43 Movement Disorders
Hyperkinetic Disorders
Huntingtons

know lateral ventricle large




Loss of caudate, loss of GABA, no inhibition = breakthrough of movement. Indirect pathway

each generation passes on more repeats to later generation = worse symptoms
anticipation: earlier symptoms with each gen
excitotoxicity mechanism
NMDA binding to glutamate toxicity

usually adopted because most people know about it before have kids
chorea: dance like abnormal movements
Treatment

Hemiballism
No subthalamic nucleus. No inhibitory of thalamus = movement breakthrough
once stroke affects IC = hemiplegia

only half of body


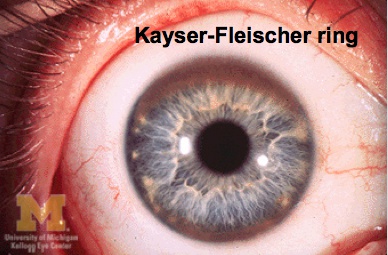
Wilson's

deposit in liver (cirrhosis)
elbows beat like wings of bird
Mood disorders at very young age
dysarthria: difficult to get words out, slow irregular speech
Tardive dyskinesia
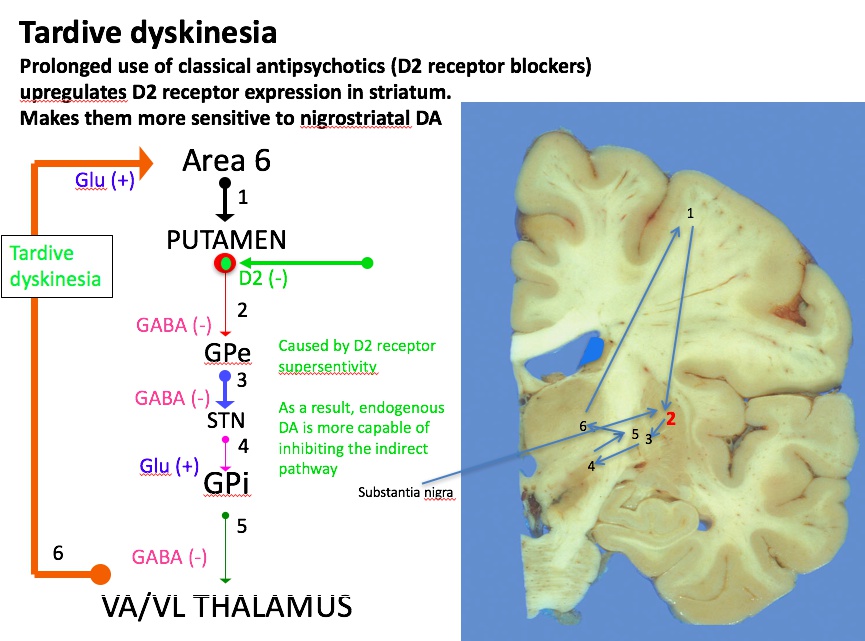

face secondary to medications
antipsychotic/antiemetic blocks D2, increase D2 sensitivity, hyperkinesia via D2 endogenous
hypersensitivity of D2 receptors
L- DOPA Dyskinesia

D2 preferentially bound = blocked inhibitory pathway = dyskinesia
Hypokinetic Disorders
Parkinson

Dopamine naturally broken down by MAO
MAO sits on outer membrane of mitochondria
result: Parkinson

pt cannot initiate movement


Loss of D1, no disinhibition, less movement


no movement in stopping/ending
initiation is difficult; once initiated, cannot be stopped = festination


Loss of D1, no disinhibition, less movement


parts of brain becomes pale because lose melanin containing dopaminergic neuron



now used to induce parkinson's in lab rats

shuffling: shuffles feet
cogwheel: moving arms stutters as if stopping on stops of cogwheel
Tremor
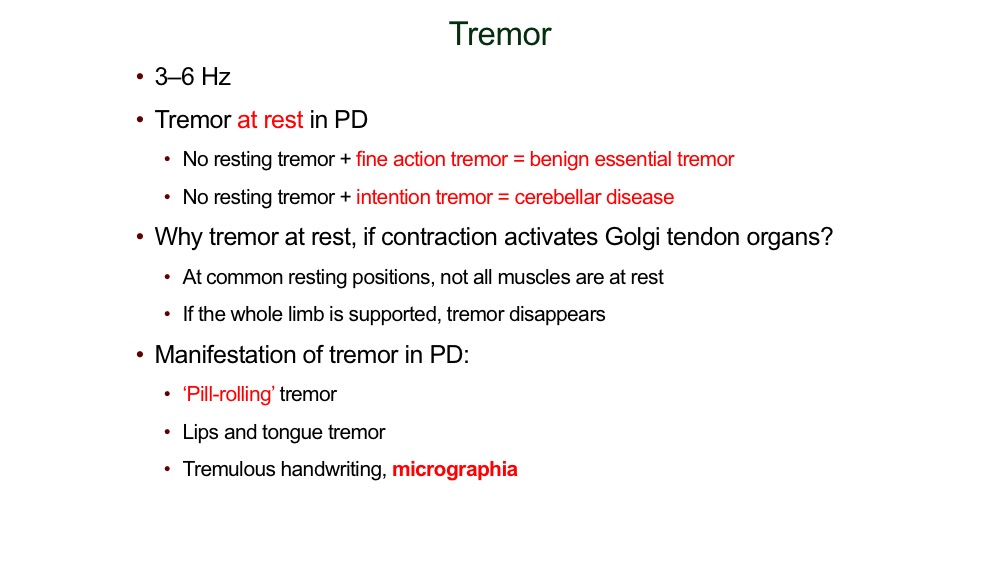
Rigidity

simultaneous activation of flexors/extensors
Treatment

propanolol for central tremor


initially usually tremor symptoms
once develops bradykinesia/rigidity, add more drugs
L dopa last

L- Dopa


vit B6 promotes conversion of L-dopa to dopamine in periphery

off so severe akinesia: no movement, frozen
dyskinesia: involuntary
Entacapone

Seleginine


SSRI raises serotonin; selegiline blocks breakdown = very high serotonin
Other Movement Disorders

myoclonus: sudden contraction once
dystonia: sustained contraction
writer's cramp: after writing for so long, arms spasm
blepharospasm: twitching of eye muscles (blinking)



Last updated