06 PV Loop
PV Loops
_..
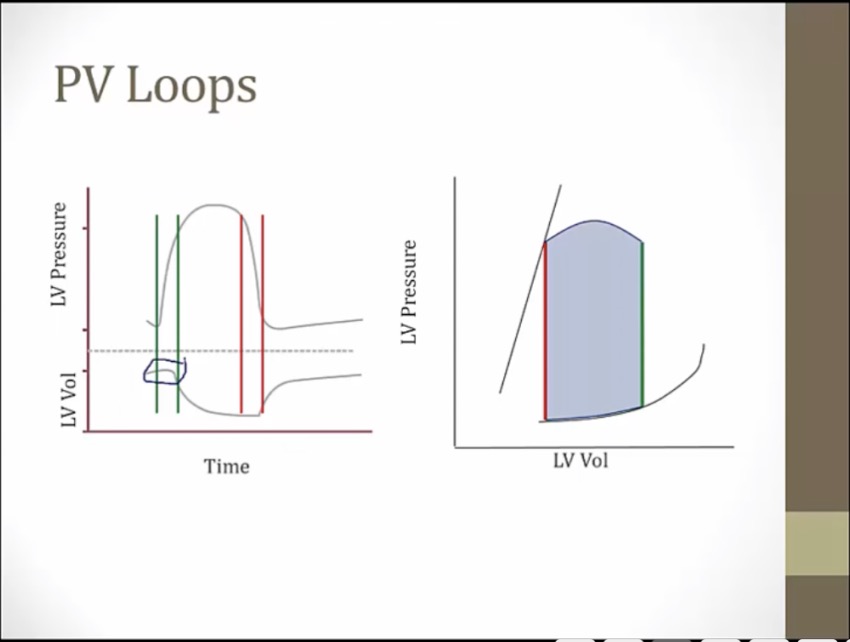
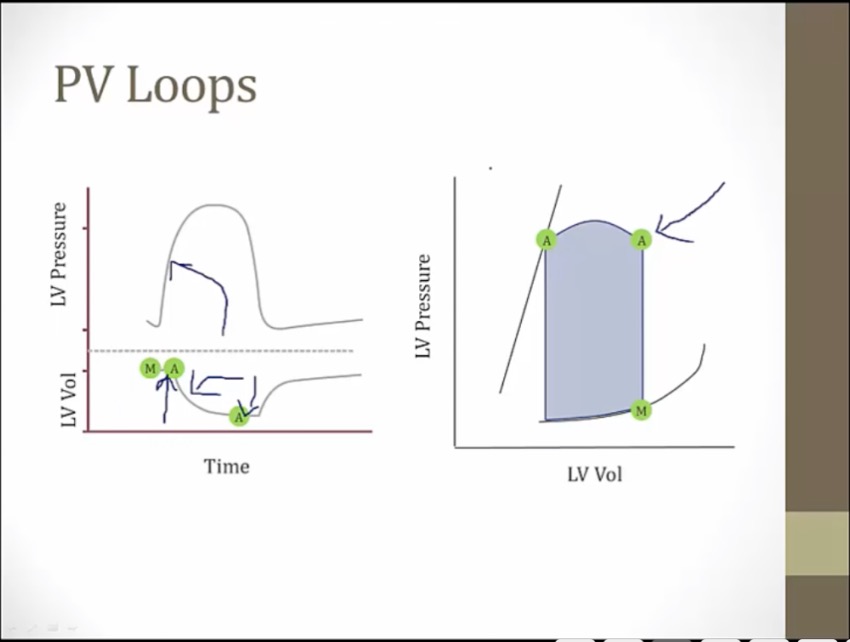
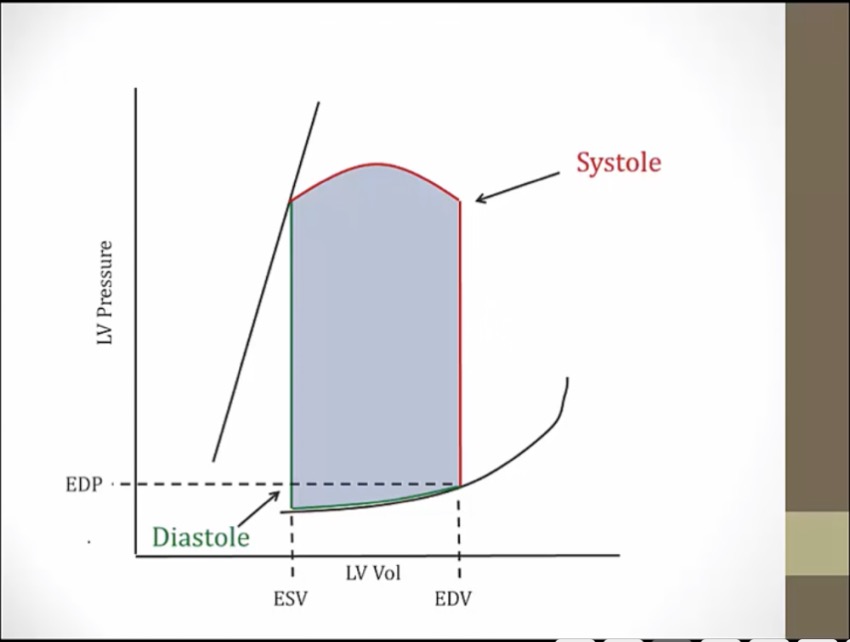
volume on bottom, pressure on top
right: take volume and pressure of each time and plot against one another
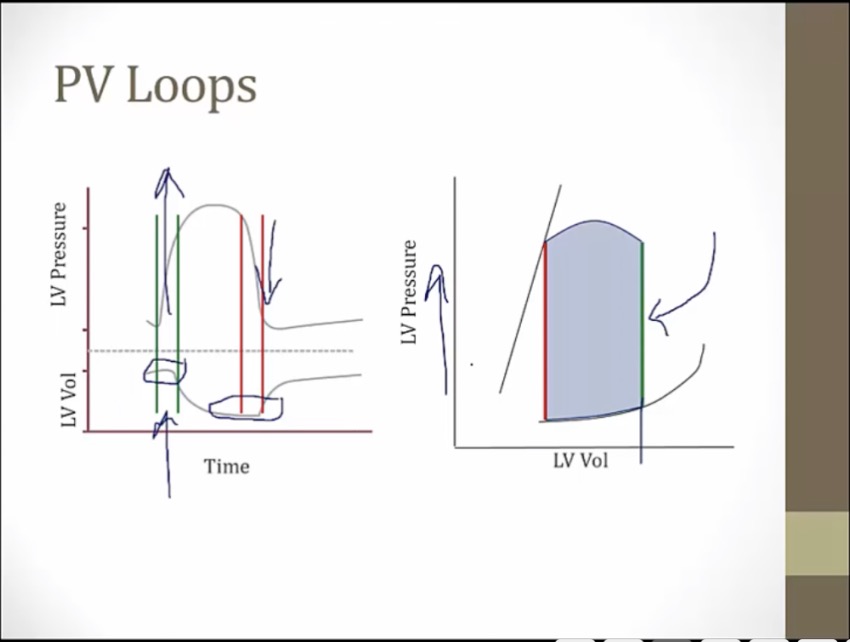
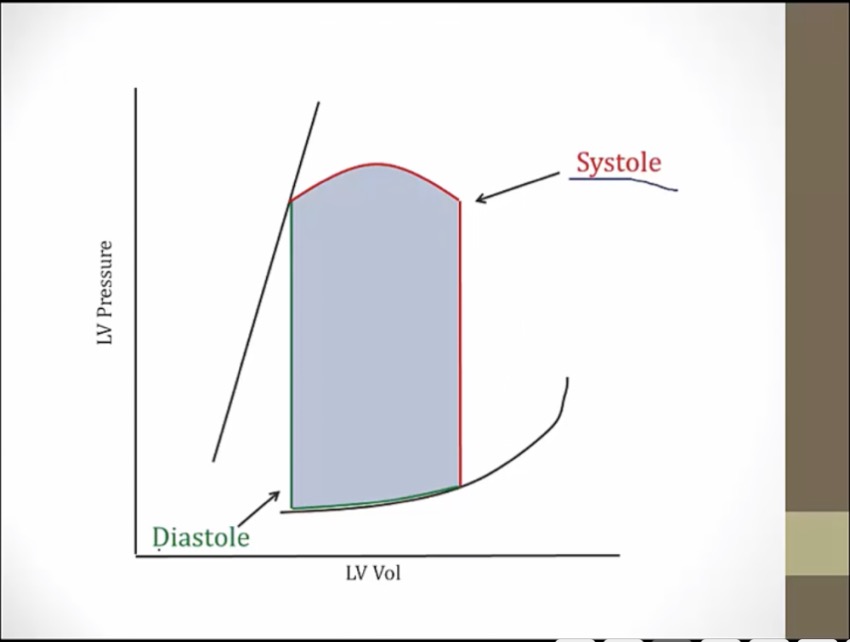
green: volume not changing, pressure go way up, isovolumic contraction. Both valves closed
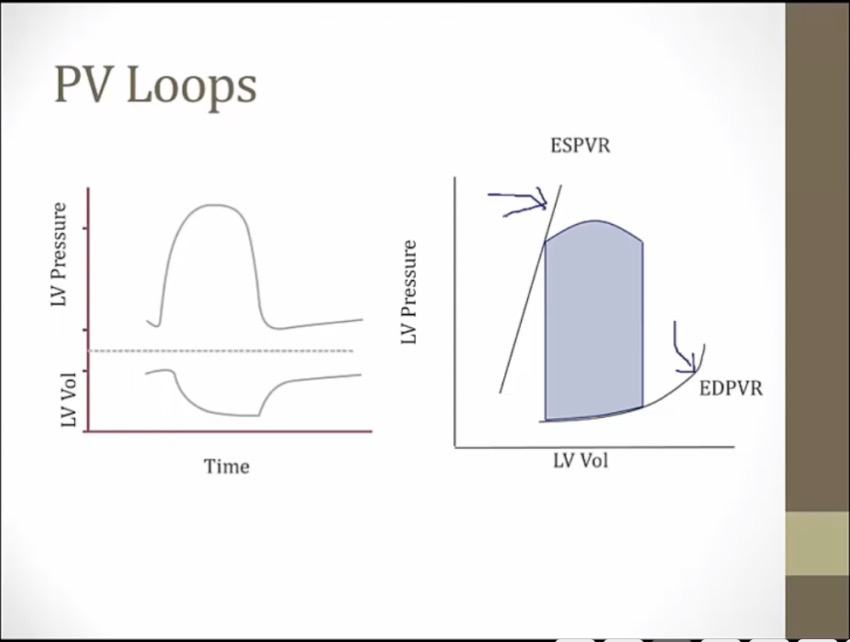
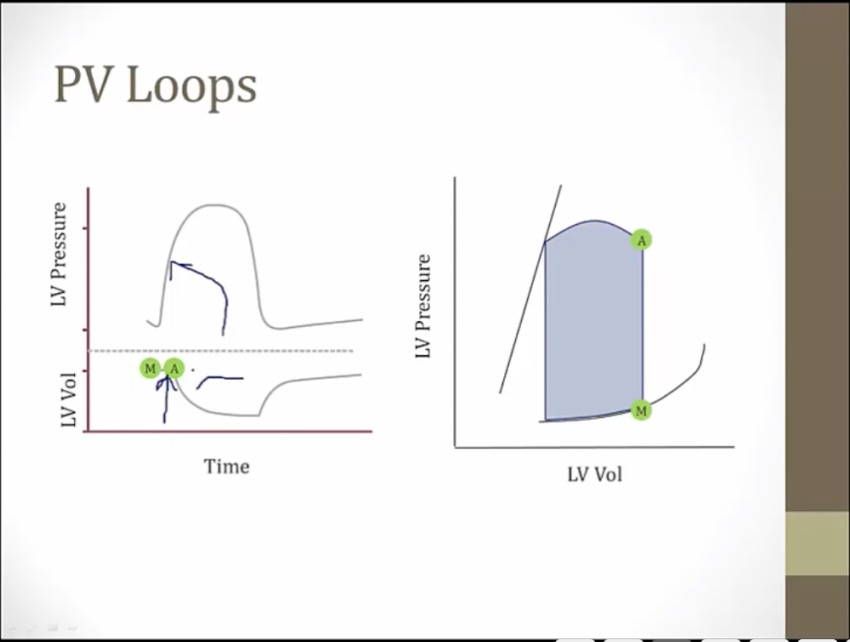
top left point: end of systole
bottom right point: end of diastole
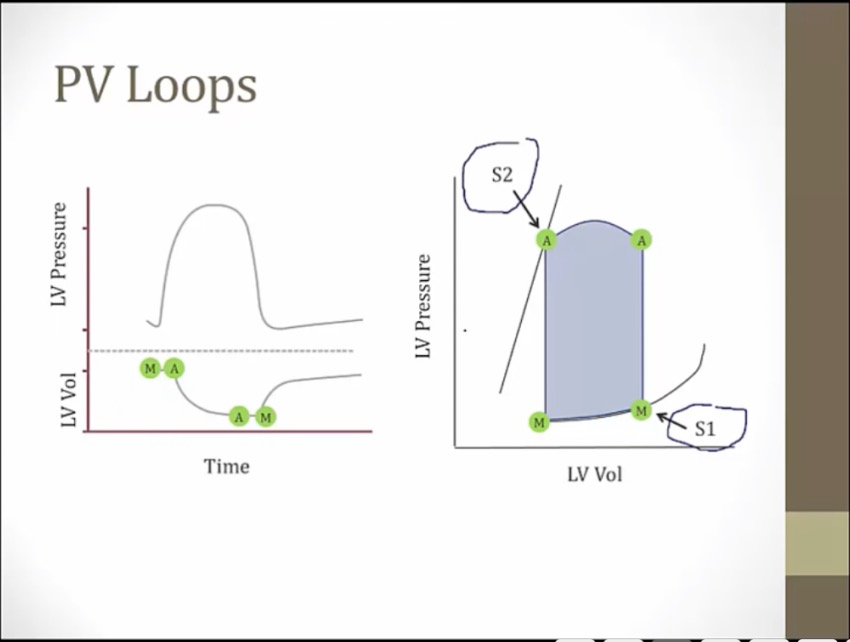
left line: end systolic pressure volume relationship, determined by myocardium characteristics. Adding/removing blood at end of systole moves along this line
right line: end diastolic pv relationship
MV closes at beginning of isovolumic contraction
pressure so high aortic valve opens
volume falls in LV, blood leaving
AV open, contraction
AV closes, isovolumic relaxation
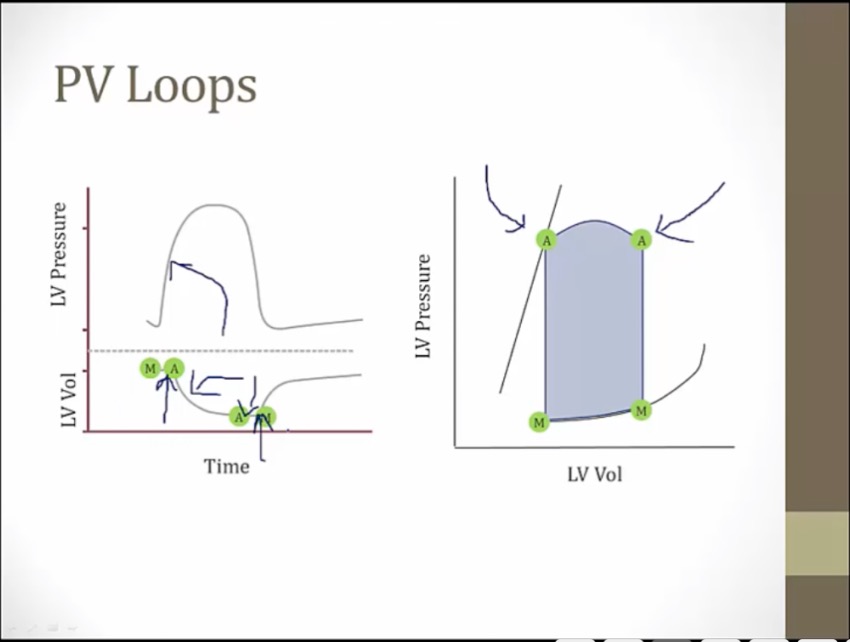
MV opens
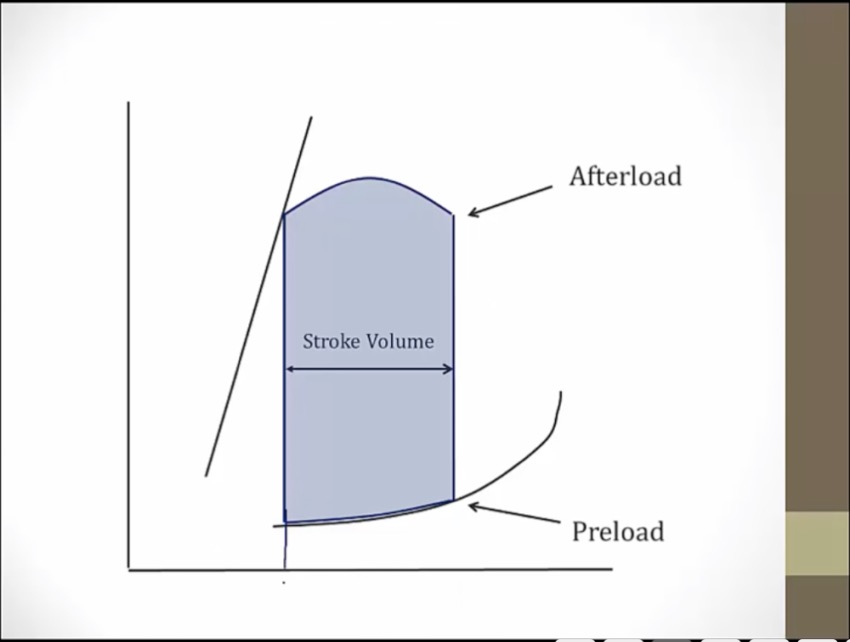
SV: difference between ESV and EDV, volume ejected
more afterload, higher pressure LV has to rise to overcome
Changes
_..
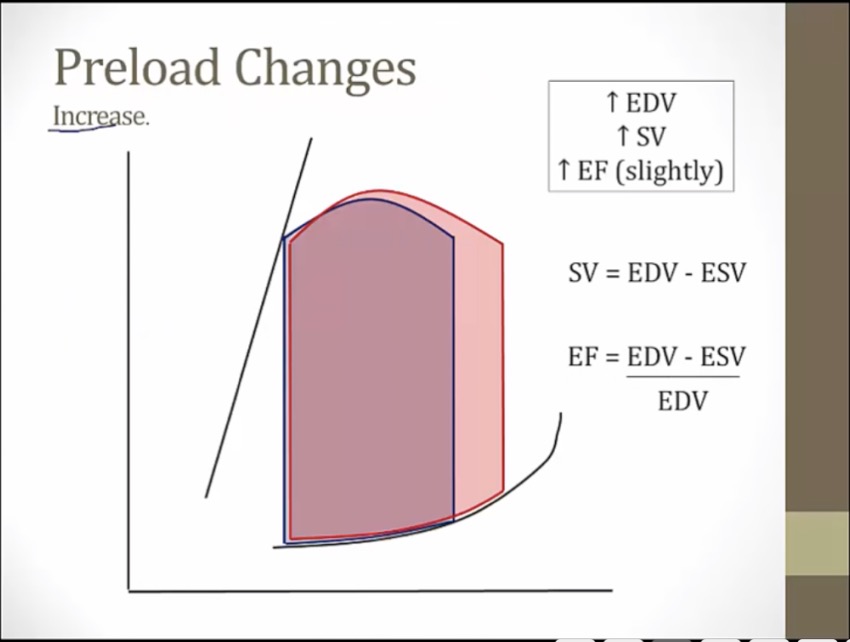
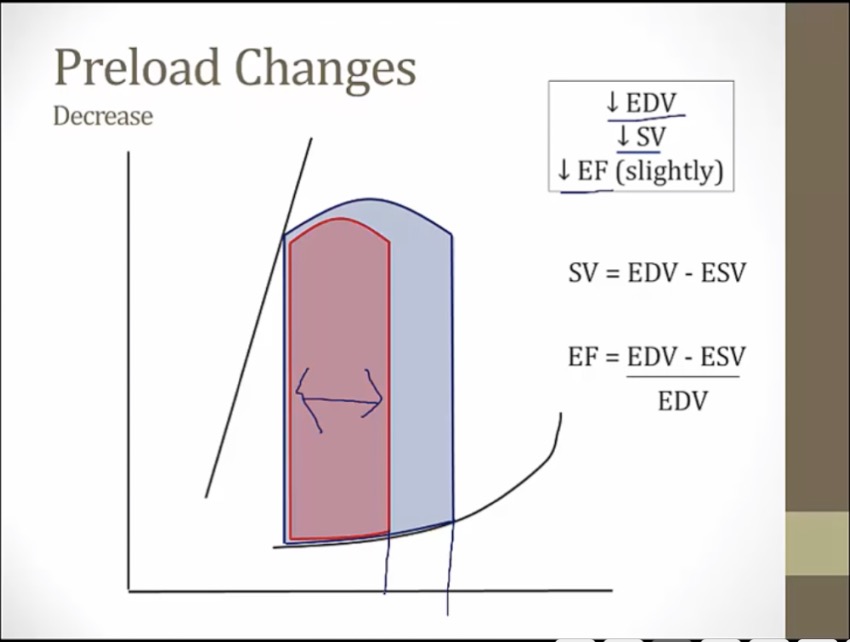
_..
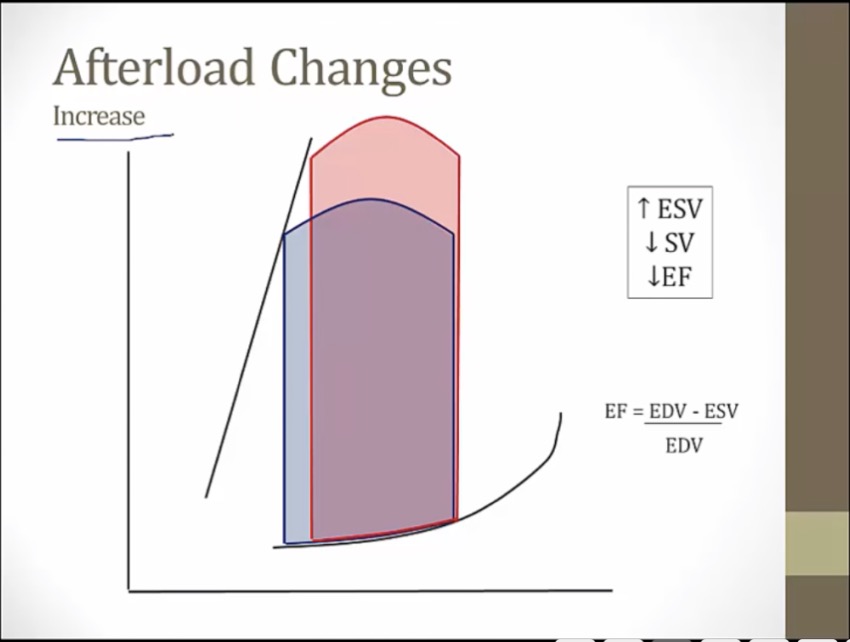
hit left line sooner, at higher volume and pressure
harder to eject blood, eject less blood
_..
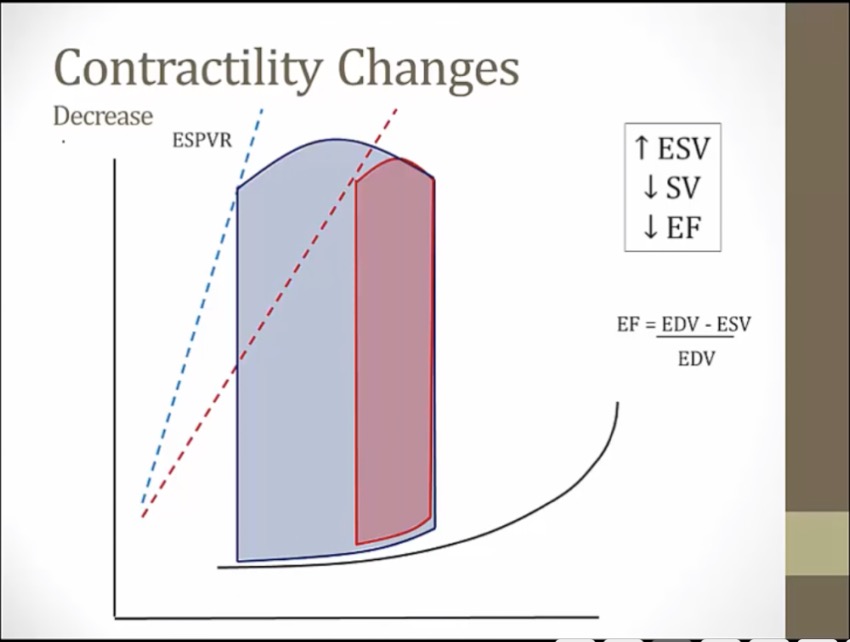
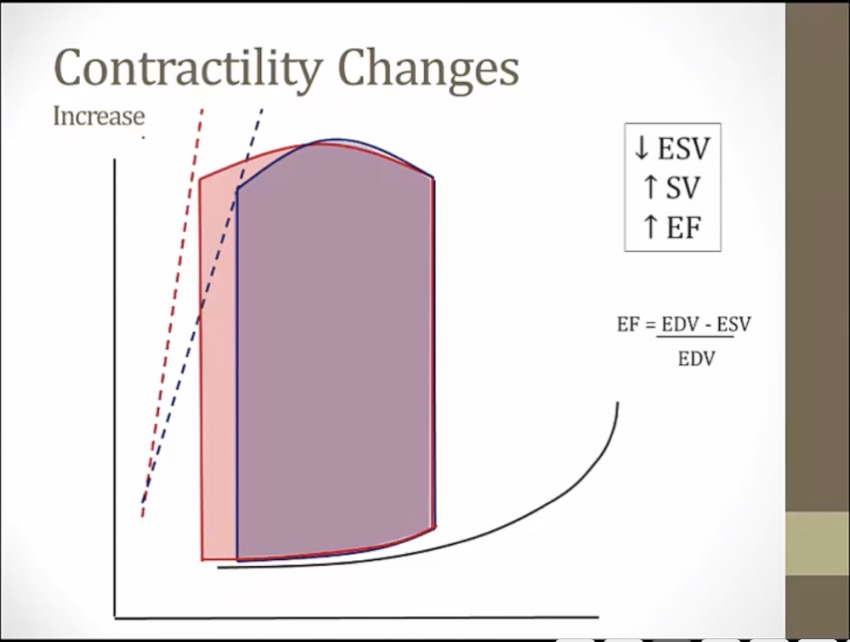
contractility determines ESPVR
less contractility, less blood pushed out, more blood left behind
_..
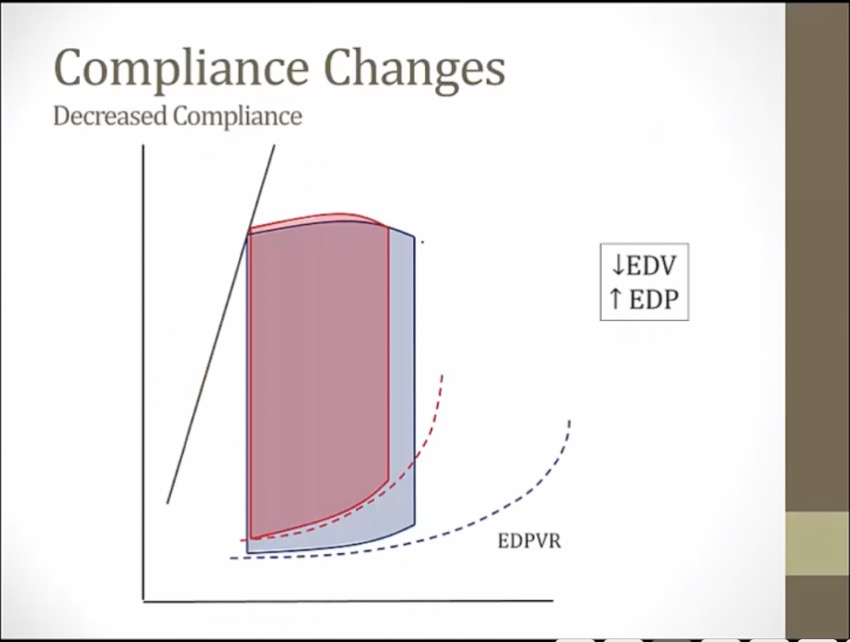
compliance determines preload
ventricle cannot fill and stiffer, higher pressure, lower volume
_..
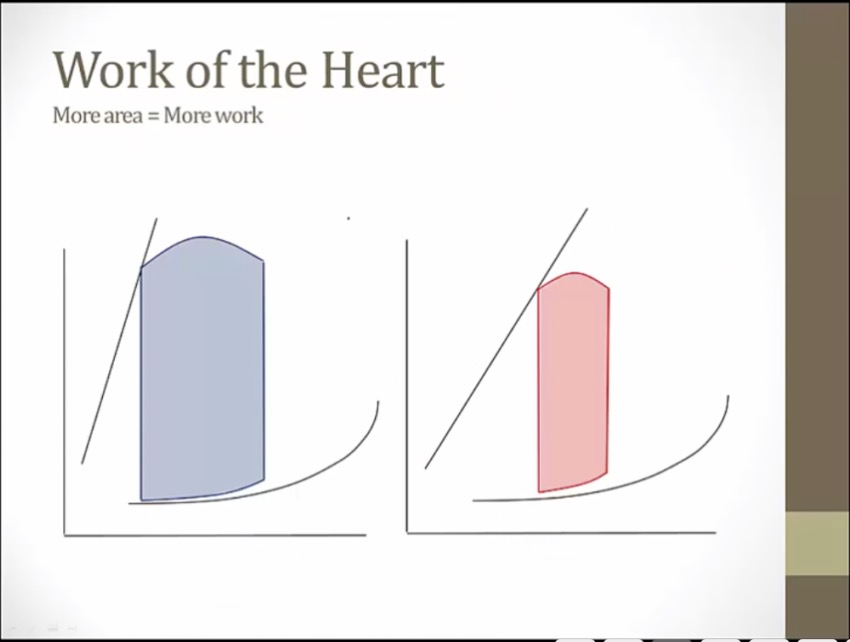
area: how much volume pumping x how much pressure generating
Pathology
_..
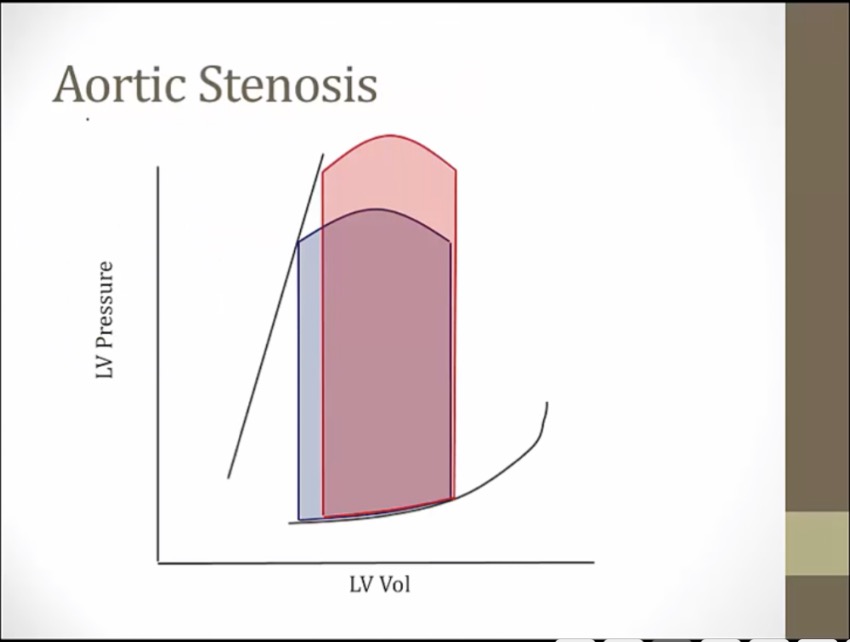
higher afterload, lower SV, higher ESV
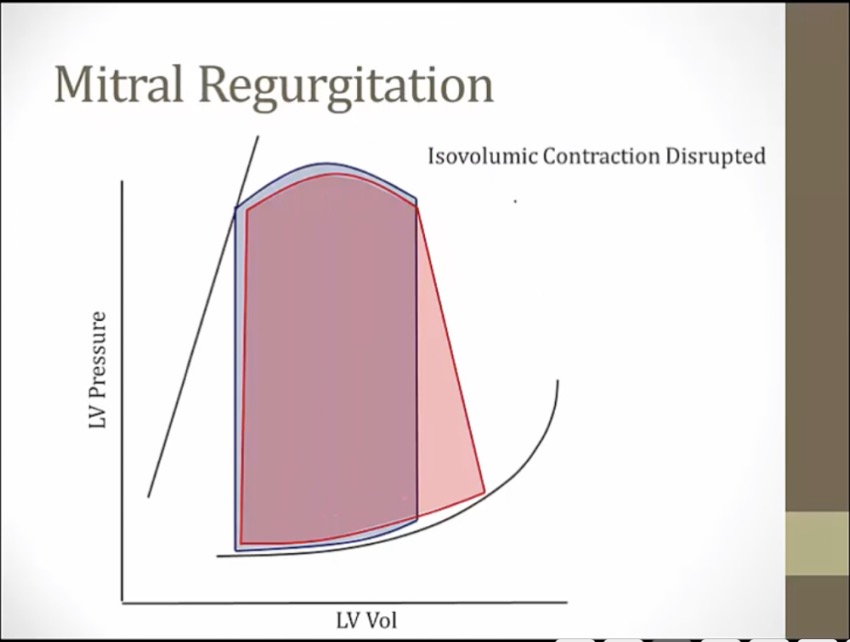
during isovolumic contraction, blood leak from LV to LA, falling
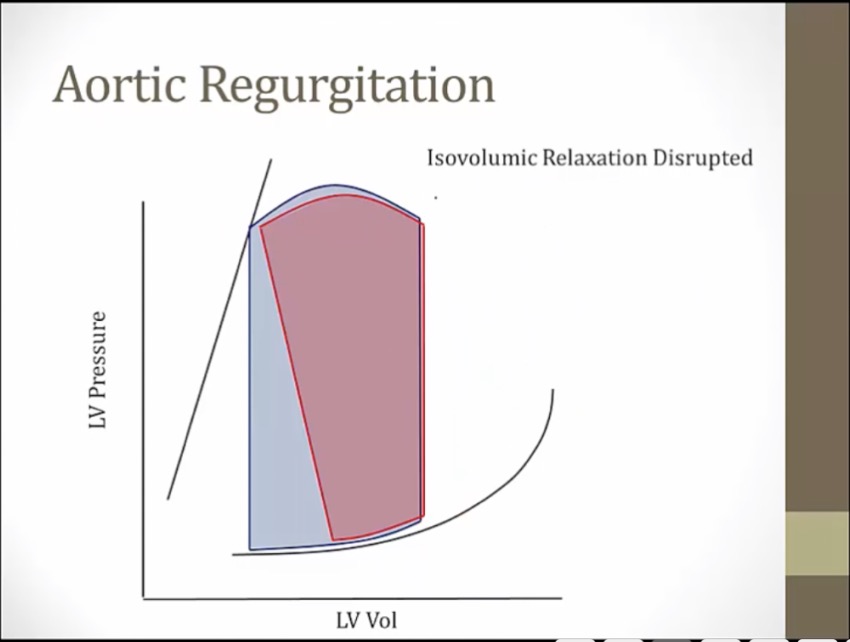
blood filling ventricle during relaxation
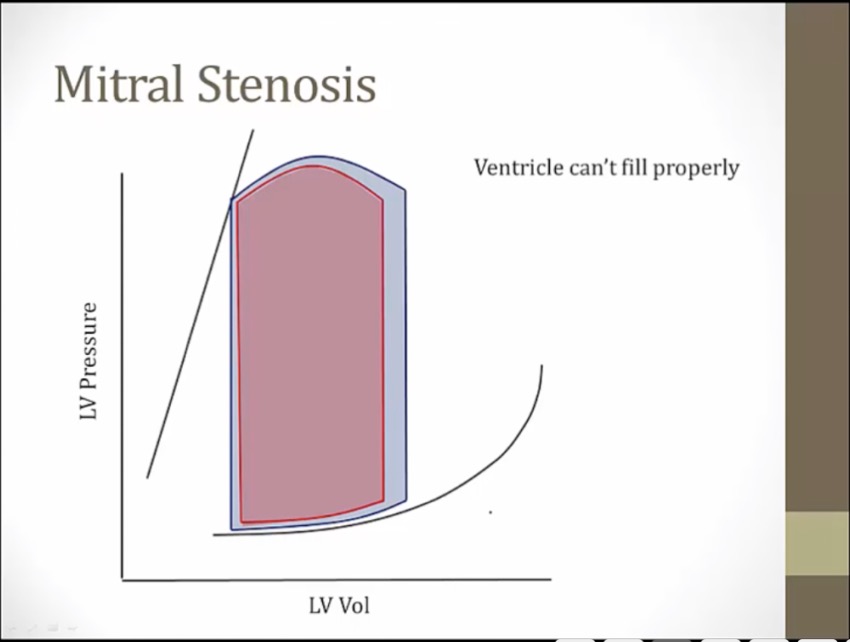
just slightly smaller
Last updated