16 Cardiac AP
Myocyte AP
_..

at rest, pumps maintain ion distribution

connected via gap junction
if 1 depolarizes with positive ions inside, some positive go to 2, 2 depolarizes

phase 4: myocyte at rest, -85
phase 0: voltage begins to rise from positive ions entering via gap junction, Na channels open, further rise positive charges, positive loop
phase 1: voltage become positive, Na channels close, K open and leak out, lower voltage
phase 2: competing Ca in and K out, cancelling one another = plateau
phase 3: Ca close, only K

-85 maintained by inward rectifier channels: K out


Soloist: class I antiarrhythmics
Soloist holding peanut butter jar: class I antiarrhythmics block sodium channels (phase 0)
Soloist tipping mic stand: class I antiarrhythmics decrease the slope of the phase 0 upstroke (slows conduction of the cardiac AP)


Ca ion trigger mechanical contraction of myocyte
excitation-contraction coupling: Ca connects electrical activity and mechanical activity of myocytes
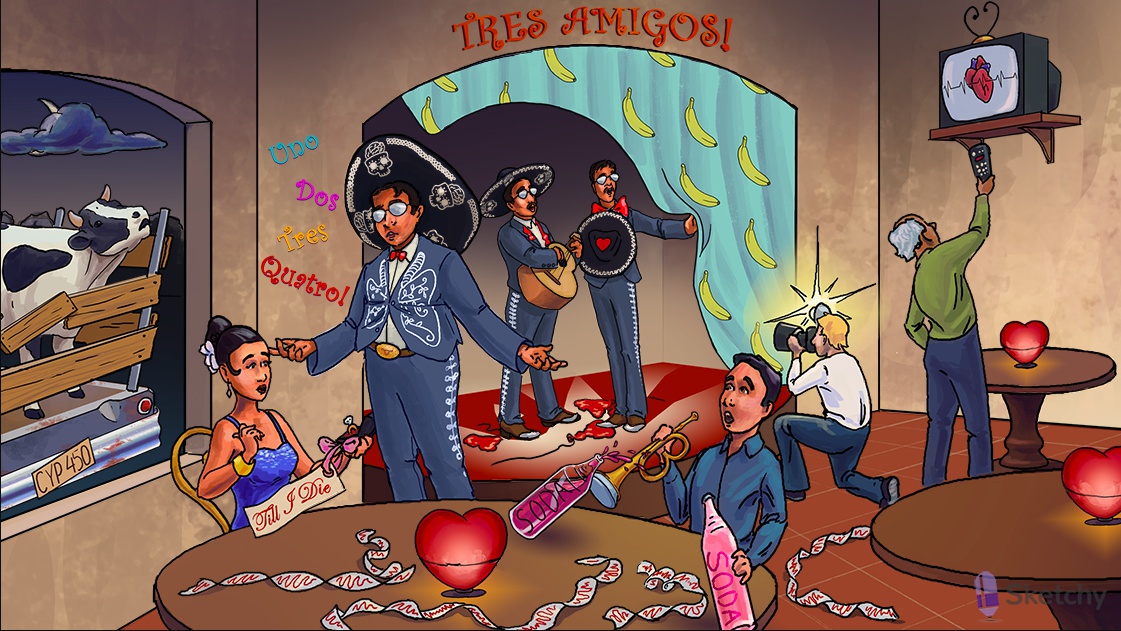


Pushing away the curtain: class III antiarrhythmics block K+ channels prolonging phase 2 and 3 of the cardiac action potential -> prolonged refractory period
_..

No Ca involvement
each cell individually depolarized by neuron
_..

Pacemaker AP
_..

slightly higher resting voltage > -85
no plateau
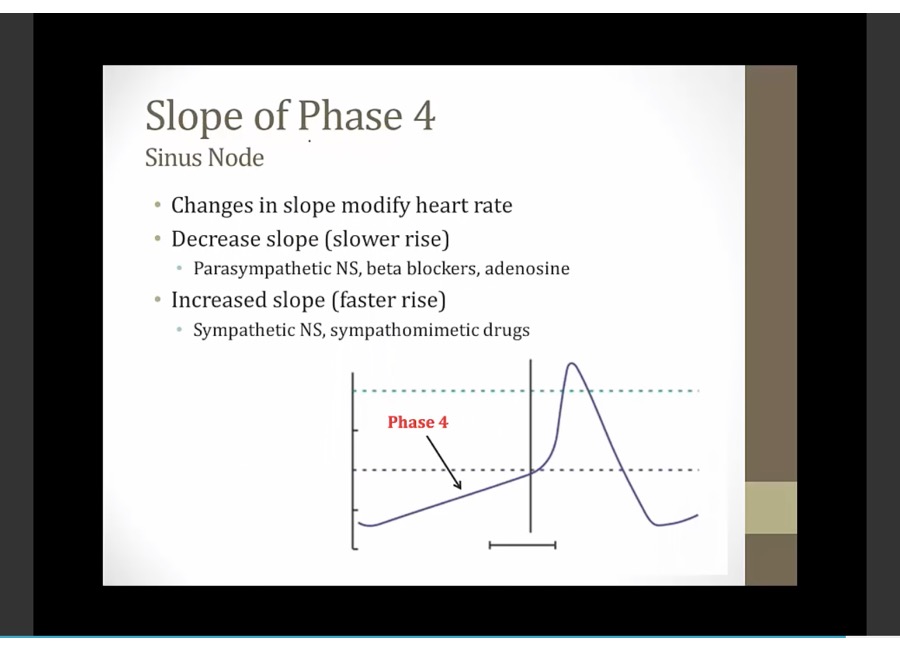
phase 4: slowly drifts upward, funny current allow Na in
phase 0: - 40 threshold, Ca open, inward Ca
phase 3: above 0, Ca close, K open

AV node, same shape, phase 4 slower, longer to reach threshold, usually depolarized by SA signal before threshold


fast Na need -85 to function: fewer inward rectifier K (-85 resting membrane) > resting always above -60 > fast Na does not work
_..

slow AV: delay conduction from atrium to ventricle

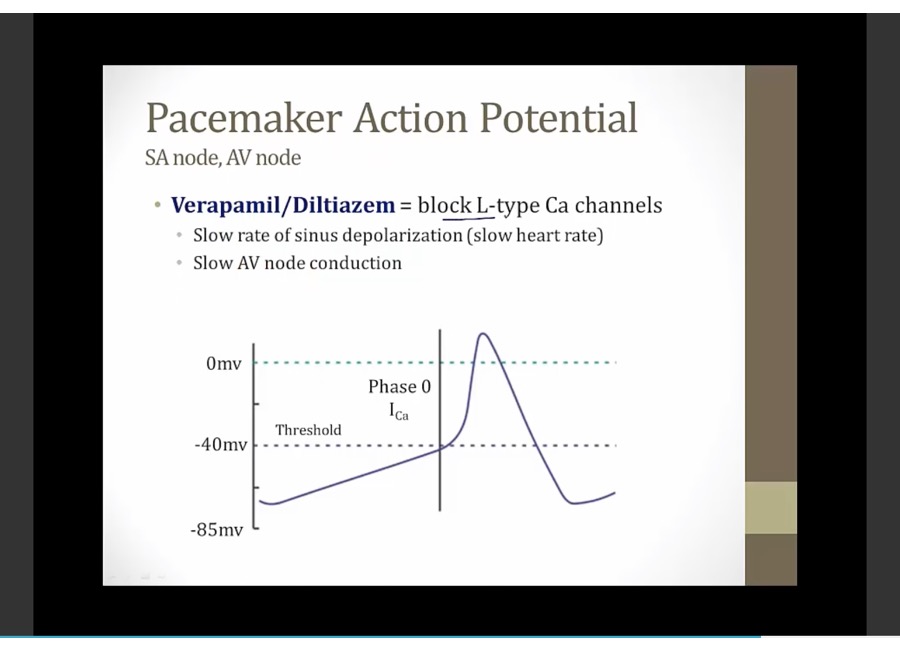
slow phase 0
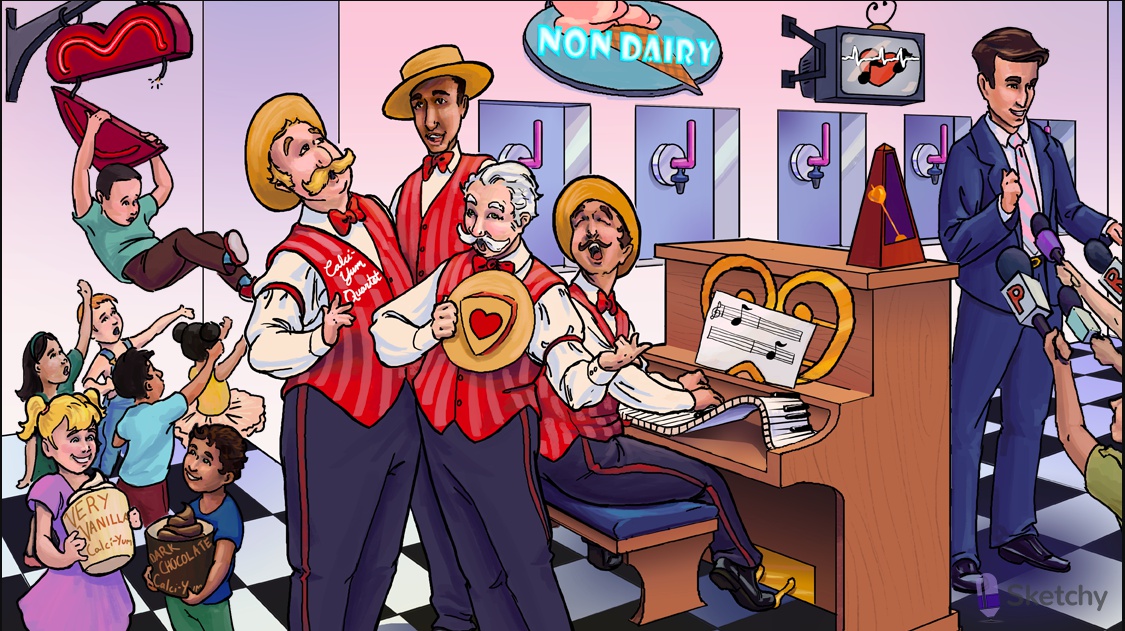

block activated and inactivated Ca channels, not resting channels. Work more on tissues fire more frequently and exclusively activated by Ca current
Notes: non-dihydropyridines (e.g. diltiazem, verapamil) treat arrhythmias by blocking Ca2+ current in the SA and AV nodes
Disconnected bottom: non-dihydropyridine CCBs decrease atrioventricular conduction
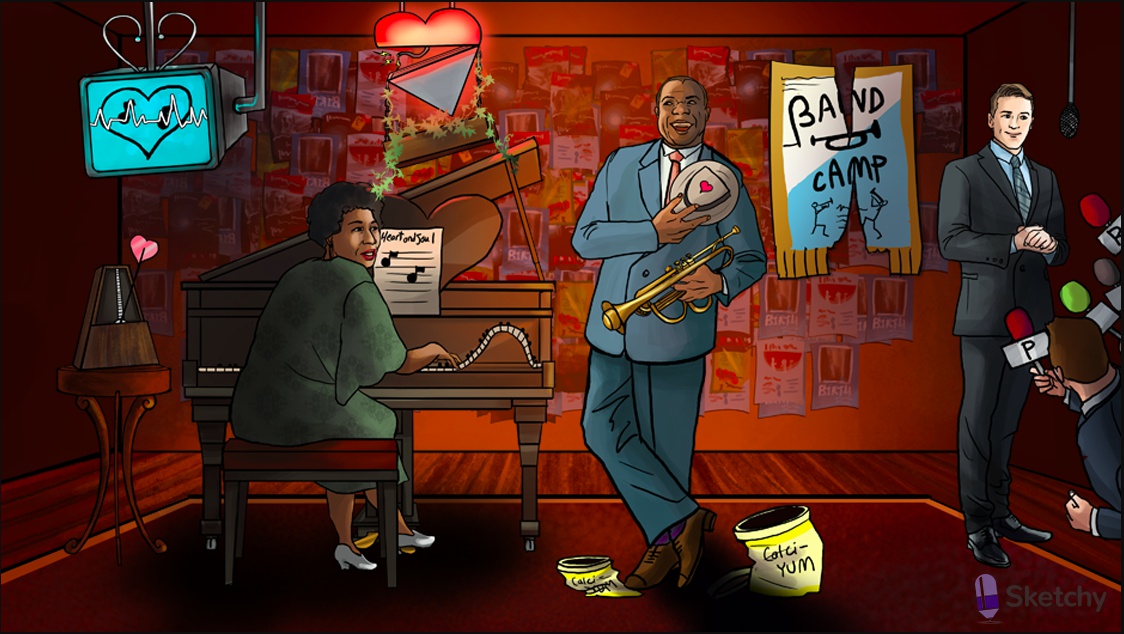



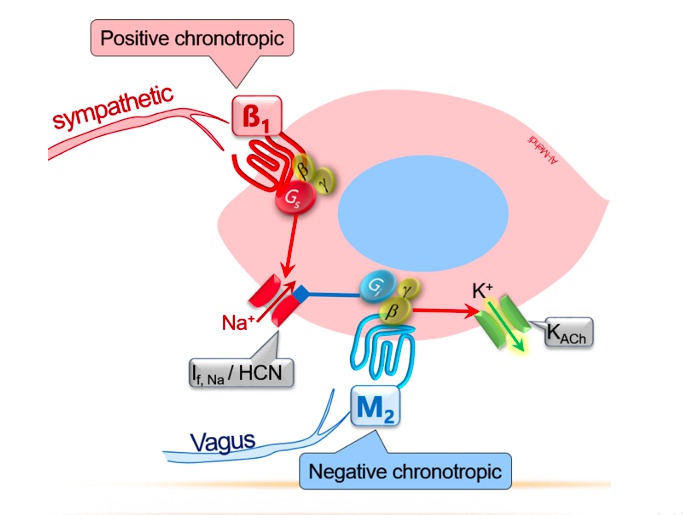
Duet: Class 2 antiarrhythmics
Muted beta bugle: beta blockers (class 2 antiarrhythmics)
notes: beta blockers treat arrhythmias by blocking sympathetic input to the SA and AV nodes
Torn band camp: beta blockers decrease cAMP
Crushed calci-YUM ice cream cartons: decreased cAMP leads to closure of membrane calcium channels
Sliding up the keys: beta blockers prolong phase 4 of the nodal action potential -> decreased pacemaker activity, prolonged conduction time and refractory period.
_..
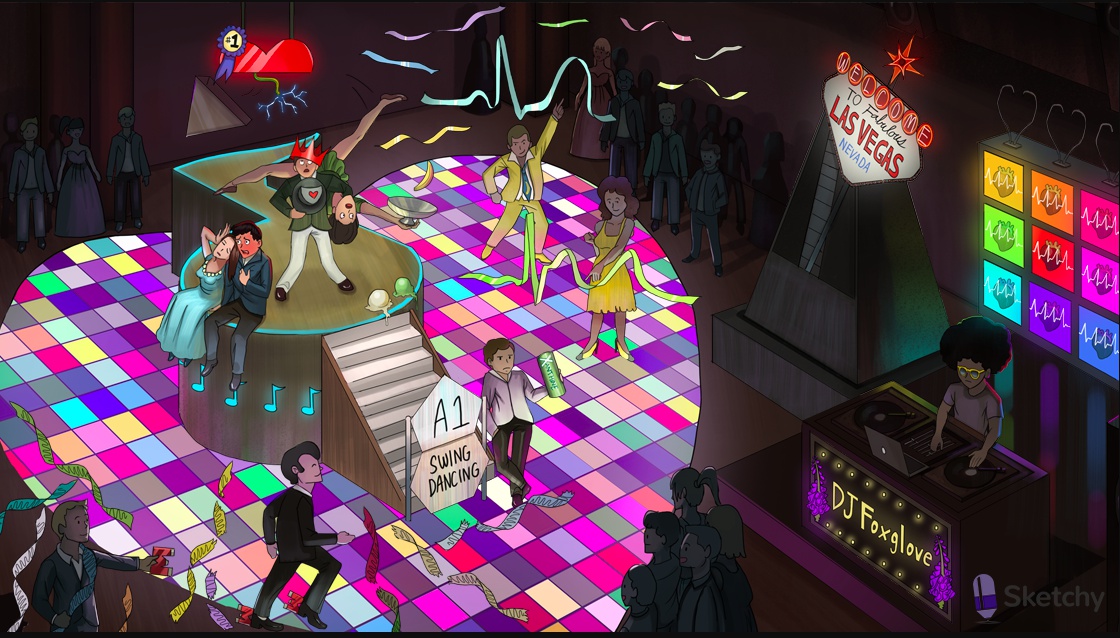

Swing dancing: adenosine (a purine nucleoside with antiarrhythmic properties)
Purine shaped gate: adenosine is a purine nucleotide
A1 Swing: adenosine activates inhibitory A1 receptors on the myocardium and at the SA and AV nodes
Falling calci-yum ice cream: activation of A1 receptors suppresses inward Ca2+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP
Banana flying out of cup: activation of A1 receptors increases outward K+ current (hyperpolarization, suppressed Ca2+ dependent AP)

Last updated