05 Spleen
_..

Lymphoid Organs
_..

_..
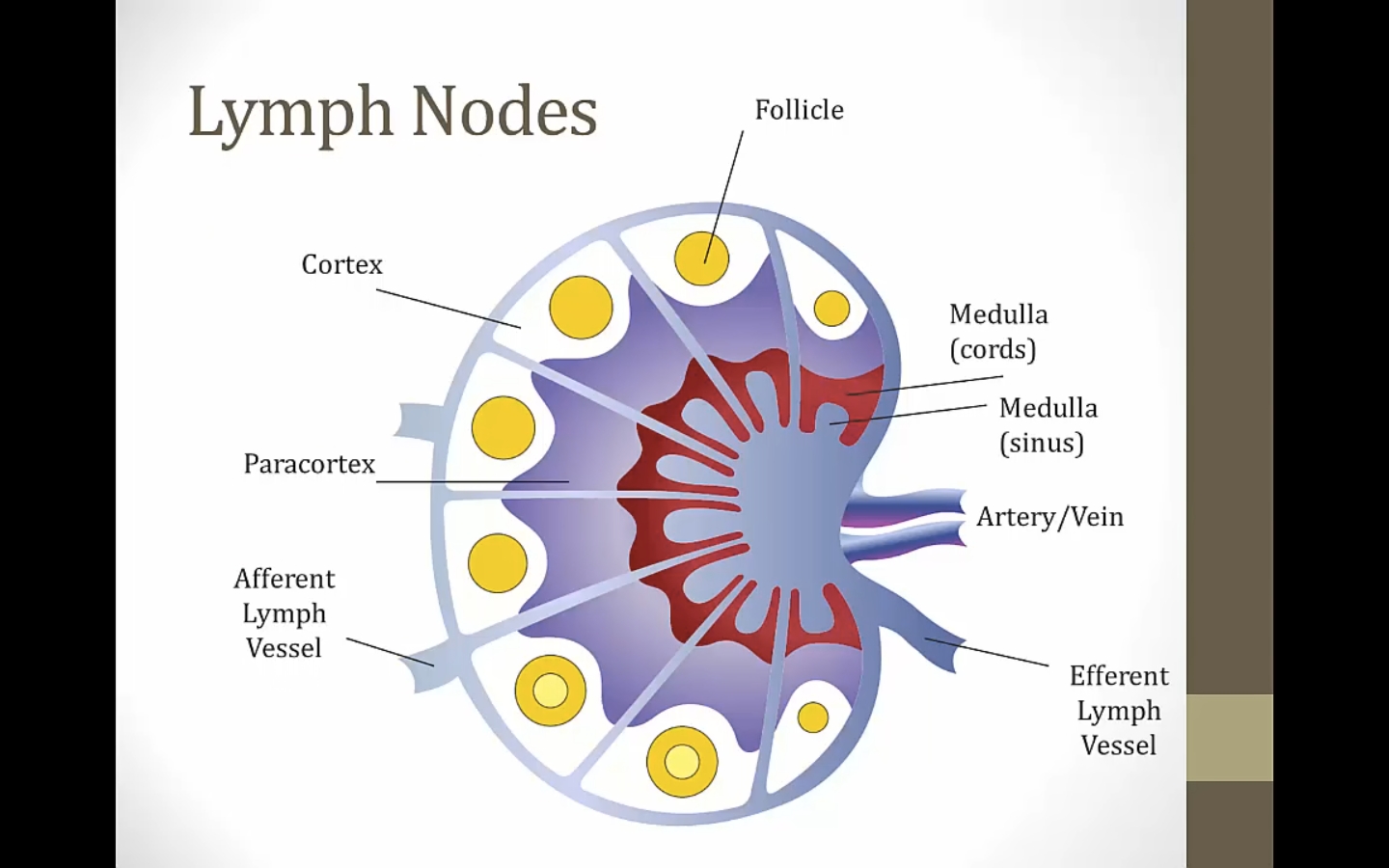
Cortex: white, contains follicle
Paracortex: T cells
Medulla with cords and sinus
Afferent lymph goes through the 3 layers, exit at 1 efferent vessel
_..

APC process free antigens
Cortex
_..

dendritic cell like velcro picking up antigens that allow B cell to react

_..


4: follicle
3: white, germinal center, thus secondary follicle
Paracortex
[_](Paracortex contains what cells. Classic disorder. How does it respond during infection. What's so special about the venules)..

HEV: spaces between endothelium to allow B and T from blood to enter lymph

Medulla
_..


Spleen
_..
not lymph filter
filters blood
everything in blood enters spleen
_..

first from artery to white pulp (white)
then blood moves through red section, red pulp
eventually back to splenic vein

White Pulp
_..


Red Pulp
_..


endothelium with barrel hoop membrane. Still large enough for blood to pass through

_..

less complement activity because needs IgG and IgM for binding Fc

antibody binding leads to MAC and c3b formation
macrophage binds to antibody and c3b, phagocytosis
_..

malaria/babesia: infected RBC can't be cleared
_..

ITP: low platelets. Take out spleen to increase platelet
spherocytosis: take spleen out, less destruction of anemia
Sickle cell: so many abnormal RBC that damages spleen when removed
_..

target cells usually cleared by spleen

Last updated