05 Nephron Physiology
_..
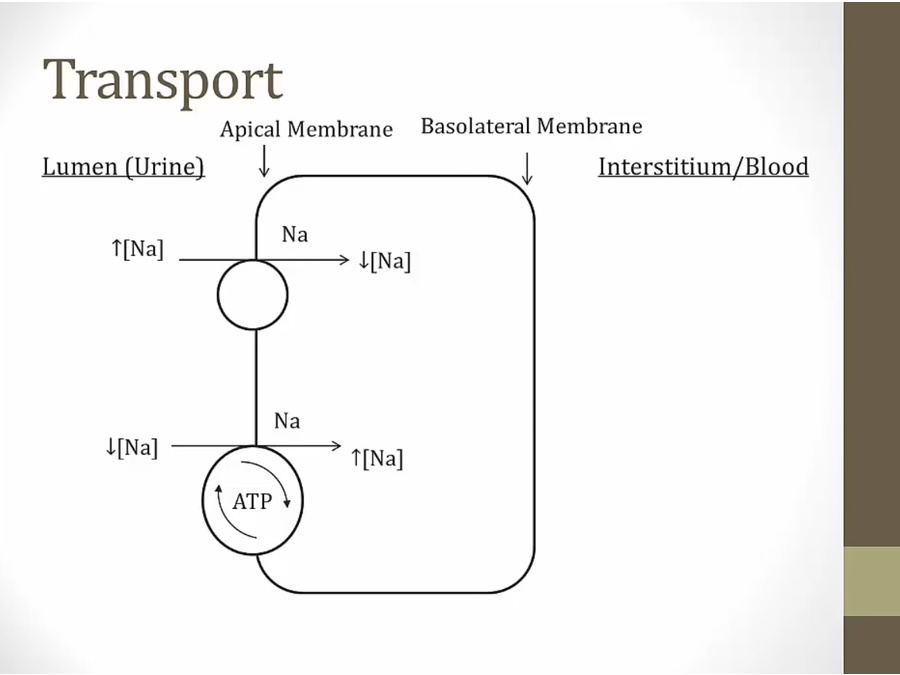
high to low concentration: no energy needed
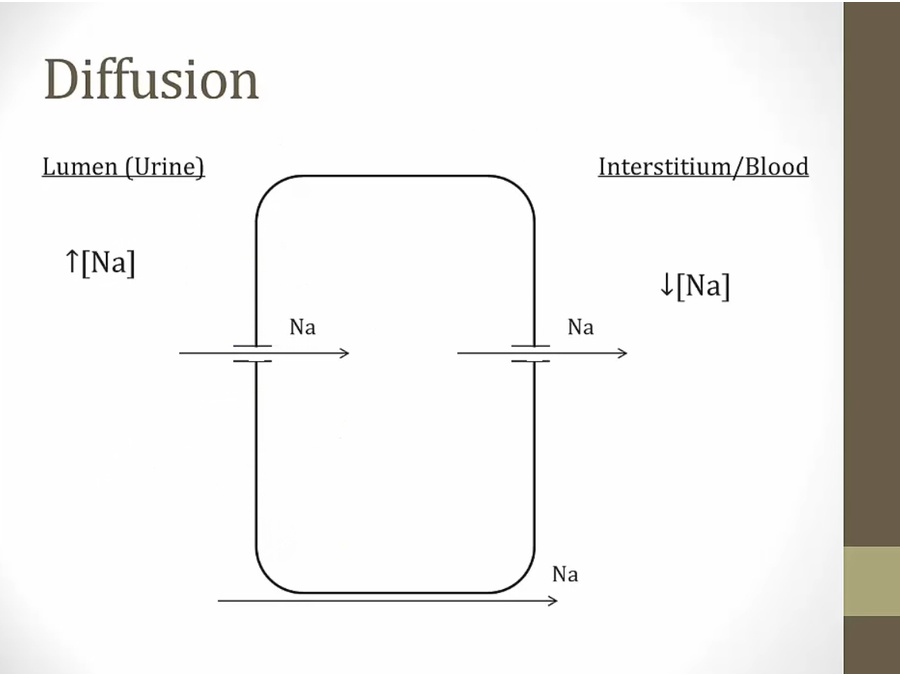
paracellular: between cells
_..
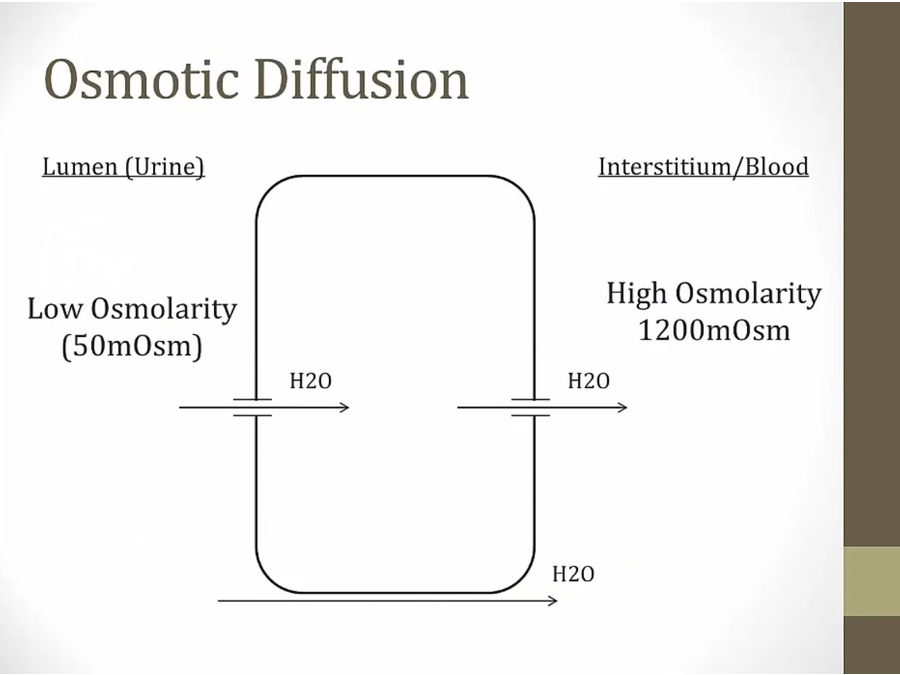
osm: how much solute dissolved in water
low osm: high concentration of water, vice versa
water move from high concentration to low concentration
_..
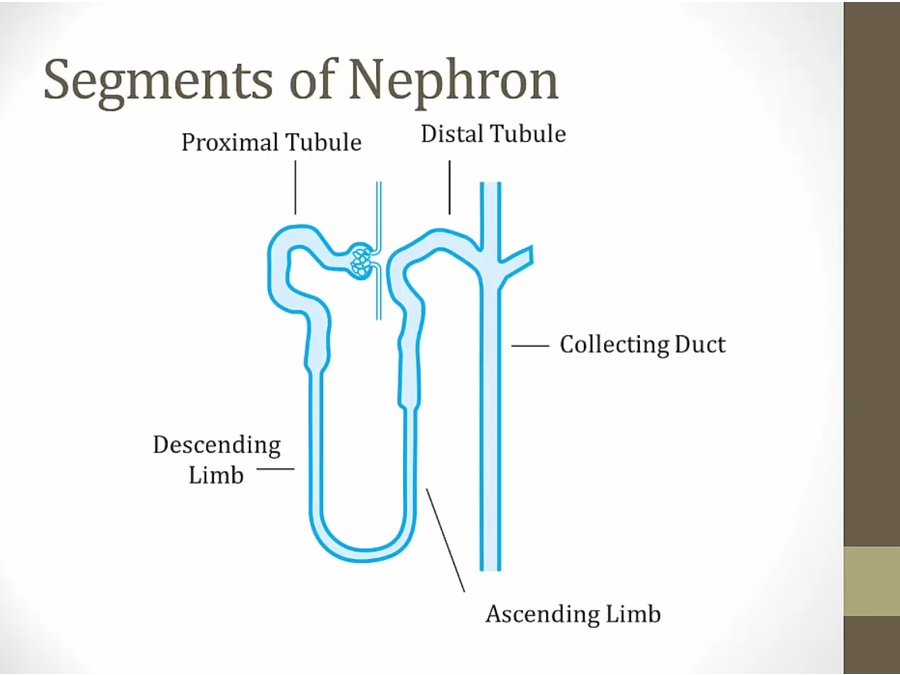
PCT
_..
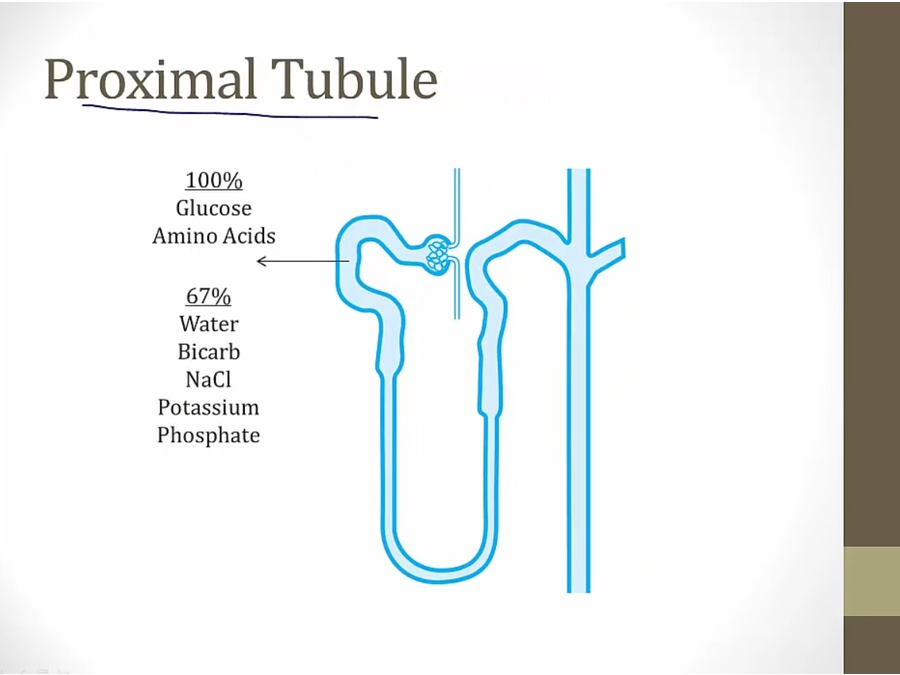
work horse of nephron
most absorption

_..
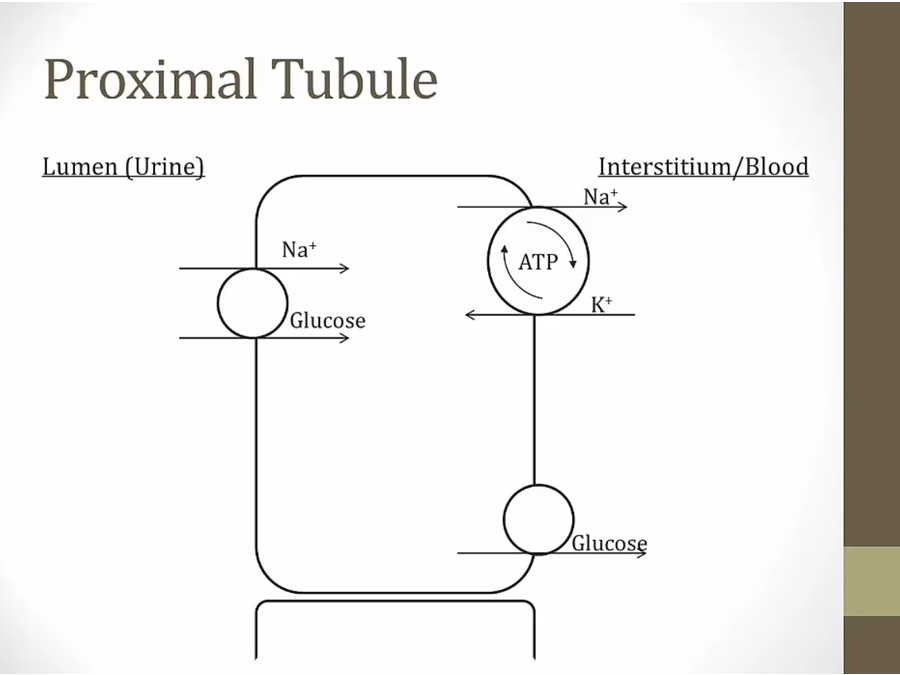
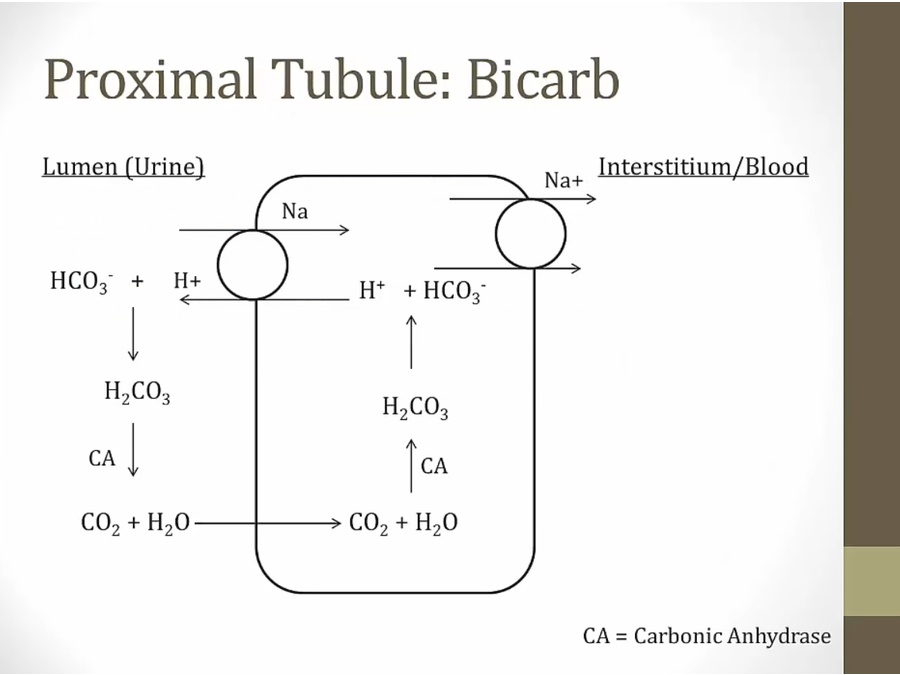
use concentration of Na to drag glucose in
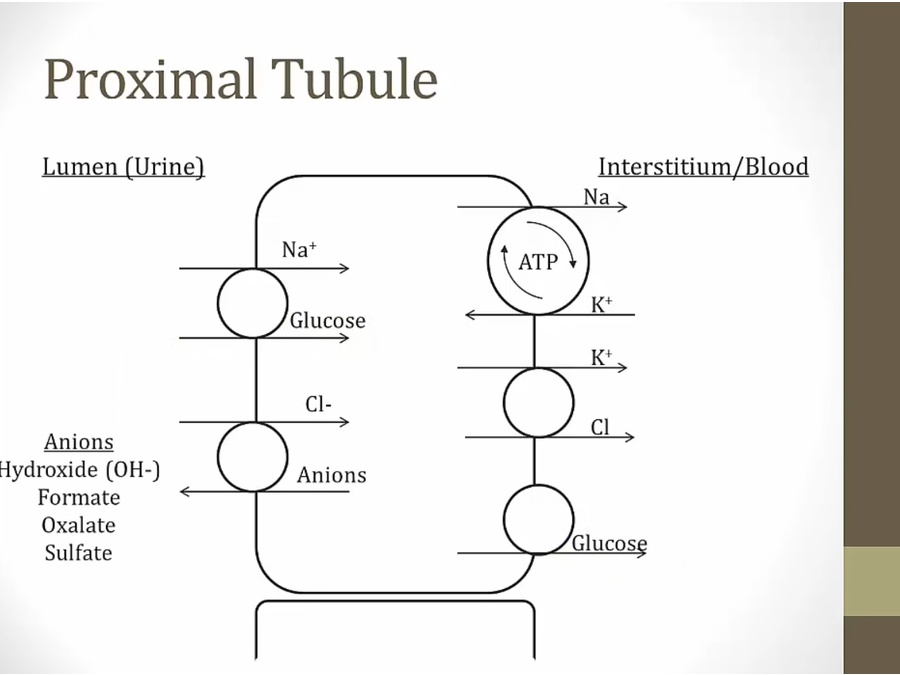
K pump into cell, diffuse out and drag Cl with it, lower Cl concentration in cell
Cl can then be pulled into cell in exchange for anion
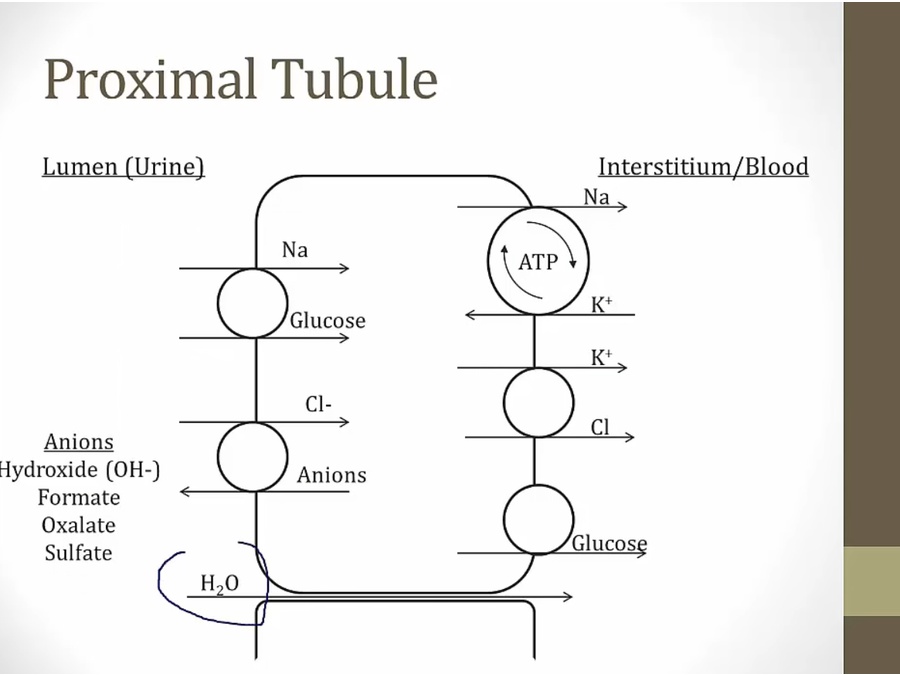
water reabsorbed paracellularly via high Na/Cl concentration in blood
Glucose Clearance
_..

_..

pellagra: B3 deficiency (niacin). Tryp converted to niacin
_..
_..

Fanconi
_..

proximal tubule disfunctional
phosphate leads to growth failure
_..

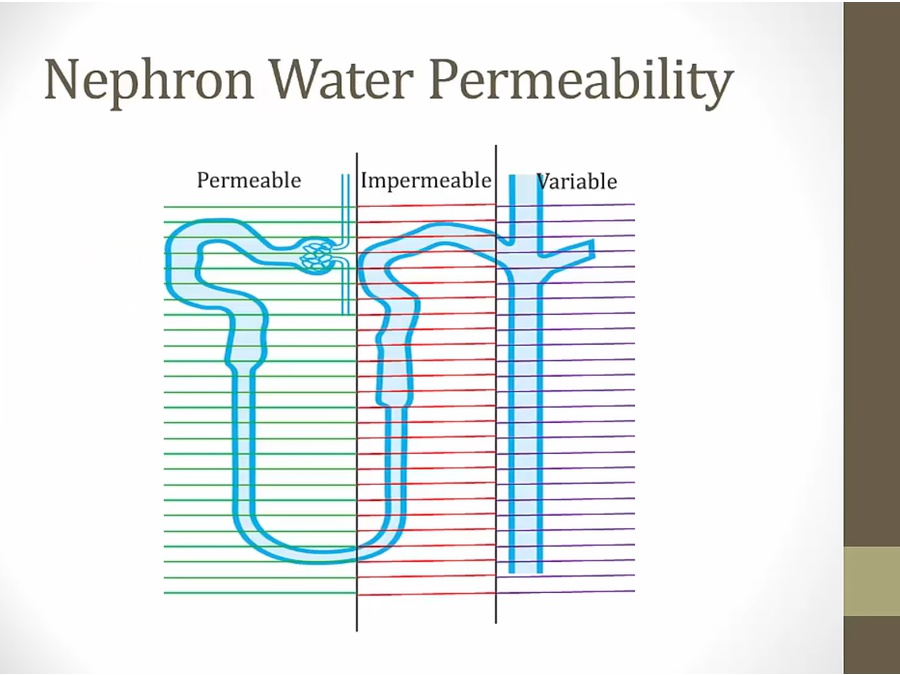
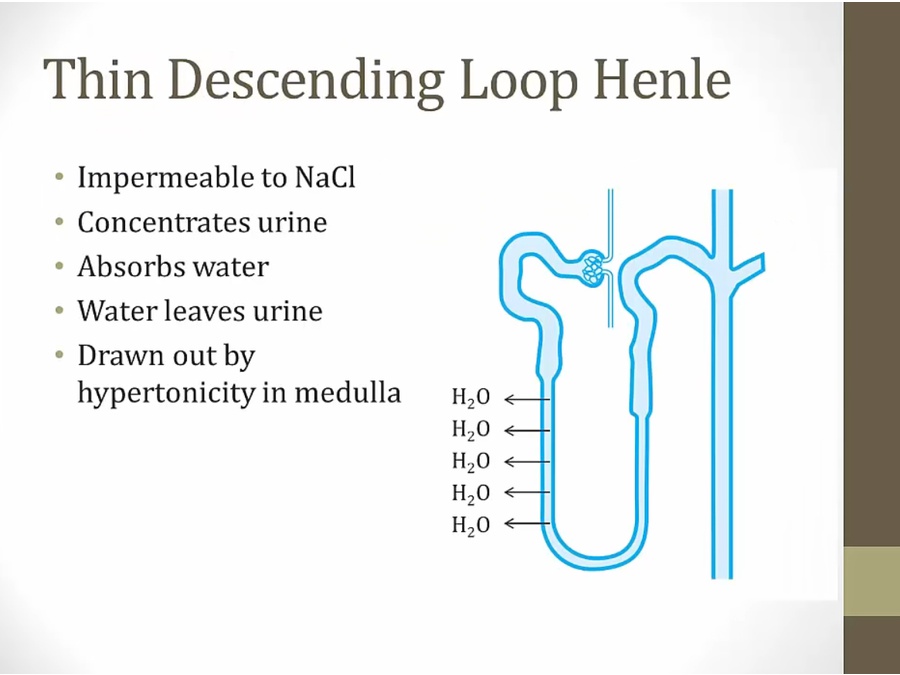
Descending Loop
_..

_..

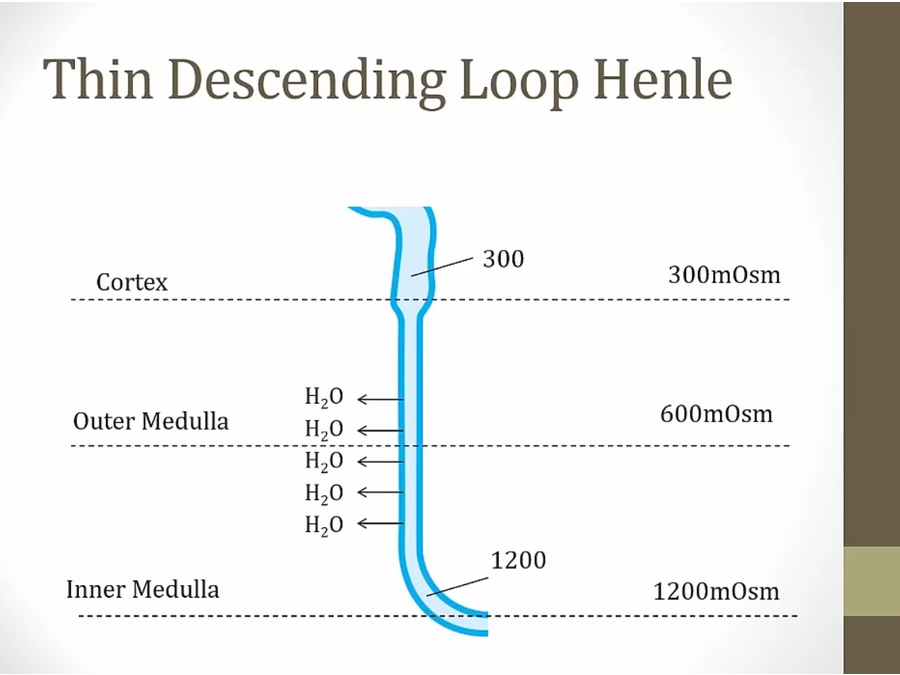
Cortex: water drawn out until lumen = 300
medulla: continue drawn out
Ascending Limb
_..
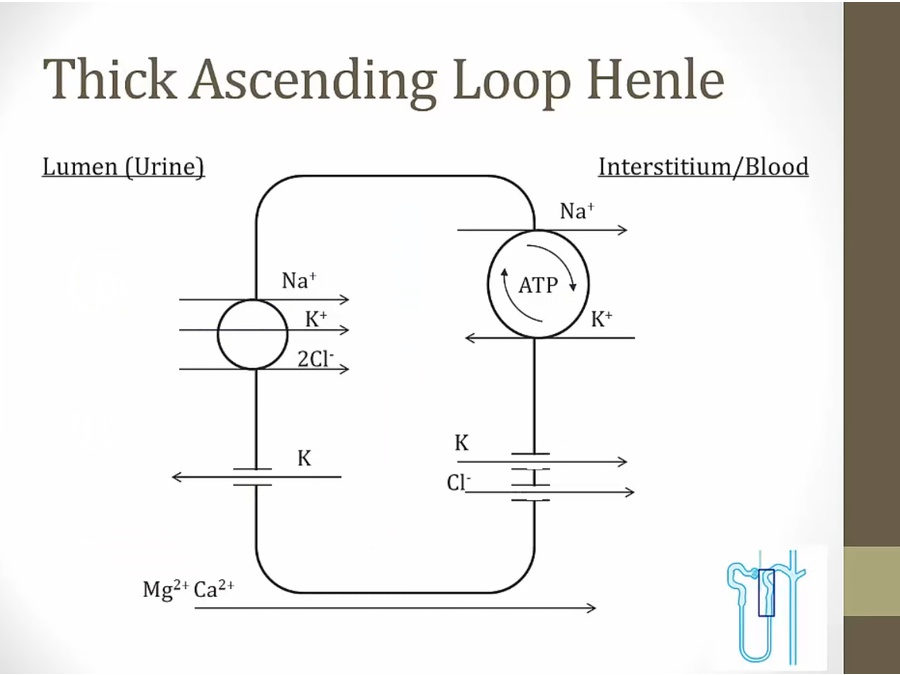
K leak into lumen, cause + charge and push cation in
NKCC: Na, K, Cl, Cl

_..
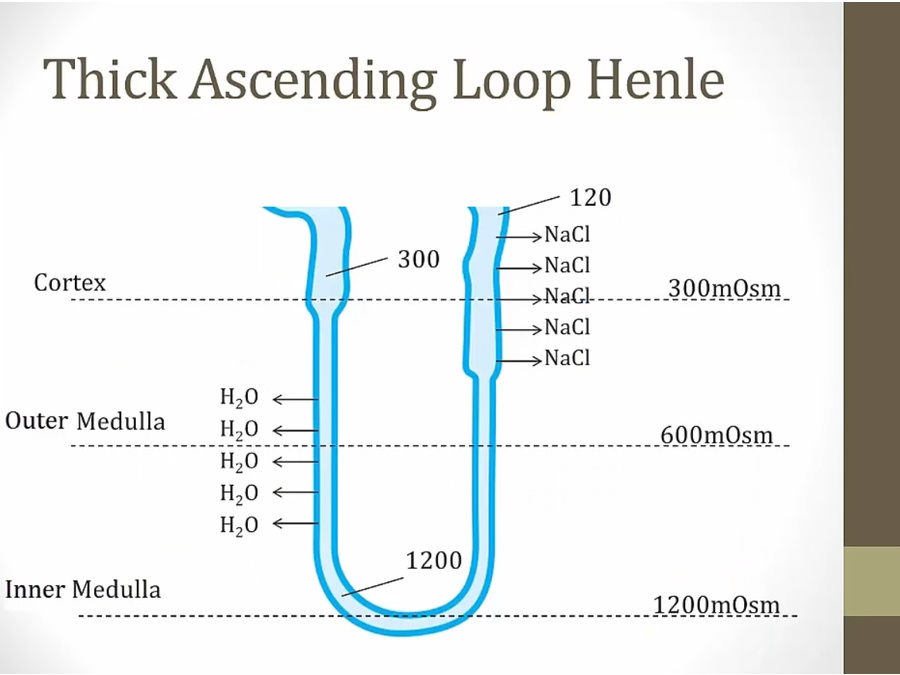
NaCl pulled out, leave water in, very dilute urine
impermeable to water

Distal
_..
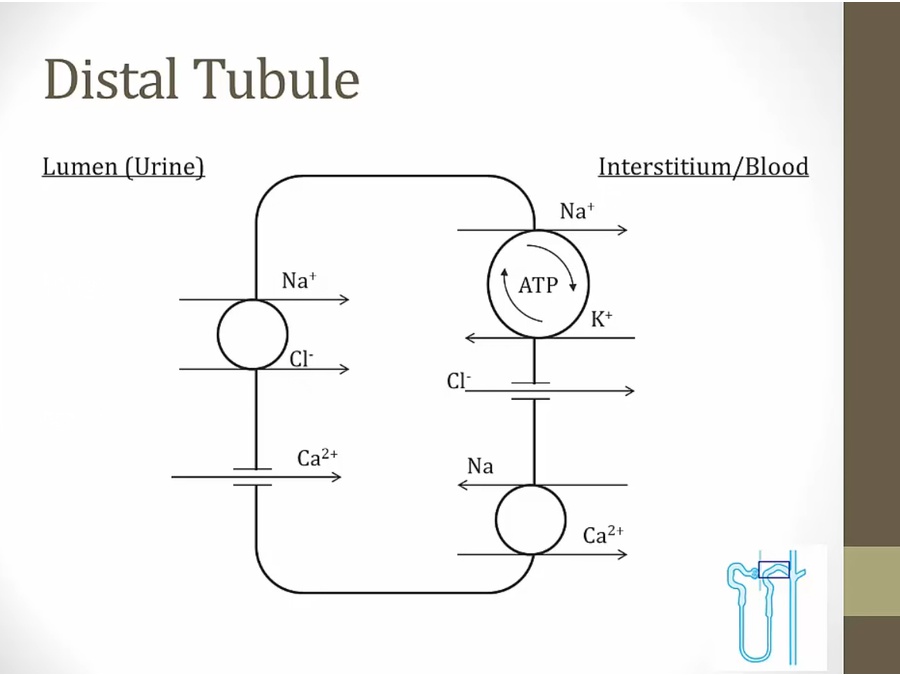
PTH and thiazide diuretics increase Ca absorption

CD
_..
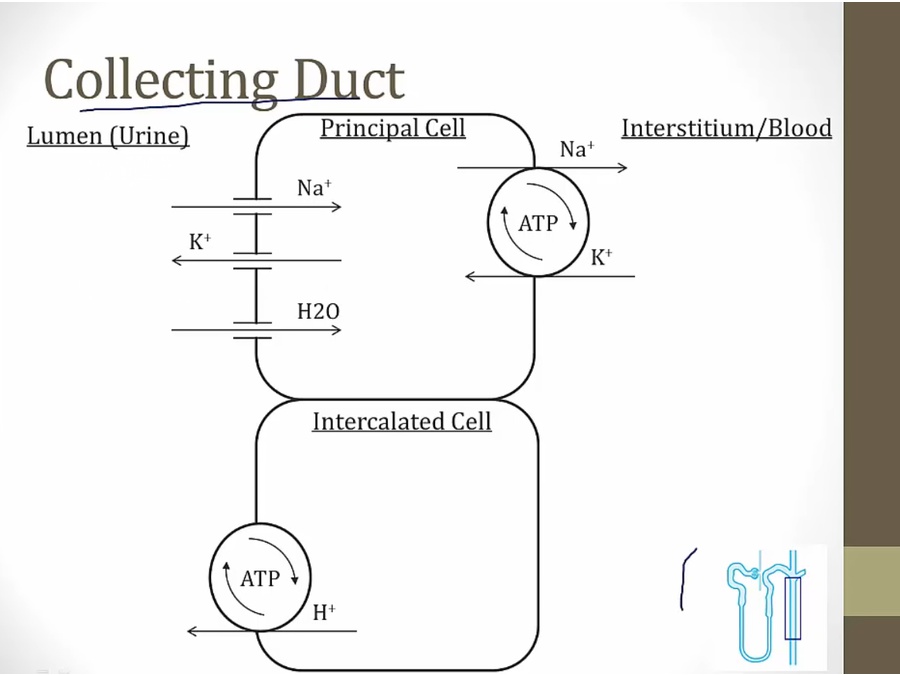

_..



_..

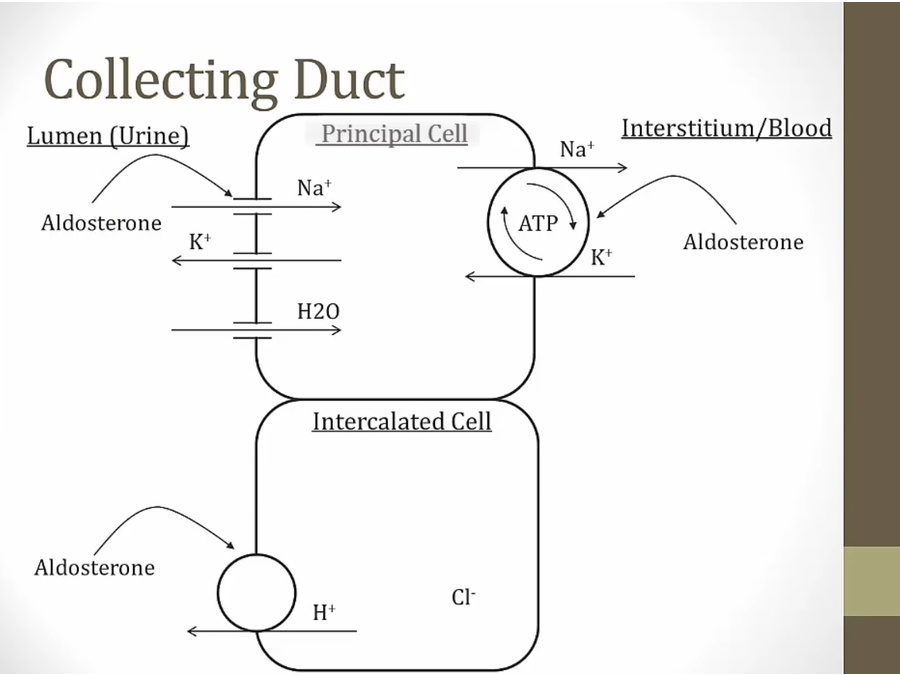

Ang II most important
ADH
_..

vasopressin: vasoconstriction
supraoptic/paraventricular
_..

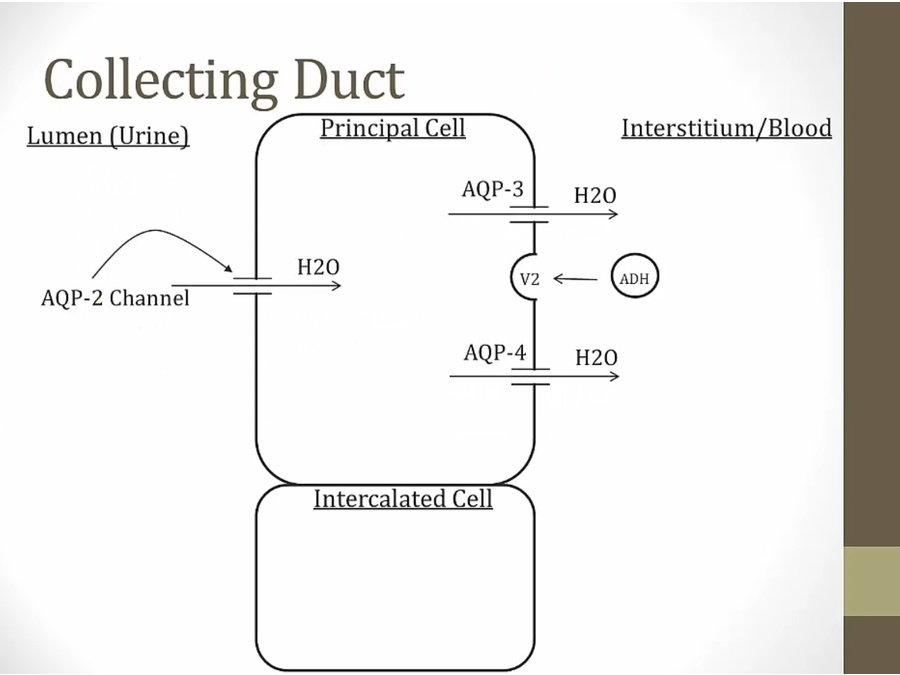
AQP 3 and 4 always present: basolateral always permeable to water
_..
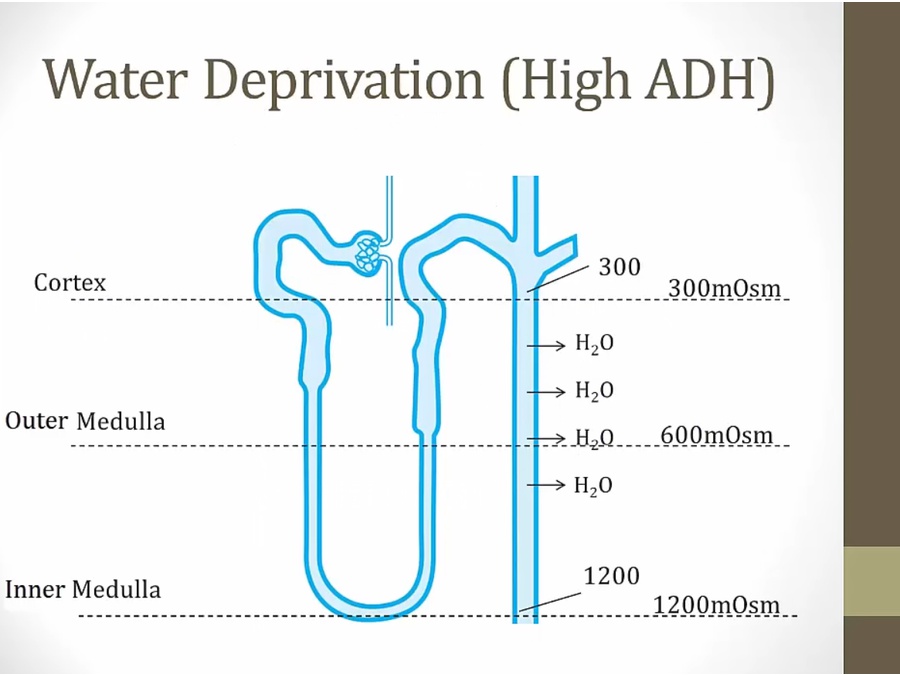
water deprived: concentrate urine by pulling it out
_..
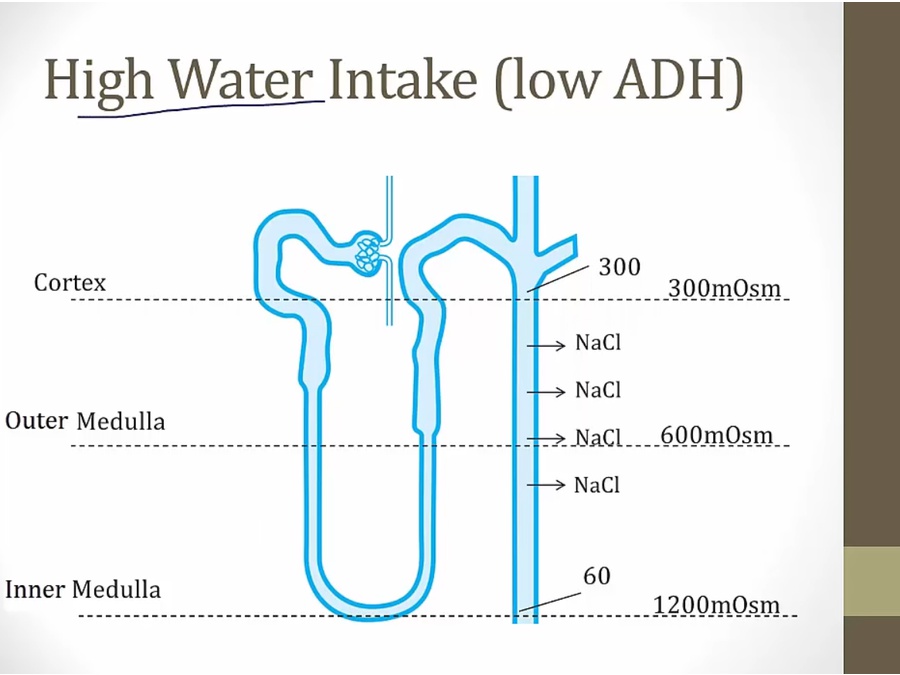
water not absorbed, NaCl absorption dilute urine
_..

high osmolarity in lumen at CD: less water leaving
_..

water leaving causes urea in lumen to be more concentrated: urea leaves via gradient
ADH promotes absorption of urea
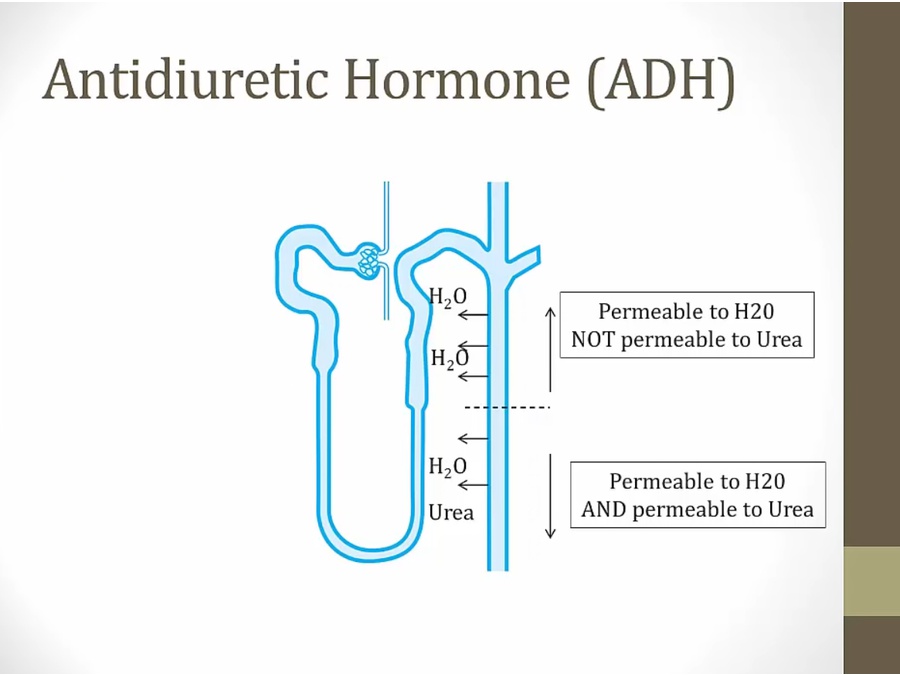
urea pushed out in distal CD
urea needed in descending loop to draw water out
Misc
_..

_..
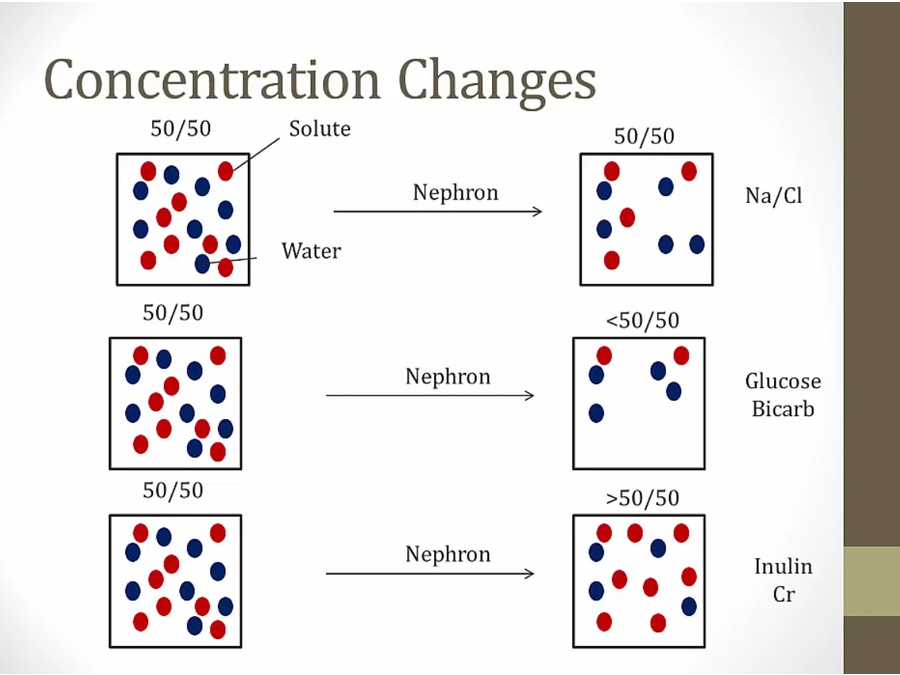
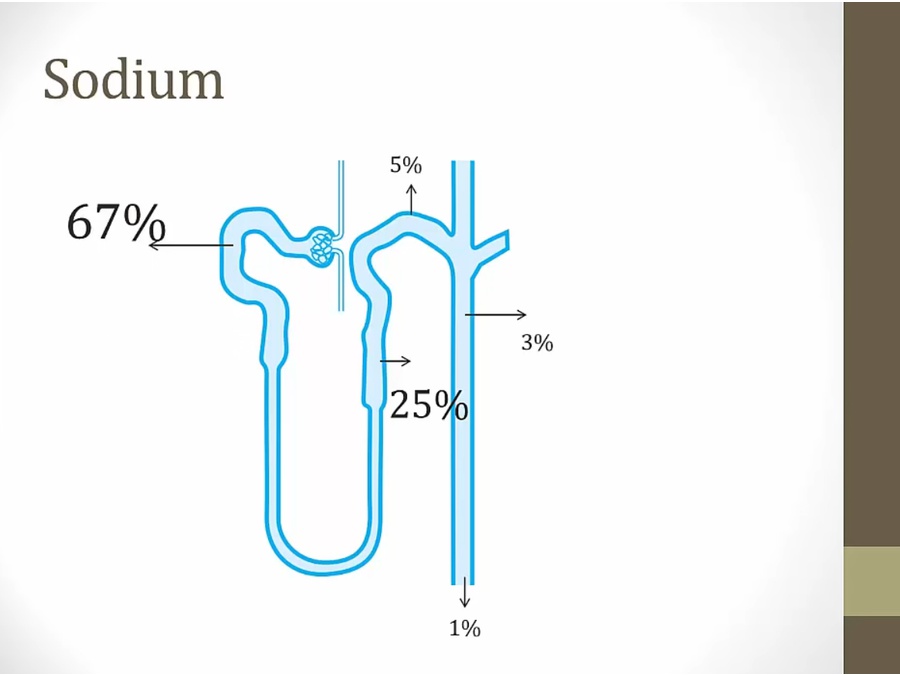
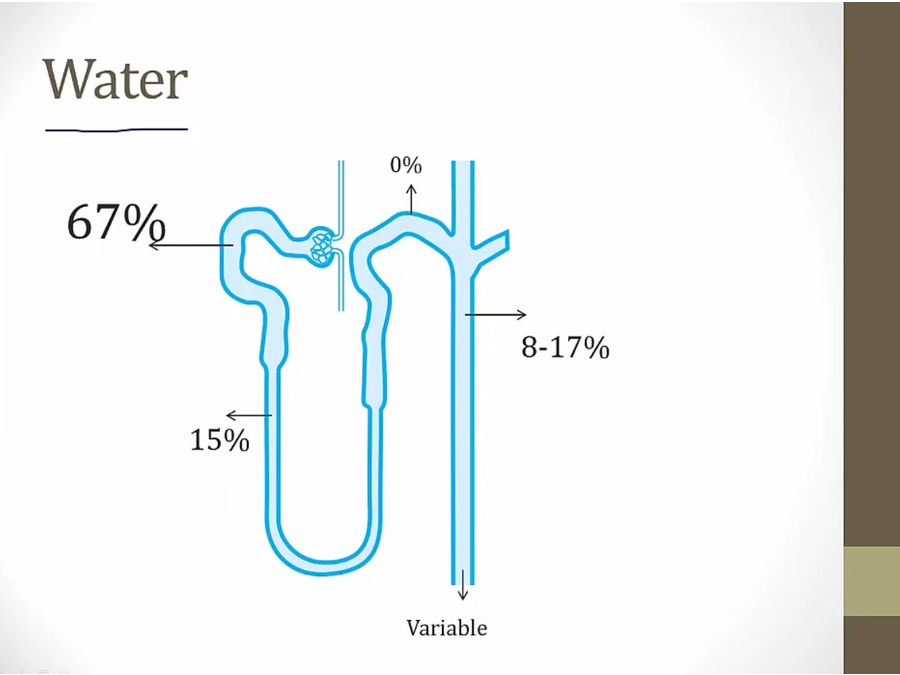
middle: pull more solute out than water, result = more dilute
bottom: pull water more than solute
_..
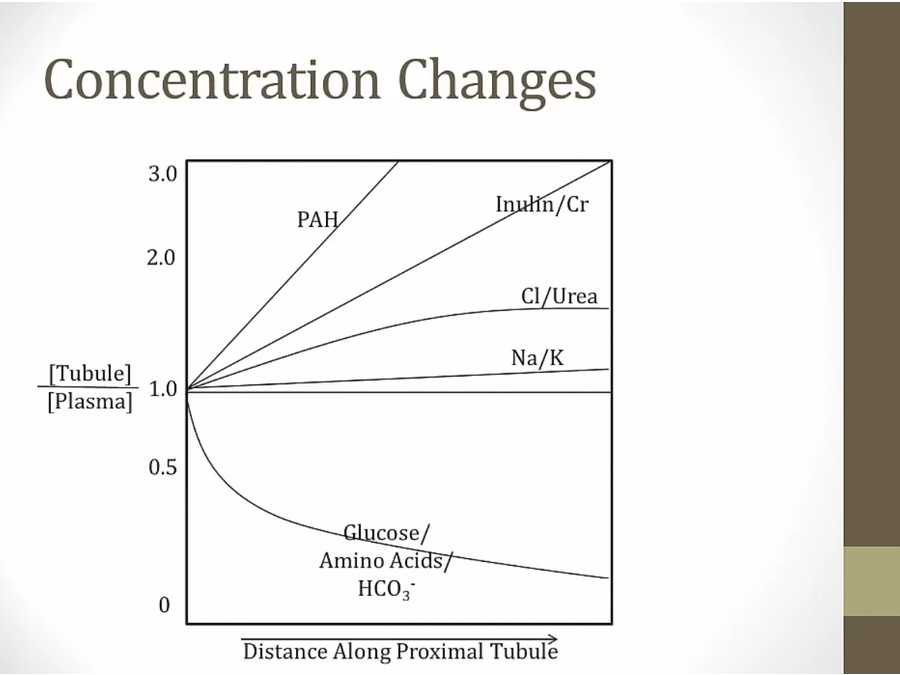
inulin/Cr: not absorbed, concentration rises
Cl/urea/Na/K: not really changed, concentration a little higher
glucose/aa/bicarb: absorbed, concentration decreases
PAH: secreted
Last updated