12 Metabolic Acidosis
Anion Gap
_..
_..

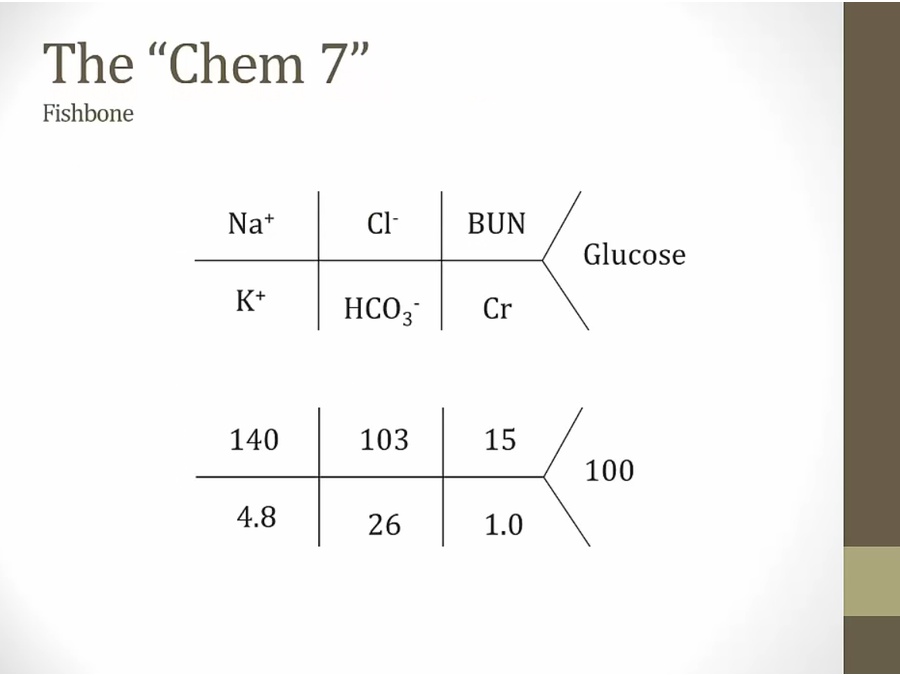
blood: total number of + must equal -
chem 7 only tells some of the positive and negative charges
Na and K (positive) minus Cl and bicarb (negative) is the gap
in reality no gap, just other ions not measured
_..

albumin predominantly responsible for negative anions besides Cl/bicarb
for every 1 g decrease in albumin, add 2.5 to AG
IgG push Na out and retain K in plasma: shrink anion gap
A low anion gap is frequently caused by hypoalbuminemia. Albumin is a negatively charged protein and its loss from the serum results in the retention of other negatively charged ions such as chloride and bicarbonate. As bicarbonate and chloride anions are used to calculate the anion gap, there is a subsequent decrease in the gap.
_..

if lose bicarb, compensate with Cl to maintain normal charge

Cl part of anion gap ion, thus normal AG
[](. <img src='images/v74QhnD.jpg' alt='' /> .)..
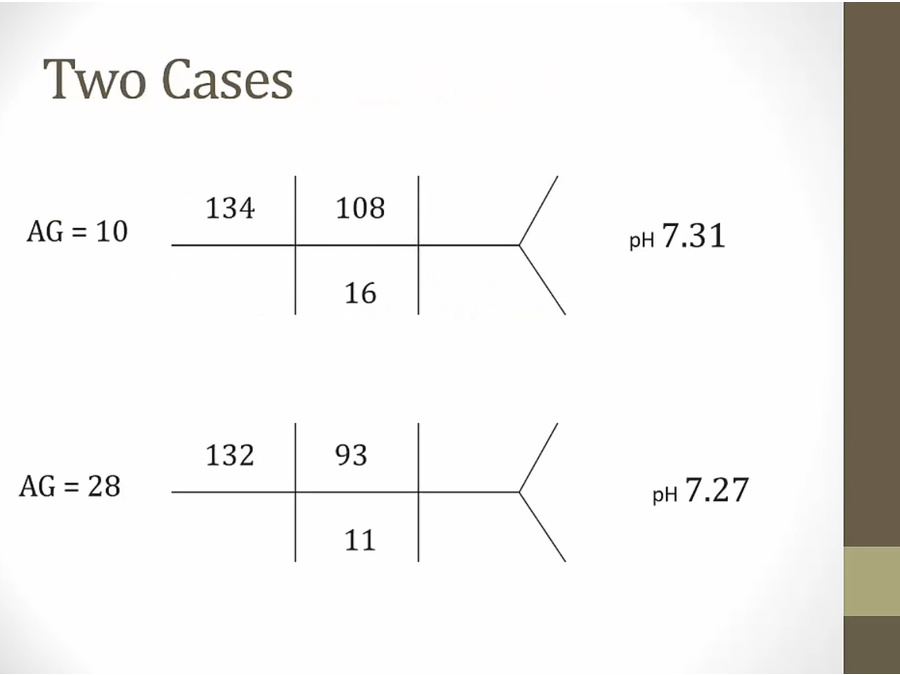
top: bicarb decreased (met acidosis). Cl increased, normal 95 (non-AG)
bottom: met acidosis, Cl not high, AG
Cl up: non-AG; Cl down: AG
Winter's Formula
[_](Winter's formula and delta ratio uses)..

[_](winter's formula use when)..

Delta Delta
_..

Winter's tell if there's secondary respiratory, Delta ratio tells if secondary metabolic

<1: bicarb driven down by metabolic acidosis also by something else
more than 2: chronic respiratory acidosis causing chronic retention of bicarb

Non- AG Causes
_..

anything that lowers aldosterone, decreases bicarb level, or increases H+ levels
addison: can't make aldosterone
saline: low aldosterone result
hyperalimentation: IV nutrition
calculate urinary AG
Na+K-Cl = urine bicarb
positive: renal loss
negative: GI loss
TB: adrenal insufficiency
AG Acidosis Causes
_..

_..

MUD PILES
Methanol
_..

destroy optic disc

child, suicide, etc.
very important: visual symptoms

Ethylene Glycol
_..

calcium oxalate in tubules

kidney symptoms instead of visual

formaldehyde: formic acid
glycoladehyde: glycolate, oxalate
Propylene Glycol
_..

Isopropyl Alcohol
_..

someone ingest toxic product but no AG acidosis
Uremia
_..

at first: can't excrete H
later: can't excrete organic acids
association with other uremic symptoms (pericarditis, confusion, hyperkalemia)
DKA
_..

or diabetic who didn't take insulin

Lactic Acidosis
_..

seizures: so much muscle contraction
Iron
_..

usually child
highly prone to bleeding
later phase: AG acidosis

ferric irons: unmeasured anions
INH
_..


Motion lines: INH may cause seizures
MUD PILES: INH may cause anion gap metabolic acidosis
Aspirin
_..


Mudpile: aspirin toxicity can cause an anion gap metabolic acidosis (S in MUDPILES)
Blowing “OH-” bubbles: aspirin causes a respiratory alkalosis, stimulate respiratory center directly
Last updated