Treponema Pallidu
_Microaerophilic spirochete that causes syphilis.
microaerophilic: need oxygen but not too much
Spiral galaxy, dark microscope  "Corkscrew shaped"
"Corkscrew shaped" 
_Mainly found in tropical areas and causes yaws, which manifest as destructive lesions of skin and bones.
_Transmission occurs via contact (sexual or casual) with skin lesions containing the spirochete, penetrating mucous membranes and causing systemic spread, or transplacentally.
Primary syphilis
_Occurs after an average incubation period of two to three weeks.
_characterized by a painless ulcerating papule known as a chancre on genitalia or mouth (Foster)
syphilis: painless, non-exudative, clean, hard base with indurated margins ("punched out base with rolled edges").
granuloma inguinale: painless ulcer with a beefy red base and irregular borders
chancroid: as a deep, undermined, painful purulent ulcer with soft ragged edges.

Primary syphillis, painless genital chancre:

Secondary syphilis
_Occurs from a few weeks to months after primary syphilis.
_Presents with a non-specific systemic illness, commonly referred to as the “great imitator.”
Can produce a wide variety of symptoms that include:
Maculopapular rash described as discrete copper, red or reddish-brown on the trunks and extremities, notably on the palms and soles.
Condyloma lata, which are raised, infectious, gray to white wart-like lesions found in moist areas and mucous membranes such as the mouth and perineum.
Systemic symptoms such as fever, headache, malaise, and myalgias (polyarthritis, compared to monoarthritis in reactive arthritis).
Lymphadenopathy
Hepatitis
Palmar rash, nonitching:  condyloma lata:
condyloma lata: 
 maculopapular rash:
maculopapular rash:  solar systems: systemic
condyloma latum on mucous membrane
maculopapular rash on palms and soles
spirochetes seen on darkfield microscopy
solar systems: systemic
condyloma latum on mucous membrane
maculopapular rash on palms and soles
spirochetes seen on darkfield microscopy 
_Contrast the wet, raised, gray to white lesions of condyloma lata (secondary syphilis) with condyloma accuminata (HPV infection), which is characterized by raised, cauliflower-like, bulky, dry lesions around genitalia.
Tertiary syphilis
_Occurs years after untreated syphilis infection and can be divided into:
Gummatous syphilis
Cardiovascular syphilis
CNS syphilis
Moon: Gummas, soft growths with necrotic center
Tree: CV
Damage to posterior columns of spinal cord 
Gummatous
_ is characterized by a gumma that can occur in the skin, bones, and internal organs. On the skin, gummas present as ulcers or granulomatous lesions with a round, irregular shape. Visceral gummas may present as a mass lesion. Gummas are usually absent of any causative organisms.  Gumma:
Gumma: 
CV
_Classically affects the ascending thoracic aorta, manifesting as a dilated aorta and aortic valve regurgitation. The pathogenesis stems from a proliferative endarteritis that affects the vasa vasorum of the aorta, leading to medial necrosis and loss of elastic fibers.
Tree branches. Destroys vasa vasorum. Tree barking appearance 
CNS
_ can be asymptomatic early on or may present with meningitis. Late neurosyphilis can include general paresis and/or more typically dorsal column demyelination, a condition referred to as tabes dorsalis. The constellation of findings in tabes dorsalis includes:
Broad-based ataxia Foster: (Tabes Dorsalis) wide gait ataxia
Argyll Robertson pupil, sometimes referred to as a prostitute’s pupil, where the eye accommodates to near objects but does not react to light.
Positive Romberg sign, where swaying is noted when the person stands with eyes closed.
Charcot joints, a neuropathic arthropathy noted by the bony destruction and deformity of joints in this case due to decreased proprioception.
Stroke without hypertension
Charcot joint + top: can no longer feel pain  Damage to posterior columns of spinal cord pupil. Very accomodating but not reacting to light
Damage to posterior columns of spinal cord pupil. Very accomodating but not reacting to light 
_Tertiary syphillis was once strongly linked to paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
_IgG cold antibody with bithermal activity (Donath-Landsteiner antibody). The antibody is directed against the P blood group antigen on RBCs. At cold temperatures, the antibody binds to RBCs and fixes complement. At warmer temperatures, the antibody detaches from RBCs and activates complement, causing intravascular hemolysis.
Congenital syphilis
_Occurs when T. pallidum is transmitted transplacentally from a pregnant woman to her fetus. Foster: Test pregnant mothers for syphilis
_Maternal syphilis infections often result in stillbirth. If the neonate survives, clinical manifestations of early congenital syphilis include:
Hepatomegaly, with or without splenomegaly, and can also cause jaundice and cholestasis.
Rhinitis, also known as the “snuffles”, usually presents during the first week of life, and discharge contains spirochetes that can be transmitted by contact.
Maculopapular lesions on the palms and soles.
Generalized lymphadenopathy
Hematologic abnormalities such as anemia and thrombocytopenia
_Late congenital syphilis occurs from scarring or persistent inflammation from early infection and is characterized by gumma formation in various tissues. These can include:
Facial features such as frontal bossing and saddle nose.
Interstitial keratitis
Sensorineural hearing loss
Oropharynx abnormalities such as hutchinson teeth and mulberry molars.
Cutaneous manifestations such as rhagades and gummas.
Intellectual disability
Saber shins: Anterior bowing of tibia
Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria
saddle nose/saber shins: constellation congenital deafness: ear muffs hutchinson teeth: kids teeth  Mulberry molars:
Mulberry molars:  Saber shins:
Saber shins:  Hutchinson teeth:
Hutchinson teeth:  Interstitual keratitis:
Interstitual keratitis: 


_Syphilis is part of the TORCH infections, a mnemonic used to remember the infectious agents, which may cross the placenta and cause congenital infection. The mnemonic is ToRCHeS:
Toxoplasmosis
Rubella
CMV
HIV
Herpes virus
Syphilis
_Diagnosis of syphilis is made via direct visualization using darkfield microscopy or direct fluorescent antibody testing, and via serology. Darkfield telescope:  Darkfield microscopy:
Darkfield microscopy: 
_Serologic tests for primary syphilis includes a screening test with a nontreponemal test such as the VDRL (venereal disease research lab).
Serologic tests for secondary syphilis includes a screening test with a nontreponemal test such as the VDRL or RPR (rapid plasma reagin) test. A positive result is then confirmed as a true positive with a treponemal test, such as the FTA-ABS (fluorescent treponemal antibody-absorption) test.
Patients with suspected neurosyphilis should undergo lumbar puncture and subsequent VDRL, FTA-ABS and/or PCR of cerebrospinal fluid.
Nontreponemal tests (eg, Venereal Disease Research Laboratory [VDRL], rapid plasma reagin [RPR]) evaluate for the presence of antibody against cardiolipin (byproduct of treponemal infection). These tests are affected by antitreponemal therapy and can be used to follow disease progression and therapeutic response.
Treponemal tests (eg, fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption [FTA-ABS], microhemagglutination assay for T pallidum[MHA-TP]) detect antibodies to specific treponemal antigens and are not affected by antitreponemal therapy; they remain positive for life.
VDRL/RPR TV screen
FTS antibody confirmatory test 
 fluorescent test:
fluorescent test: 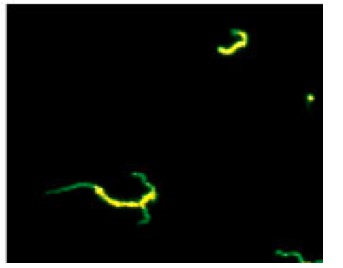
_False positive VDRL may be a result of:
Viruses (mononucleosis and hepatitis)
Drugs (for example hydralazine and procainamide)
Intravenous drug use
Rheumatic fever
Lupus and Leprosy

_The treatment of choice for early syphilis is intramuscular penicillin G benzathine, which releases penicillin G slowly from the muscle. This results in antimicrobial plasma concentrations of penicillin G for 1 month.
Pens everywhere: 
_Administration of antibiotics for syphilis may lead to a response to the release of endotoxin-like factors from the lysis of T. pallidum organisms that manifests as fevers, chills, and myalgias.
Comet: 
Last updated