vasopressin is also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and arginine vasopressin (AVP).
The hypothalamus directly synthesizes hormones, which are complexed with neurophysins and shipped into the posterior pituitary for storage and secretion. The hypothalamic-pituitary hormones that utilize this non-capillary secretion mechanism include arginine vasopressin (aka antidiuretic hormone) and oxytocin...
ADH
_A nonapeptide that is synthesized predominately in the supraoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus, and secreted from the posterior pituitary upon stimulation of these cell bodies. .,
_Travels down the nerve axon in neurosecretory granules to be stored in the nerve terminals, lying in the posterior pituitary gland. Neurophysins are the carrier proteins which make this transport possible.,
[_](ADH's 2 main effects)Vasopressin has an antidiuretic effect (reabsorbs water) and is also a moderate vasoconstrictor. ..
_The primary stimulus for antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion is an increase in serum osmolarity. A loss of intracellular water from hypothalamic osmoreceptor neurons bathed by hyperosmolar blood will stimulate ADH release. Other factors that increase ADH secretion include:
Pain/stress
Hypoglycemia
Nausea
Volume contraction
Nicotine and opiates
Angiotensin II..
_The primary inhibitor of ADH secretion is a decrease in serum osmolarity. Other factors that decrease ADH secretion include:
Alpha-agonists
Ethanol
Atrial natriuretic peptide
Cold..
_Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) has two primary functions:
Regulate serum osmolarity
Maintain (increase) blood pressure..
_ADH increases water reabsorption by binding to V2 receptors on the capillary (basal) side of principal cells in the renal collecting duct:
ADH binding activates adenylyl cyclase, which increases cAMP and activates protein kinase A.
Activated protein kinase A phosphorylates aquaporin-2-containing vesicles, stimulating their transport and fusion with the luminal plasma membrane
The insertion of more aquaporin channels allows water to move rapidly from the tubular lumen into the collecting duct cell, reclaiming more water.
The result is an increase in blood volume and a decrease in plasma osmolarity.
 ..
..
_Vasopressin also causes vasoconstriction of arterioles through binding to V1 receptors, stimulating a IP3/Ca2+-mediated response. This vasoconstriction leads to a direct increase in arterial pressure.
Note: this function can be remembered by the latter half of the hormones name -pressin (remember, a pressor is any agent that increases blood pressure by stimulating constriction of blood vessels)...
_Antidiuretic hormone also increases the permeability of the inner medullary collecting duct to urea. This increases the osmotic gradient created by the countercurrent multiplier, facilitating the production of concentrated urine (i.e. increasing urine osmolarity)..
Last updated