10 Obstructive
_..

_..


Chronic Bronchitis
_..

completely arbitrary clinical definition
_..

a lot of mucous and glands
normally: mucous layer 0.4 of total bronchiole wall. > 0.5 = severe bronchitis

cough from inflammation
wheezing from obstruction
crackles from mucous

left filled with mucous
left become hypoxemic
100% O2 will not help

Emphysema
_..

think smoke rising up to upper lobe

acinus: "berry"
smoker: branch portion, centriacinar or centrilobular
deficiency: everything


bronchus collapse during exhalation
_..

big white space, thin septa (tissue dividing space)
left lower: black spots, evidence of centrilobular damage
_..

hyperventilation: to get remaining functioning alveoli to do more work
hyperventilating = more work = weight loss
_..

emphysema: blue line shift to left, less elastic recoil
FRC shift up, higher volume at end of quiet breath, barrel chest
_..

AAT
_..

balance elastase

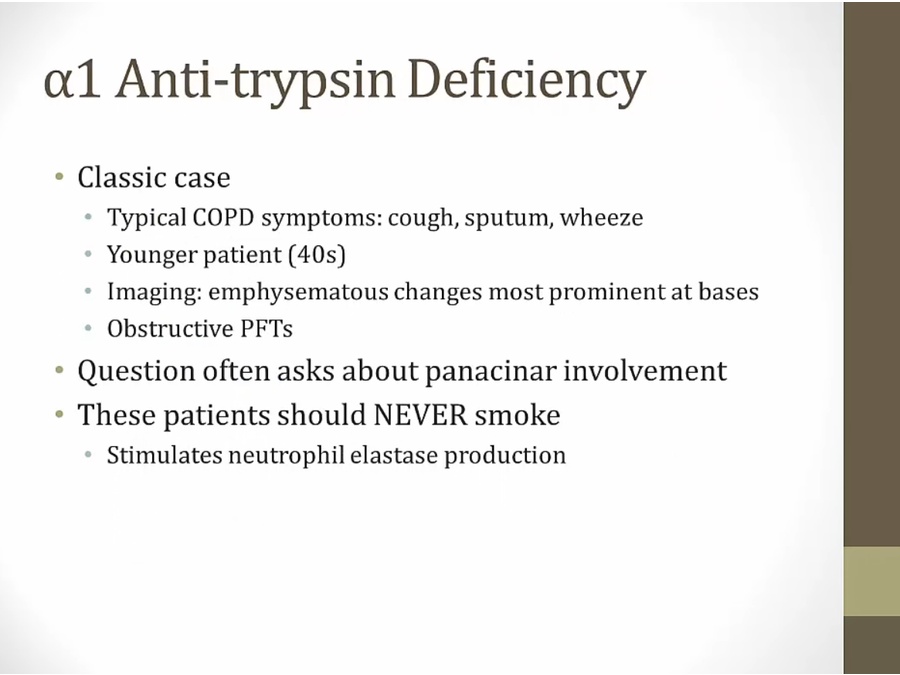
smoking: 60s-70s
COPD
_..

usually just include chronic bronchitis and emphysema; asthma has its own treatment
Asthma
_..

reversible: go back after acute episode
overreact to stimulus and bronchorestrict

_..

cold

triggered by taking aspirin
triad: asthma, rhinosinusitis, nasal polyposis
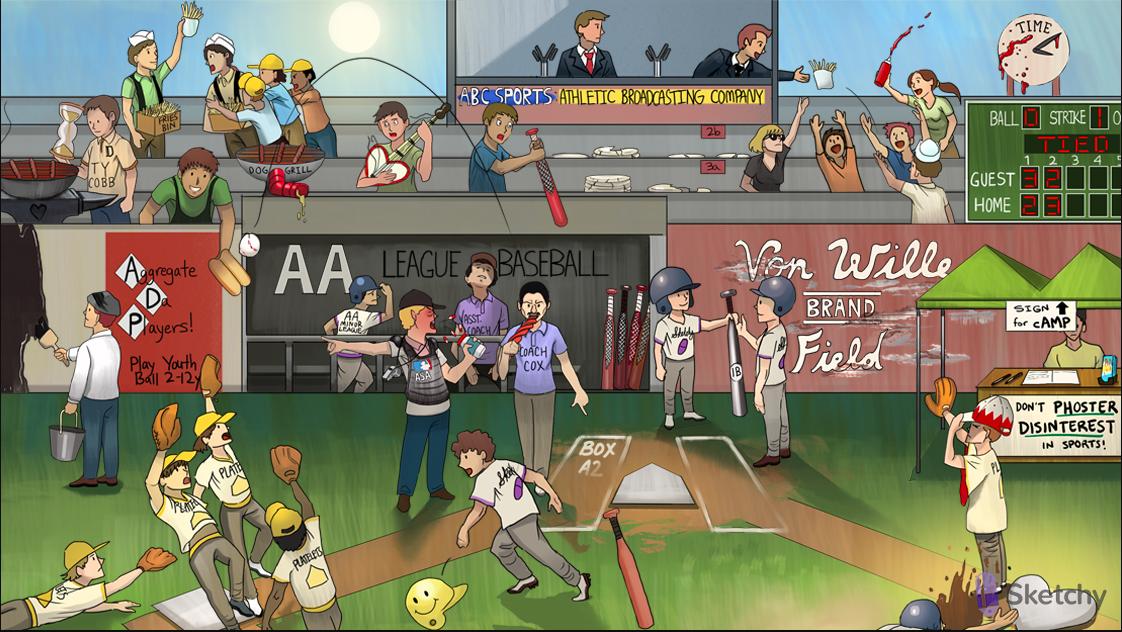

Swollen ASA umpire: aspirin “pseudo-allergy” due to excess leukotriene synthesis (use clopidogrel instead)

ASA umpire grabbing Coach Cox: inhibition of COX shifts the AA metabolism to the LOX leukotriene pathway (exaggerated in aspirin-induced asthma)
_..

normal I/E: 1 to 2
asthma: expiratory phase prolonged, longer for air to get out. 1/4 or 1/5
reduced peak flow (image). Highest velocity of air flow
status asthmaticus: severe, hypoxia
_..


in mucous plugs in sputum: epithelial cells that shed and form whirls
eosinophils and eosinophil membrane proteins making crystals

drop in systolic blood pressure with inspiration, usually by pericardial effusion and tamponade
Bronchiectasis
_..

chronic inflammation causing permanently dilated airways
obstruction: small airways thickened
_..

_..

infection both cause and consequence
rare cause of amyloidosis: anything causes chronic inflammation can lead to secondary amyloidosis
_..

tumor: can't clear mucous, backs up
smoking: either direct or by infection
CF: recurrent infection

Ciliary Dyskinesia
_..


either dynein absent or abnormal
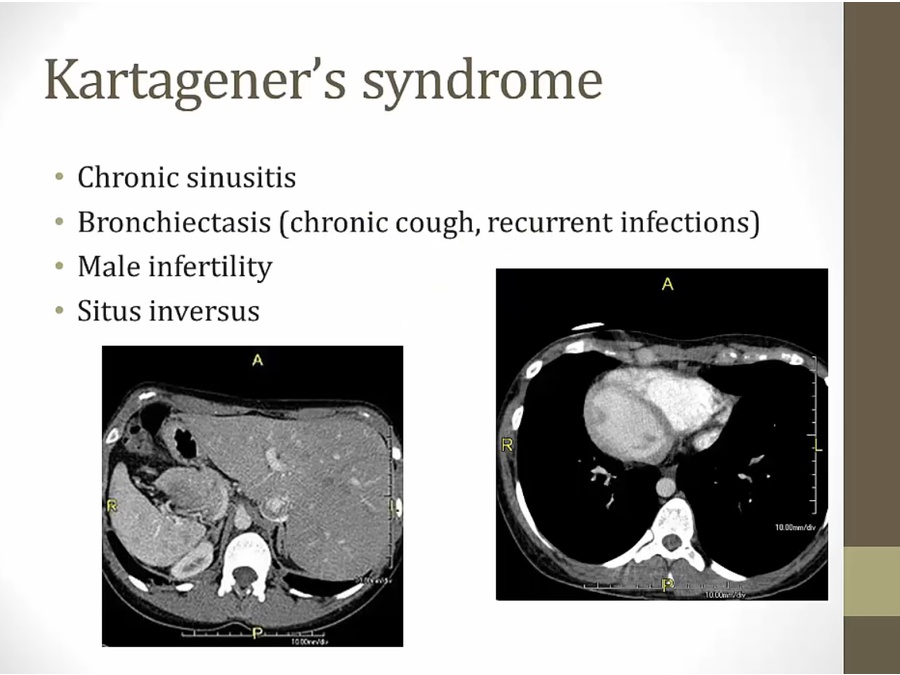
chronic sinusitis: poor ciliary function
infertility: abnormal sperm ciliary

ABPA
_..
only immunocompromised (asthma, CF)
eosinophilia: important

important: symptoms + blood IgE and eosinophils
steroids: treat inflammation/allergic reaction
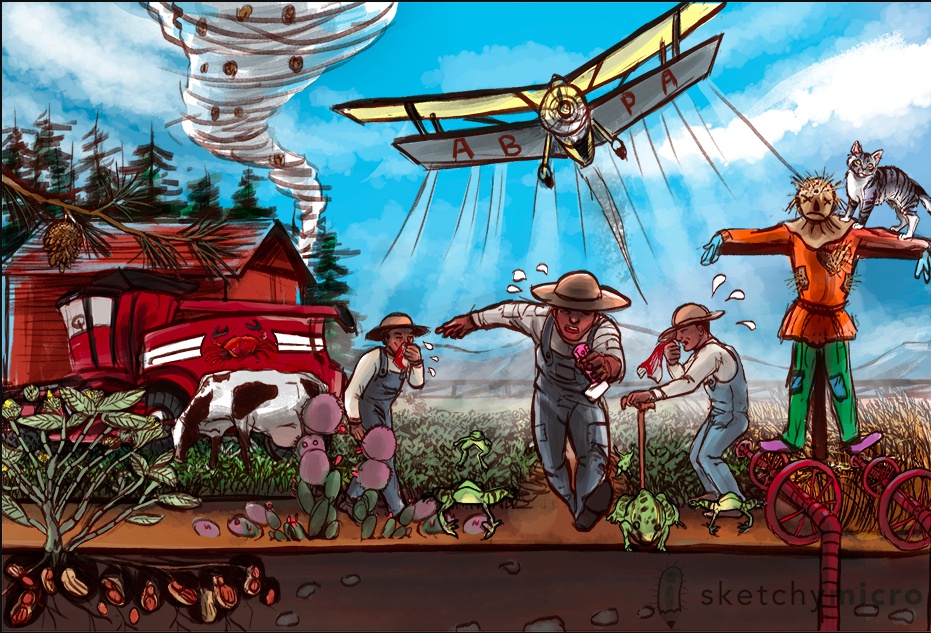

plane with letters. Farmer running/migrating, sweating, inhaler in hand: ABPA (allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis) is a type I HSR that causes wheezing, fever and migratory pulmonary infiltrates. Also association with CF patients
IgE on inhaler: ABPA is associated with asthma and may show increased IgE levels in the serum

Last updated