20 Tubulointerstitial Disease
ATN
_..


like heart attack


cat scan
multiple myeloma: bence jones protein

Rusty downspout draining muddy water: acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
muddy cast on urinalysis
_..
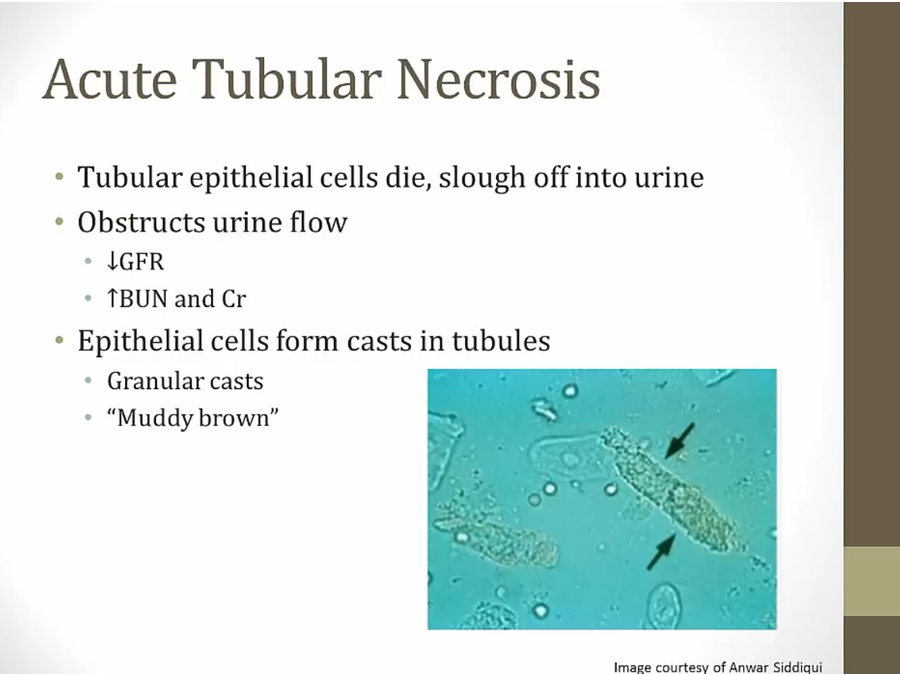
epithelial cells squeeze through nephron and form casts



phase 1: clinically silent
maintenance: acute RF, a few days later
metabolic acidosis: can't excrete acids
phase 3: fast urine output, drop K with urine
know hyperkalemia in phase 2 and hypo in phase 3

AIN
Acute
_..



Kidney bag with little blue candies: interstitial nephritis

Blue star clusters in kidney nebula: drug-induced interstitial nephritis

Baseball-filled kidney containers: NSAIDs can cause acute interstitial nephritis

Kidney filled with blue tickets: loop diuretics can cause interstitial nephritis (blue cells on histology )

Kidney sharps: IV acyclovir can cause interstitial nephritis or crystalline nephropathy


don't need to know individual bacteria
_..

WBC casts: inflammation of nephron
no bladder symptoms (frequency, urgency, burning urination) association with pyelonephritis (ascending infection from bladder to kidney)
eosinophilia: allergic reaction


Chronic
_..

longterm NSAIDS exposure
NSAIDS
_..


Constricted proximal end of hose: NSAIDs cause afferent arteriole vasoconstriction, decreasing GFR
Bursting from high pressure: NSAIDs can increase blood pressure due to COX inhibition in the kidney, decreasing sodium excretion
Baseball-filled kidney containers: NSAIDs can cause acute interstitial nephritis
Sloughing off cleat spikes: NSAIDs can cause renal papillary necrosis (sloughing of renal papillae)
Elevated “lift-ium” balloons: NSAIDs can increase serum lithium concentrations
Depleted mineral mine: NSAIDs can cause hypoaldosteronism (decreased mineralocorticoids)
Big K: NSAID induced hypoaldosteronism can cause hyperkalemia. Type 4 RTA
Papillary Necrosis
_..

Gray-white or yellow necrosis of the distal two-thirds of the renal pyramids is seen macroscopically and corresponds microscopically to coagulation necrosis with preserved tubule outlines; cortical surface scars can develop subsequently as inflammatory foci are replaced by fibrous depressions.
Symptoms are due to sloughed papillae (sometimes visible in urine as tissue flecks) and include dark or bloody urine and colicky flank pain (due to ureteral obstruction).


phenacetin: analgesic no longer used

Baseball-filled kidney containers: NSAIDs can cause acute interstitial nephritis



Cortical Necrosis
_..

i in cortical stands for ICU and DIC: critically ill
caused by massive tissue destruction
_..

kidney diseases as either glomerular diseases (biopsy) or tubulointerstitial diseases (clinical diagnosis)
Last updated