32 Hypertension
Etiology and Cause
_..

pressure changes throughout day
_..


drink alcohol: resistant htn


HTN screening important because association with number of diseases
Complications
_..

rupture of atherosclerosis leads to MI

glassy appearing
leakage of protein materials out of arterial wall

much less common
malignant: BP rises rapidly and a lot in short amt of time
bp so high, basement membrane replicating
symptoms can occur (usually asymptomatic)

lower density of arterioles

increased afterload, increased work of heart
left: nl voltage. Right: higher
diastolic HF, S4
LV concentric hypertrophy:

lumen same size, wall much thicker
_..

systolic/diastolic rises
pulse pressure also rises
when C compliance falls, delta P, change in pressure goes up
left: compliant vessel, blood flow in and stretch vessel, pressure does not increase that much
right: vessel can't stretch, pressure increase much higher
Urgency
_..


confusion
afterload so high, no blood to heart

microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
_..

rapidly progressive and fatal in 1-2 years
now definition: severe HTN difficult to control
Secondary HTN
_..

secondary HTN either raise CO or raise TPR

cannot excrete Na normally
sympathetic ramped up from repeated episodes of apnea

PGE2 vasodilator




diltiazem drug of choice to treat HTN caused by these 2 drugs



no sign of volume overload

low plasma renin, high aldosterone. Important

catecholamines released in episodes

steroids for RA
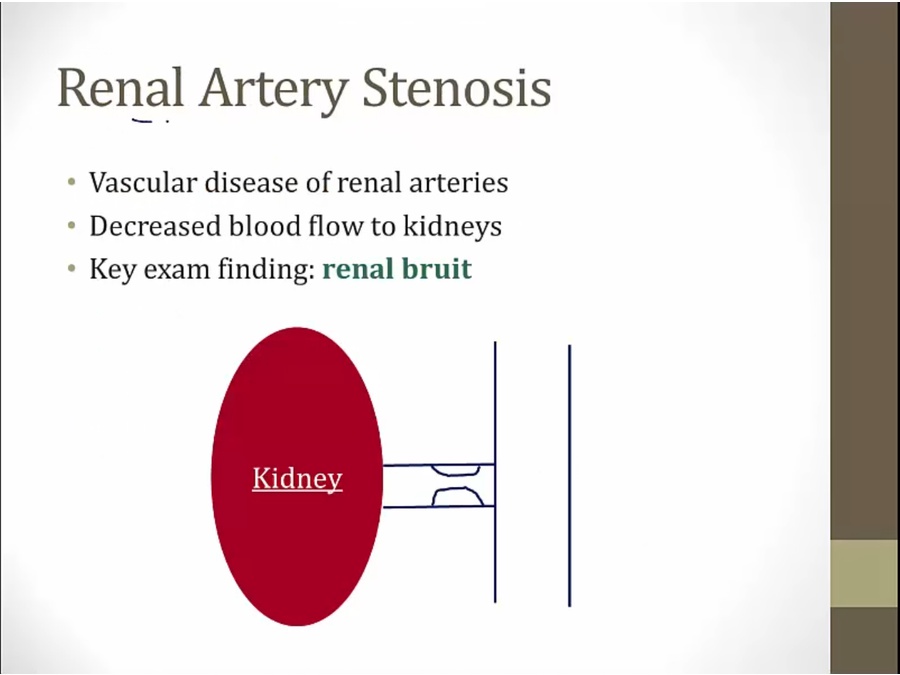
know renal bruit

normal kidney compensates for volume retention

pressure natriuresis: autoregulation. One kidney releasing more renin/Na causing the other to release less
increased RAAS/BP: normal kidney can't compensate

in setting of renal artery stenosis, pts depend on Ang II's efferent vasoconstriction to maintain GFR

association and can develop renal artery stenosis
healthy women in 40s develop HTN resistant to therapy and has bruit over renal artery

upper body HTN

Last updated