10 Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
pyruvate dehydrogenase to acetyl coa to TCA
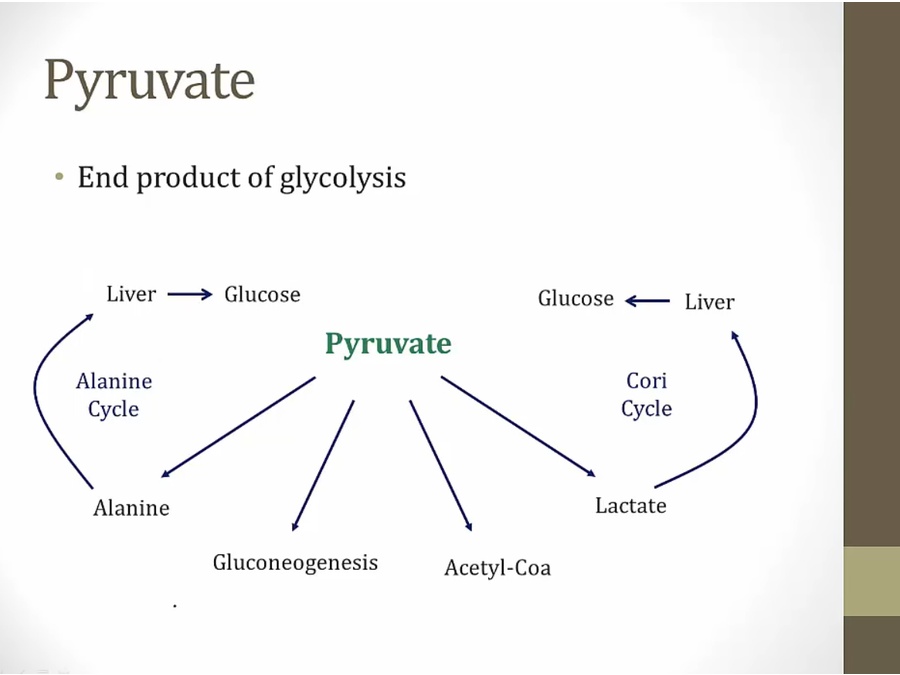
lactate: RBC without mitochondria and muscles. Muscles release lactate to blood to go back to liver
alanine: alanine carry nitrogen to liver, extract nitrogen to urea
must enter mitochondria for gluconeogenesis and acetyl coa

1st step for gluconeogenesis in mito
outer: just a pore
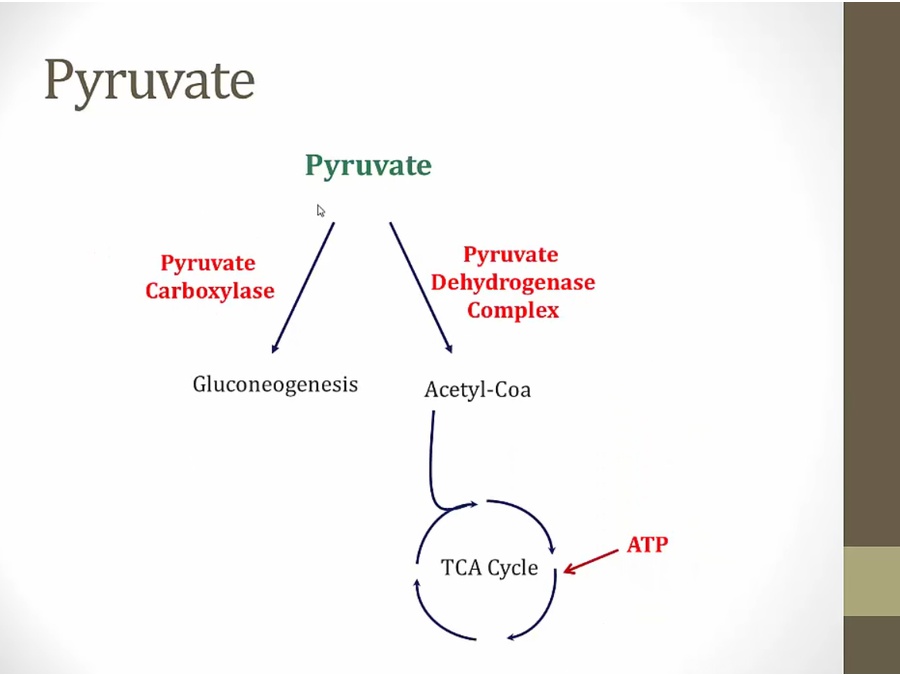
once inside mito
high ATP, slow TCA, high Acetyl- coa and activates pyruvate carboxylase, preferential shunt towards gluconeogenesis
acetyl coa also inactivates pyruvate dehydrogenase
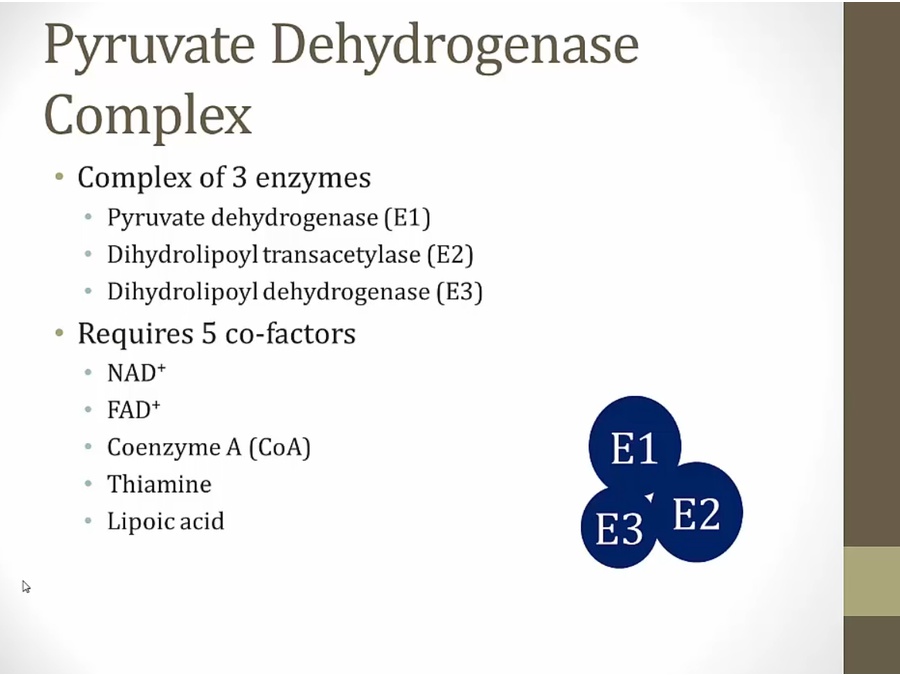
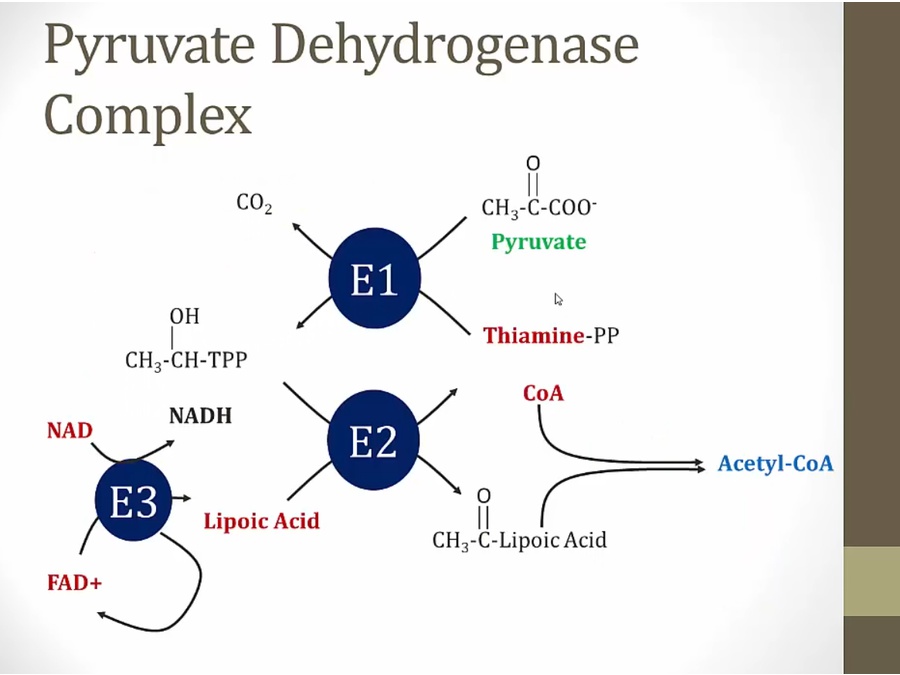
E1 adds thiamine PP to pyruvate and release CO2
E3 keeps lipoic acid in proper form
Thiamine
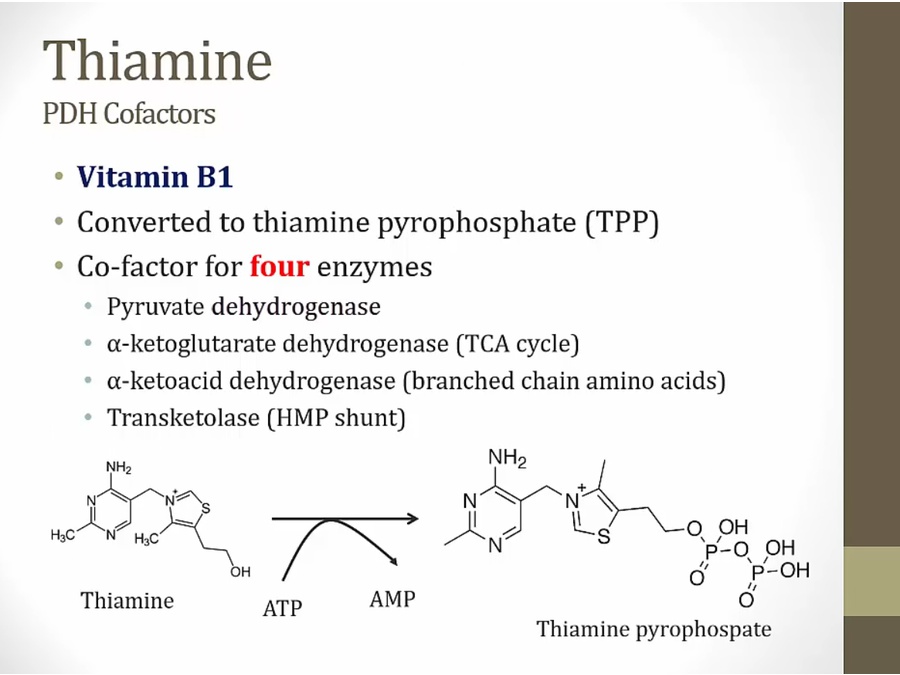
TPP active form, 2 phosphates from ATP
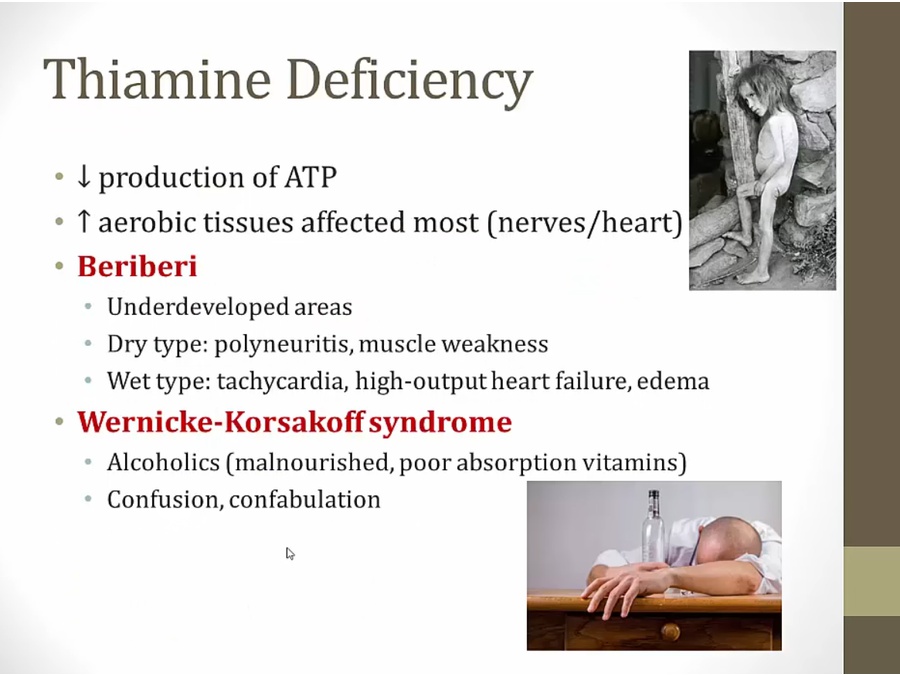
thiamine deficient, cannot convert pyruvate to acetyl-coa, no ATP

FAD
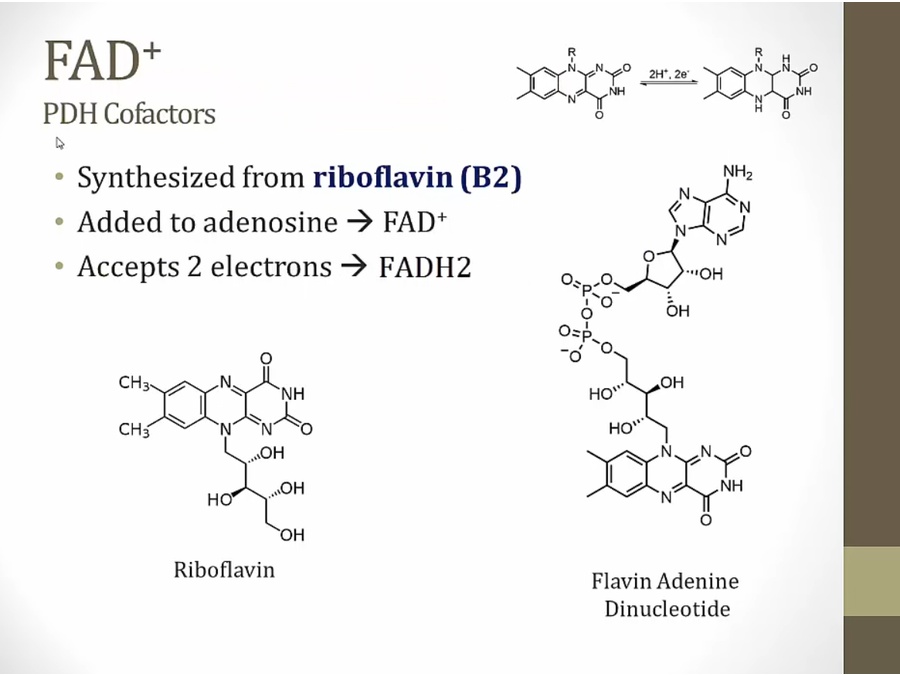
used in oxidative phosphorylation
NAD

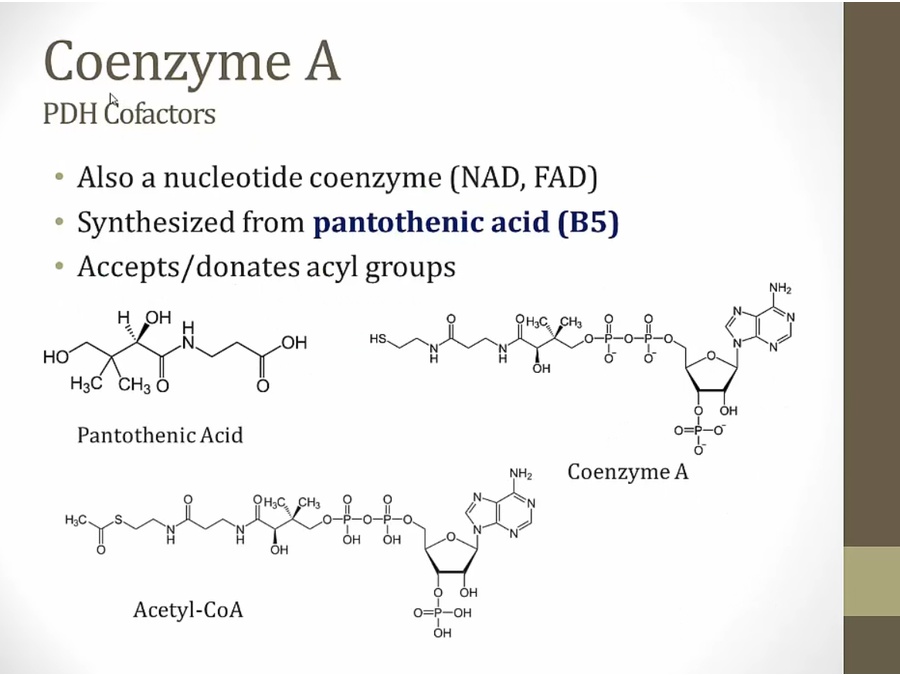

first 4 all used in pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes
Lipoic

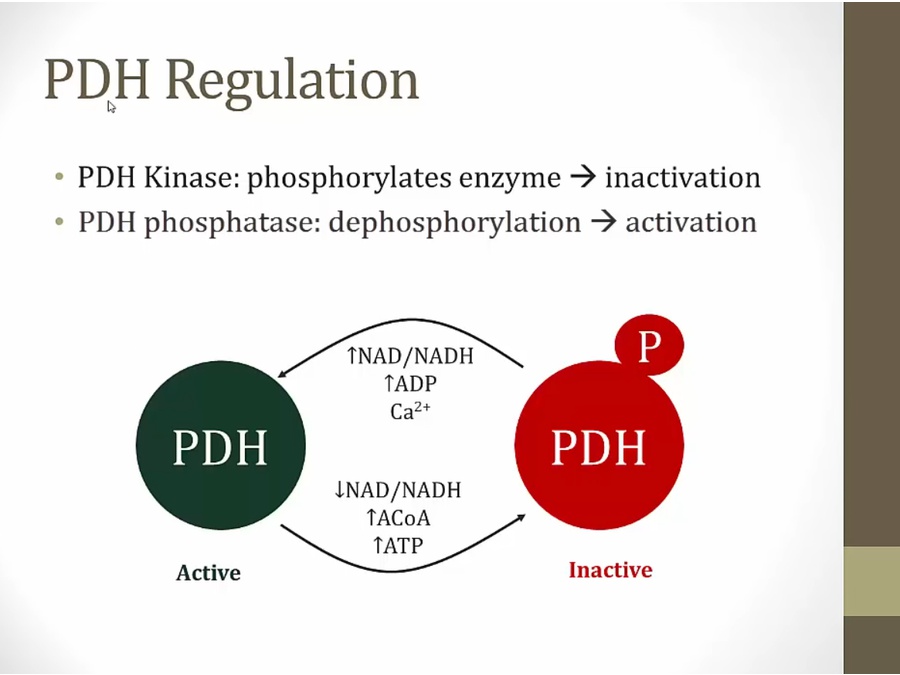
Ca activator in skeletal muscles when exercising

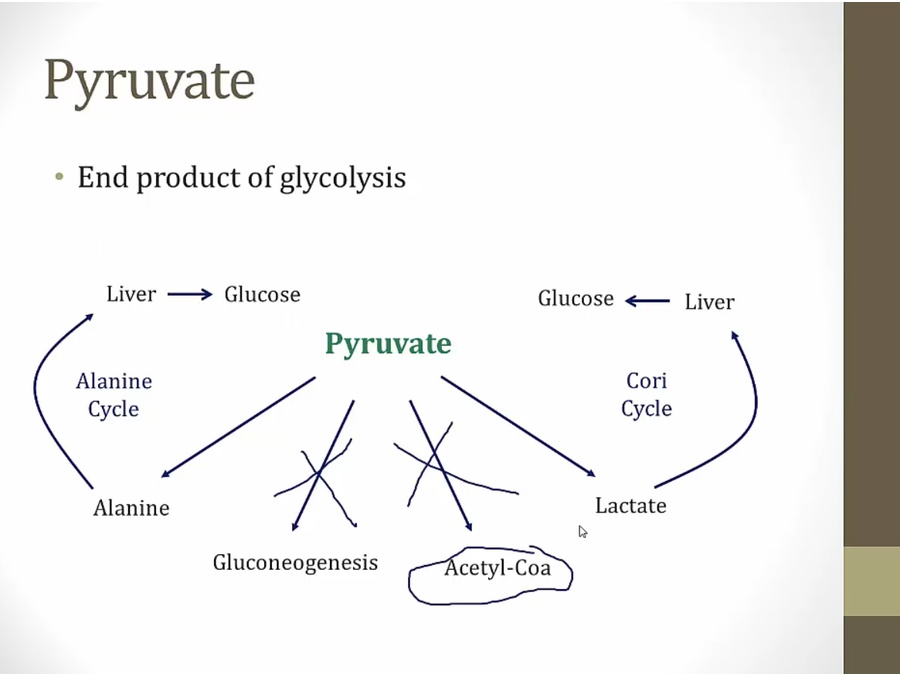


whenever pyruvate not metabolized, build up in mito and shunted towards lactate

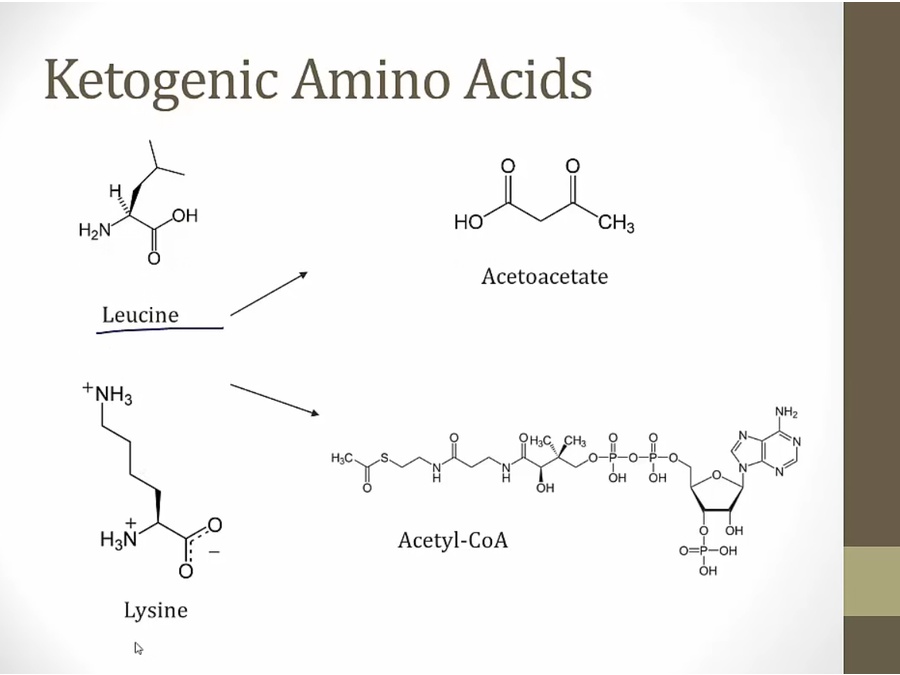
fat converted to acetyl coa without going through pyruvate
Last updated