02 Pulmonary Physiology
Lung Volumes
_..

TLC: average person, 6 L total
RV: 1 L residual volume
TV: quiet breathing, 2.5 - 3L
Inspiratory Reserve Volume: volume inhaled after inspiration TV
ERV: same with expiration TV
FRC: functional residual capacity, volume left after TV expiration


VC: everything but residual volume

IRV
TV
ERV
RV
bottom 2: FRC
top 2: IC
top 3: VC
all 4: TLC
Ventilation
_..

Dead Space
_..

not all alveoli exchange gas
apex largest contributor to dead space

ratio of physiologic (not anatomic) deadspace to TV
Lung and Chest Wall
_..

lung like a balloon

no pressure: no volume
maximum point: no increase in volume with pressure increase

no pressure: still has a volume
positive pressure increase volume
negative pressure withdraw volume

at 0: no air movement
at FRC: tendency for lungs to collapse balanced by tendency of chest wall to expand, no pressure on air molecules inside alveoli

Pressure
_..
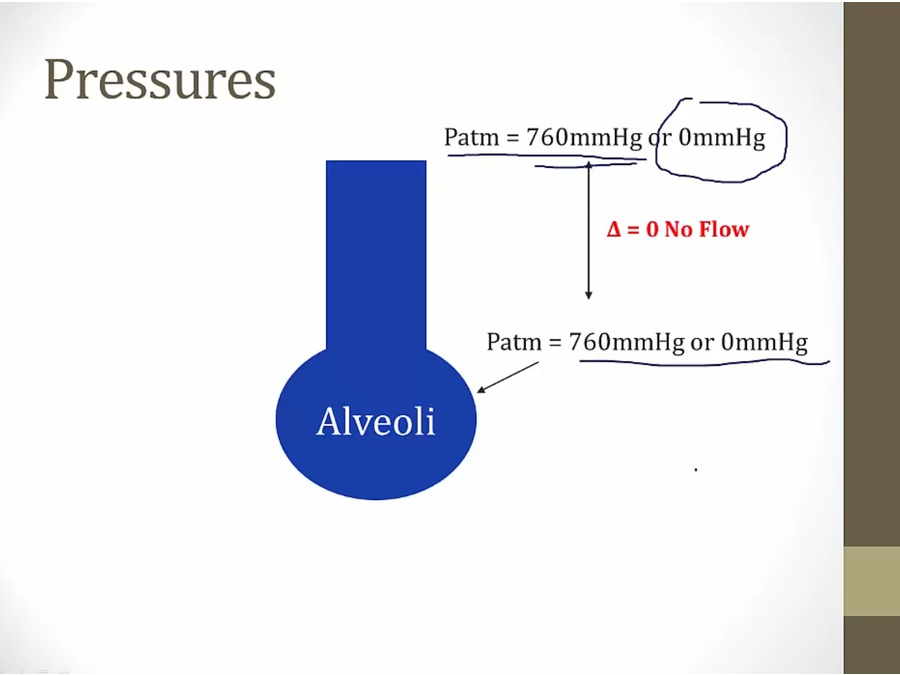
by convention, 0 mmHg, no difference between alveoli and atmospheric
at end of expiration/inspiration, no movement of air, pressure equal
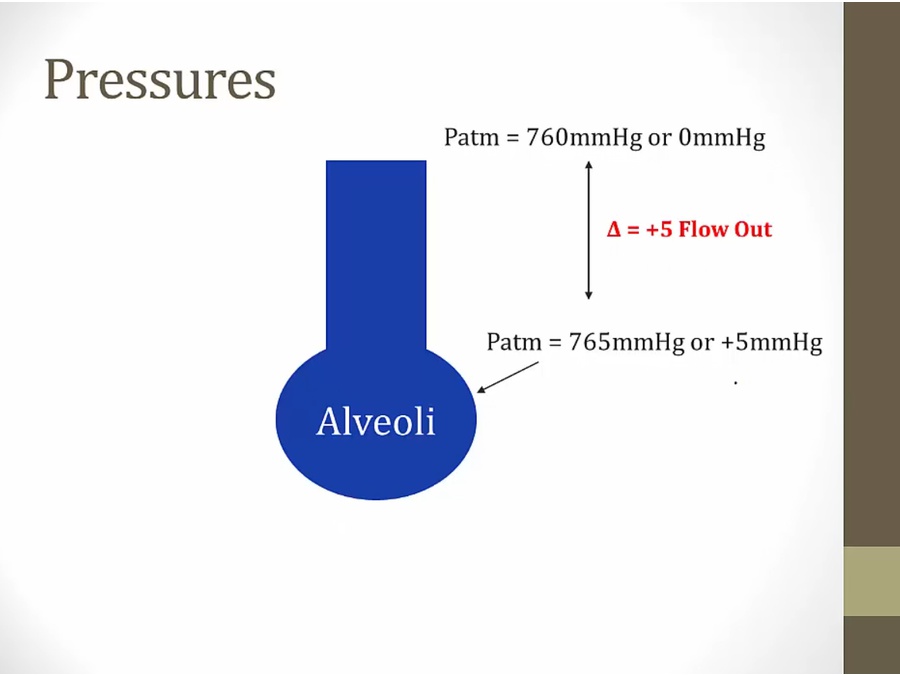
exhale: pressure inside becomes positive, drive air out

inhale: pressure inside becomes negative, drive air in
Pleural Space
_..

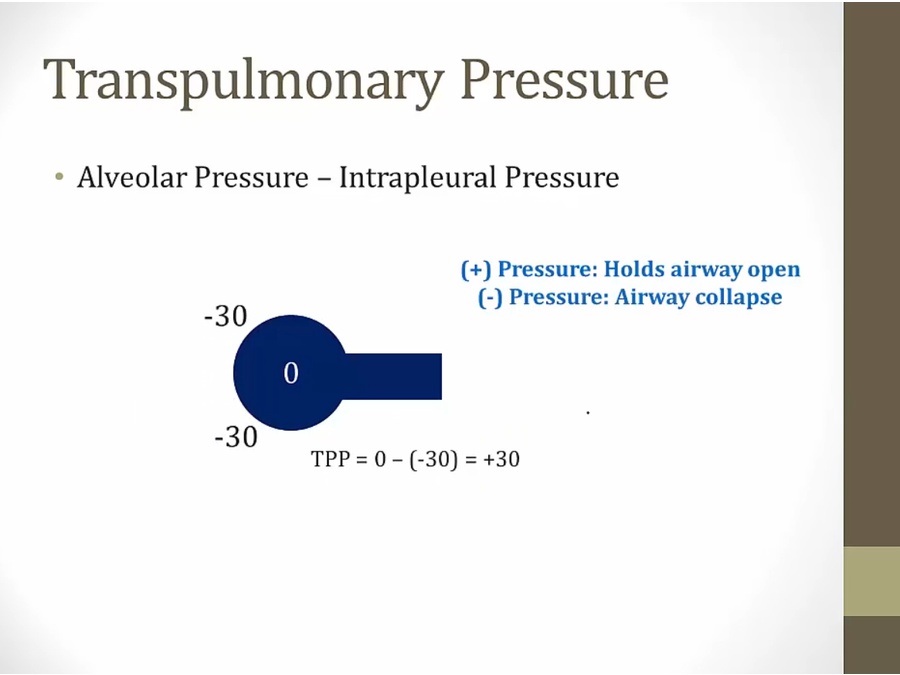
for pressure in alveoli to be 0 (no airflow), pressure in pleural space must be negative
positive pressure of lung to collapse balanced by negative pressure of pleural space

intrapleural space: always negative during normal breathing

_..
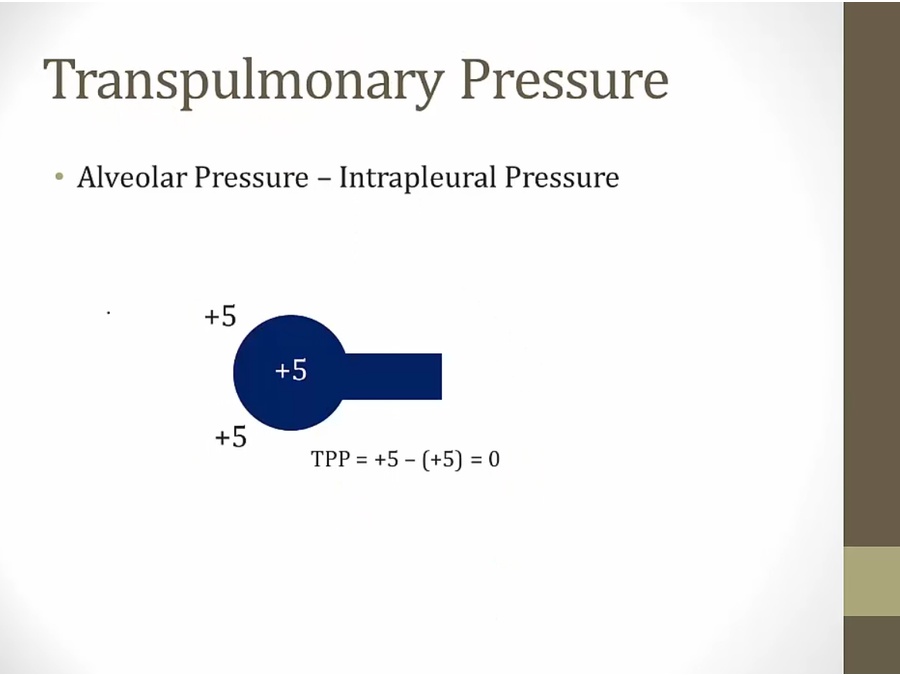
net sum of pressure differences acting on pleural tissue
pressure +5 pushing in and +5 inside pushing out = 0
_..

pressure surrounding alveoli become equal to pressure in alveoli
resistance flow slowly drops pressure inside alveoli
beyond equal pressure point: airway collapse prevented by cartilage

bronchitis: +60 closer to alveoli
emphysema: instead of +90, +70 in alveoli
Lung Compliance
_..

stiffness of lung
compliant: easy to stretch or move air


infiltrate in lung: stiff (water, fibrosis)
Aging: lung compliance increases (loss of elasticity). Chest wall compliance decreases (rib calcification, stiffening). RV increases (air trapping, like emphysema). FVC decreases (air trapping from increased RV). TLC stays same (decreased chest wall compliance balances lung compliance).
_..
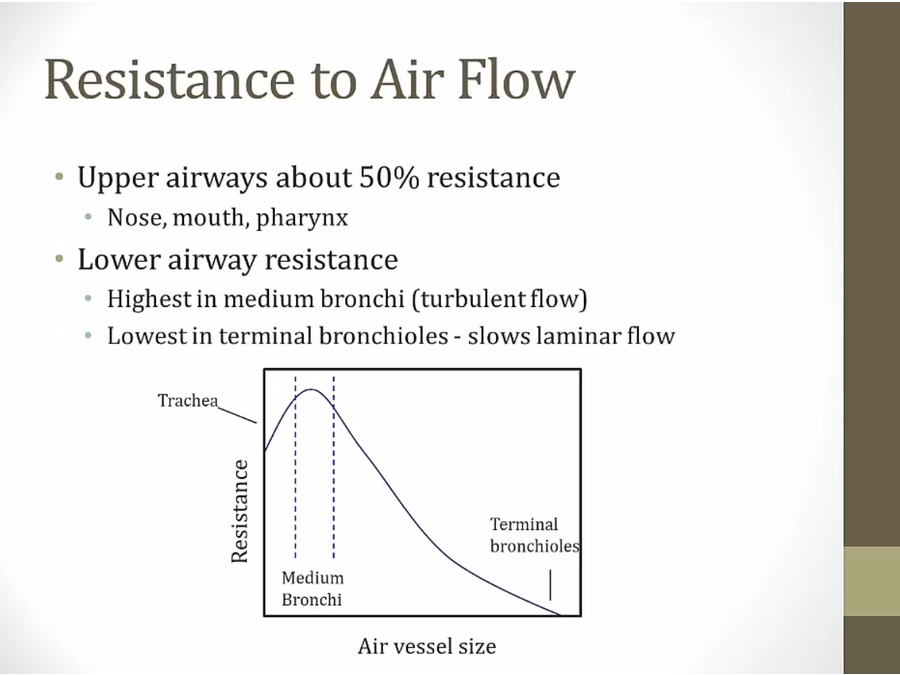
very slow laminar flow good for O2 transmission
Last updated